Value Chain Analysis
Value chain analysis is a strategic analytical and decision-support tool that highlights the bases where businesses can create value for their customers. The framework can also be applied to identify sources of competitive advantage for businesses. Value chain is a set of consequent activities that businesses perform in order to achieve their primary objective of profit maximization.
Most sources explain the essence and application of value chain analysis assuming their audience is businesses aiming to increase the level of their competitiveness. Here, we adopt an alternative approach. Below is an explanation of value chain analysis for business students who have been assigned to apply this strategic analytical tool as part of assignment given by their educational institution.
Theory of Value Chain Analysis
The concept value chain analysis was introduced by Michael Porter in 1985[1] and its significance and relevance to strategic management and marketing has not diminished during 30 years of its existence.
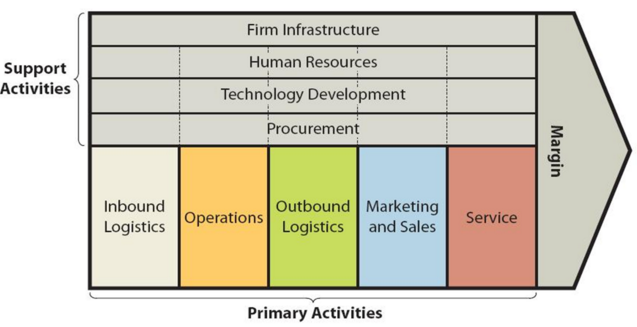
The framework divides activities that generate value into two categories – primary activities and support activities. Primary activities comprise a set of activities that contribute to the creation of value in a direct manner. Support activities consist of functions and tasks that are intended to support primary activities.
It is important to clarify that the relevance of value chain analysis is not limited to manufacturing businesses and the framework can be applied towards service firms as well.
Primary Activities
Inbound logistics involve receiving and storing raw materials and their usage in manufacturing as the necessity arises.
Operations relate to the processes of transforming raw materials into finished goods. For businesses operating in services sector operations relate to the process of providing the service.
Outbound logistics is associated with warehousing and distribution of finished products.
Marketing and sales refer to the choice and implementation of marketing strategy to communicate the marketing message to the target customer segment and generation of sales.
Service relates to support provided to customers after the sale.
Support Activities
Infrastructure of a company comprises its organizational structure, its departments and committees, organizational culture etc.
Human Resource Management involves a wide range of activities related to employee recruitment and selection, training and development, appraisals, motivation and compensation.
Technology development involves the use of technology to increase the effectiveness of primary activities in terms of value creation.
Procurement relates to the purchasing practices of raw materials, tools and equipment.
Businesses need to engage in value creation via their primary and support activities in order to survive in the marketplace. Value can be created in one of the following two ways.
a) Cost advantage: Businesses can reduce the costs of activities wherever possible and use the cost benefit to reduce the price of their final products or services
OR
b) Differentiation: businesses can focus on activities closely associated with their competitive advantage. Investing in activities adapted as sources of competitive advantage allows the business to increase the quality of their products and services and sell them for higher prices.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Value Chain Analysis
Application of value chain analysis offers the following advantages:
1. Value chain analysis can play an instrumental role in terms of detecting organizational, tactical and strategic issues related to the business.
2. The tool assists businesses to appreciate potential sources of competitive advantage.
3. The strategic framework can be applied to any type of business regardless of the industry and the size of the business.
As it is the case with any other theoretical framework or model, the concept of value chain is not free from limitations. These can be summarized into the following points:
1. The framework assumes that it is possible to achieve a clear separation of company operations into different primary and support activities. This may not be the case in real life taking into account increasing level of complexity of business operations.
2. Application of the tool in practice can be overly time-consuming process, since it requires a comprehensive analysis of all business operations.
3. It may be difficult to find all the required information in order to conduct value chain analysis in an appropriate manner.
Application of Value Chain Analysis
You can follow the following stages in order to conduct value chain analysis as a part of your assignment:
Stage 1: Explaining the theory and the essence of value chain analysis
Write a brief introduction to the theory of value chain analysis. You may want to add the figure of value chain analysis (do not forget appropriate referencing). Inclusion of a brief discussion about advantages and disadvantages of the framework as mentioned above will contribute to your mark.
Stage 2: Researching primary and support activities of your case study company
Value chain analysis can be applied in relation to a business unit, operating segment, business division or a company. If you have a choice, business unit is the most appropriate level for conducting value chain analysis from the practicality point of view.
Some students prefer to choose their employer as a case study. However, student employers often happen to be small or medium sized business and it is difficult find necessary amount of relevant data to conduct value chain analysis in an appropriate manner.
Selection of a multinational company is a more desirable scenario to be able to produce a quality value chain analysis due to the availability of needed company-specific data. Company annual report is the most comprehensive source of data and you can also find useful information on official website of the company.
Alternatively, you can purchase company reports on major multinational enterprises form this portal. Reports comprise detailed value chain analyses of respective companies to be used as examples and template. Reports are kept updated regularly.
Stage 3: Illustrating how each activity is facilitated by the case study company
This stage consists of two parts:
Firstly, write about the manners in which the business conducts each activity. For example, for inbound logistics primary activity you can mention about the nature of raw materials the company uses and write about the numbers and location of suppliers. Similarly, when writing about operations primary activity you can discuss specific nature of company’s operations, as well as, numbers and locations of manufacturing units.
Secondly, identify and discuss activities and sub-activities that create the most value for the company you are analyzing. This depends on the choice of cost advantage or differentiation business strategy by company. If the company benefits from cost advantage strategy, you have to specify which activities contribute the most to the achievement of cost leadership. In other words, you have to explain where the company saves the most cash and how.
Alternatively, if the company focuses on differentiation business strategy, you will need to find and discuss activities that the company has adapted as sources of its competitive advantage. Remember to justify each argument by referring to relevant statistical or non-statistical data from reliable sources.
It has to be noted that there are also some general value adding strategies that can be used by businesses following both strategies – cost advantage AND differentiation. For example, Just-in-Time