Search results for: Ansoff Matrix

Apple marketing strategy is based on the founder Steve Jobs’s philosophy that customers do not always know what they want. Accordingly, instead of conducting marketing researches to identify customer needs and wants, the multinational technology company prefers to install innovative features and capabilities in their products, making customers to want Apple products. Under the leadership of Tim Cook since 2011 certain aspects of the business such as management style and company’s stance towards CSR have changed. However, the dismissal of marketing research remains to this day. Apple marketing strategy expresses the brand in minimalist, yet highly efficient ways. The world’s largest IT company by revenue is one of the first companies to successfully associate the brand image with being innovative, rebellious and non-conformist. Apple 7Ps of marketing is marked with a particular focus on the product element of the marketing mix and the company’s segmentation targeting and positioning initiatives are aimed at targeting users of premium products. Moreover, marketing communication mix of Apple Inc. places greater emphasis on print and media advertising and personal selling in Apple Stores and the company rarely uses sales promotions as part of its marketing strategy. Generally, Apple marketing strategy integrates the following: 1. Focusing on attractive value proposition. Apple’s value proposition is “beautiful design that works right out of the box with ever-smaller packaging”[1] The world’s largest IT company by revenue has been able to avoid price wars with competitors by emphasizing its unique value proposition in its marketing communication messages. Apple is a unique company in a way that it is a design firm, a media platform, a publishing company, a software powerhouse and a computer manufacturer – all at the same time. Such a position allows the company to communicate its value proposition to target customer segment in a cost-effective manner.…

Apple marketing communication mix explains the company’s stance towards individual elements of the marketing communication mix such as print and media advertising, sales promotions, events and experiences, public relations, direct marketing and personal selling. The main aim behind Apple marketing communications mix is to communicate the marketing message of the brand to the target customer segment through elements listed above. Apple is effective in using elements of the marketing communication mix in an integrated manner to ensure the consistency of the marketing message. Apple Print and Media Advertising Since its foundation more than 40 years ago Apple has been using print and media advertising extensively to promote the brand in general and new products in particular. Some of the ads by the tech giant have become truly iconic raising the bar for advertisement globally. The following is the list of the most memorable print and media advertising campaigns launched by Apple: “1984” campaign directed by Ridley Scott and first shown during 1984 Super Bowl is widely considered as one of the most successful marketing campaigns of all times “The Quadra Revolution” is 1991 campaign that was a successful attempt by the tech giant to further itself ahead of the competition at the beginning of the digital age of 90s “Misunderstood”, a Christmas ad of 2013 won Emmy Award for the year’s most “Outstanding Commercial.” “40 Years in 40 Seconds” is a viral video that chronicles 40 years of the company in 40 seconds “Meu Bloco na Rua” (2017) is the latest ad released in Brazil for the Rio Carnival, highlighting the iPhone 7 Plus’ new portrait photography mode Apple also uses celebrity endorsements in print and media advertising extensively. In the past Apple’s ‘Think Different’ print and media advertising materials featured the images of innovators and pioneers in different areas…

Apple segmentation, targeting and positioning represents the core of its marketing efforts. Segmentation, targeting and positioning is needed because no company or product can be all things to all people. Apple segmentation targeting and positioning initiatives include the following stages: 1. Segmenting the market. Segmentation involves dividing population into groups according to certain characteristics. Specifically, customers can be segmented on the basis of their place of living, demographic variables, behavioural traits, psychographic characteristics and other variables. Market segments need to be measurable, accessible, sustainable and actionable in order to be used for marketing purposes. 2. Targeting selected segment(s). This stage involves identifying segments that are most attractive for the business. In other words, targeting implies choosing specific groups identified as a result of segmentation to sell products to. The multinational technology company positions itself as a premium brand offering products and services with advanced functions and capabilities for additional costs. Accordingly, Apple target customer segment comprise well-off individuals who are willing to pay extra for technology products and services with advanced design, functions and capabilities. A common set of characteristics shared by Apple target customer segment include appreciating design, quality and performance of technology products and services over their prices. 3. Positioning the offering. Positioning refers to the selection of the marketing mix that is the most suitable for the target customer segment. It is the final process, where companies attempt to associate their products and services with needs and wants of selected customer segment. Apple targets its customer segment by tailoring products, services and overall business approach to appeal to the members of segment to a maximum extent. Under the leadership of late Steve Jobs, Apple mainly used mono-segment type of positioning, appealing to the needs and wants of a single customer segment. However, after Tim Cook became CEO,…

Nvidia marketing communication mix includes the use of various communication channels to transmit the marketing message to the target customer segment. These channels are print and media advertising, sales promotions, events and experiences, public relations and direct marketing. Nvidia Print and Media Advertising Nvidia uses print and media as an effective advertising platform systematically. Specifically, the multinational technology company runs advertising campaigns on TV and radio channels, as well as magazines and newspapers popular with their target customer segment. Additionally, Nvidia places large billboards in crowded area in large metropolitan cities. The software and fables company also uses viral marketing extensively on popular social media platforms such as Twitter, LinkedIn, and YouTube. Nvidia also uses product placement strategy by Nvidia include a science fiction movie “Blade Runner 2049” released in 2017 and Steven Spielberg film “Ready Player One” released in 2018. Nvidia Sales Promotions Nvidia uses various sales promotions techniques regularly to increase its revenues. Specifically, the multinational technology company uses the following sales promotions techniques: – Seasonal sales promotions. Nvidia uses seasonal sales promotions to boost its revenues during holidays and festive seasons. Additionally, the company runs promotions during major industry events such as the Consumer Electronics Show or the Game Developers Conference. – Money off coupons. Nvidia does not offer money off coupons to end-users directly, but its distributors use this particular sales promotions technique regularly. – Free gifts. The company offers free gifts occasionally as part of its marketing strategy. For example, in 2023 Nvidia offered Marvel’s Midnight Suns Captain Marvel’sMedieval Marvel Suit free of charge to users of graphics cards GeForce GTX 10 and above. Nvidia Corporation Report contains a full analysis of Nvidia marketing communication mix and Nvidia marketing strategy in general. The report illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic…

Nvidia ecosystem refers to the network of interconnected components, technologies, and partners that work together to support the company’s products and services. The following are the key elements of Nvidia ecosystem: 1. Products. The core of Nvidia’s ecosystem is its products, which include graphics cards, data centre products, and system-on-a-chip (SoC) products. These products form the foundation of the ecosystem and are used by developers, data scientists, and other users to create and innovate. 2. Developer Tools and Platforms. The company offers a range of developer tools and platforms to support the development of software and applications that leverage Nvidia’s products. These tools and platforms include CUDA, TensorRT, and the Nvidia Deep Learning Institute. 3. Partner Network. Nvidia has a broad partner network that includes hardware and software vendors, cloud providers, system integrators, and other partners. These partners help to integrate Nvidia’s products and technologies into a wide range of solutions and services, further strengthening its ecosystem. 4. AI and HPC Applications. Nvidia’s ecosystem is used to support a wide range of artificial intelligence (AI) and high-performance computing (HPC) applications. These include, but not limited to deep learning, computer vision, and scientific simulations. These applications leverage Nvidia’s products and technologies to achieve breakthrough performance and efficiency. 5. Community and Support. The multinational technology company has a strong community of users and developers who support each other through forums, user groups, and other online communities. The company also offers customer support services to help users troubleshoot issues and optimize their use of Nvidia’s products and technologies. To summarize, Nvidia ecosystem is dynamic and comprises interconnected network of products, technologies, partners, and communities that work together to support innovation and growth. By fostering a strong ecosystem, the company aims to drive innovation and accelerate the adoption of AI and HPC…
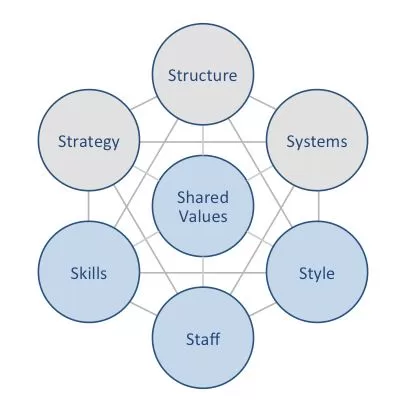
Nvidia McKinsey 7S model illustrates the ways in which seven elements of businesses can be aligned to increase effectiveness. According to the framework strategy, structure and systems represent hard elements, whereas shared values, skills, style and staff are soft elements. McKinsey 7S model stresses the presence of strong links between elements in a way that a change in one element causes changes in others. The model positions shared values are positioned at the core remaining elements, because shared values guide employee behaviour with implications on their performance. McKinsey 7S model Hard Elements in Nvidia McKinsey 7S Model Strategy. Nvidia business strategy benefits from first mover advantage systematically. This has been the case with GPU, Computer Unified Device Architecture (CUDA) and invented deep learning hardware accelerators, such as the Tesla V100 and T4 GPUs and a range of other products. However the sustainability of this strategy in the long-term perspective requires the regular pipeline of new products through effective investment in research and development. Structure. As one of the largest multinational technology companies in the world Nvidia organizational structure integrates the elements of functional and hybrid structures. Within the company business processes are divided into various divisions with highly specialised employees with the relevant skills and competencies attached into respective divisions. Furthermore, the senior management forms temporary project groups to develop new products or for other initiatives and group members report to multiple superiors for the duration of project. Systems. Nvidia depends on a wide range of systems for the business to operate smoothly. These include, but not limited to employee recruitment and selection, team development and orientation, transaction processing, customer relationship management, business intelligence and knowledge management. Each system has its KPIs and controls in place and they are monitored systematically. Nvidia Corporation Report contains a full analysis of Nvidia…
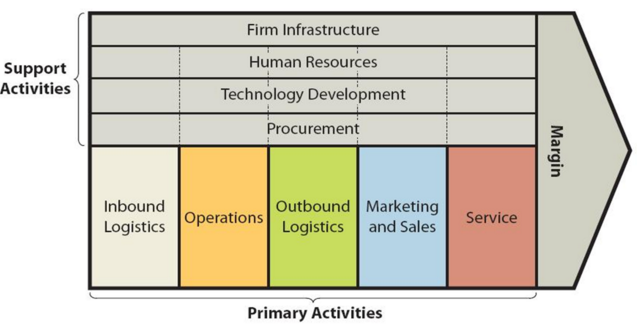
Nvidia value chain analysis is an analytical framework that assists in identifying business activities that can create value and competitive advantage to the business. Specifically, business leaders can create competitive advantage through dividing the business into various activities and analysing each activity individually from value creation perspective. Figure below illustrates the essence of Nvidia value chain analysis. Value chain analysis Primary Activities in Nvidia Value Chain Analysis Nvidia Inbound logistics Nvidia inbound logistics involves managing the supply chain of components and raw materials into the premises of its contract manufacturers. The multinational technology company performs quality checks of semiconductors and other spare parts using test equipment purchased from industry-leading suppliers such as Advantest America Inc. Nvidia benefits from the economies of scale in inbound logistics activities due to the large amount of spare parts and components it purchases. Furthermore, the company has strategic relationships with its key suppliers in place and these relationships play an instrumental role in new product development. Nvidia Operations Nvidia employs fabless manufacturing strategy. It employs third party companies outside of United States for all phases of the manufacturing process, including wafer fabrication, assembly, testing, and packaging.[1] Nvidia does not engage in any of these activities directly and chooses to focus the design, marketing and distribution of its products. The company works with world-class manufacturers to produce its products. Semiconductor wafers are produced by leading companies such as Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company Limited and Samsung Electronics Co. Ltd, adapter card products and switch systems are produced by the likes of Flex Ltd., Jabil Inc., and Universal Scientific Industrial Co., Ltd. and Fabrinet manufactures Nvidia cables. Assembly, testing and packaging of products and platforms are done by Amkor Technology, King Yuan Electronics Co., Ltd., Omni Logistics, LLC, Siliconware Precision Industries Company Ltd., Wistron Corporation…
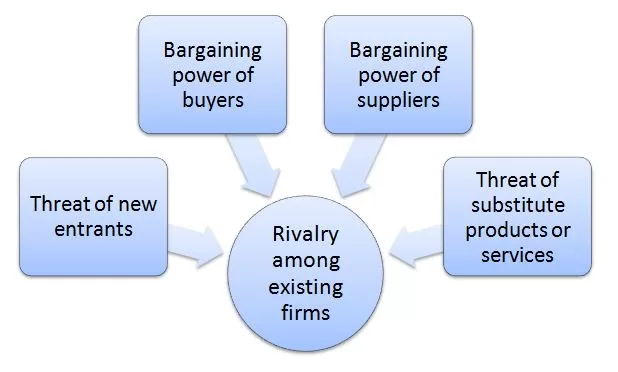
Porter’s Five Forces analytical framework developed by Michael Porter (1979)[1] consists of five individual forces that shape an overall extent of competition in the industry. Nvidia Porters Five Forces are illustrated in figure below: Porter’s Five Forces Threat of new entrants in Nvidia Porter’s Five Forces Analysis Threat of new entrants into graphics processing unit (GPU) industry is low. The below are the main factors that determine the level of threat of new entrants: 1. Time of entry. GPUs are highly saturated market with dominant market players already in the business for decades. Moreover, customer loyalty towards dominant players such as Advanced Micro Devices (AMD, Intel Corporation, Qualcomm Inc., Broadcom Inc. and Arm Holdings (a subsidiary of Softbank Group) is high this fact crates entry barrier for potential market entrants. 2. Massive investments. GPU producing requires massive capital requirements of millions of dollars. It will be very challenging for potential market entrance to secure funding for producing GPUs unless they offer unique competitive advantages with the potential to disrupt the market. 3. Specialist knowledge. GPUs are highly advanced technological products. The production requires highly specialist knowledge and technological know-how. New market entrants will face substantial difficulties in terms of finding employees with specialist knowledge who will agree to join a new company in a highly saturated market. Bargaining power of buyers in Nvidia Porter’s Five Forces Analysis The bargaining power of buyers for Nvidia products is generally insubstantial. The following considerations need to be taken into account in this regard: 1. Switching costs. Nvidia’s products are often integrated into larger systems and it is often difficult to replace these products with similar products produced by competitors due to massive costs and expertise knowledge involved. Such a situation limits buyer bargaining power with positive implications for Nvidia. 2.…

Nvidia segmentation, targeting, and positioning (STP) is a strategic approach to marketing that involves dividing the market into smaller groups of consumers (segmentation), selecting one or more of these groups to target with a specific marketing mix (targeting), and then positioning the product or service in the minds of consumers in a way that differentiates it from the competition (positioning). Nvidia uses the following types of product positioning. – Anticipatory positioning. Anticipatory product positioning is a strategy in which a company positions its products or services in a way that anticipates future trends or needs in the market. Nvidia has used this strategy effectively by positioning its products in a way that anticipates the increasing demand for high-performance computing solutions and emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and autonomous vehicles. For example, Nvidia recognized in early 1990s the potential of AI and positioned its products accordingly, investing heavily in research and development to create GPUs that are specifically designed to accelerate AI workloads. As a result, Nvidia has become a key player in the AI market, with its GPUs powering many of the most advanced AI applications in industries such as healthcare, finance, and automotive. – Quality product positioning. Quality product positioning is a strategy in which a company positions its products or services as high-quality, reliable, and superior to those of its competitors. Nvidia has used this strategy effectively by emphasizing the quality and reliability of its products and by investing in research and development to continually improve its offerings. Accordingly the company creates high-performance GPUs for a wide range of applications, from gaming to data centre workloads. The following table illustrates Nvidia segmentation, targeting and positioning: Type of segmentation Segmentation criteria Nvidia target customer segment Geographic Region Taiwan, China, United States, other countries Density Urban…

Nvidia marketing mix (Nvidia 7Ps of marketing) comprises elements of the marketing mix that consists of product, place, price, promotion, process, people and physical evidence. Product Element in Nvidia Marketing Mix (Nvidia 7Ps of Marketing) Nvidia develops and sells graphics processing units (GPUs) and related software for a wide range of applications. Nvidia products are used for gaming, professional visualization, data centre and cloud computing, artificial intelligence, autonomous vehicles, and other high-performance computing applications. Moreover, the multinational technology company also sells system-on-a-chip (SoC) products for mobile devices, development kits, and software development tools for AI and GPU computing. Place Element in Nvidia Marketing Mix (Nvidia 7Ps of Marketing) The company uses a number of sales channels in an integrated manner to deliver its products to the end user. These include the following: – Direct Sales. The software and fables company offers its products through its online store at www.store.invidia.com. Also the company has some physical retail stores called “Nvidia GeForce Experience Stores” located in major cities worldwide such as Los Angeles, London, Munich, Stockholm and Sydney. – OEM Partnerships. Nvidia partners with original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) to sell its products as part of their systems. Their main OEM partners are major computer manufacturers such as Dell, HP, and Lenovo. – Distribution Partnerships. The company also relies on distributors to sell its products to retailers and system integrators. For example, Micro, Synnex, and Tech Data are major distributors for Nvidia. –E-tailers. Major e-tailers, such as Amazon, Newegg, and Best Buy also sell Nvidia products to end users. – System Integrators. These are the companies that build custom systems for customers, incorporating Nvidia’s products as part of the solution. – Cloud Service Providers. Cloud service providers such as Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud offer GPU-accelerated computing…
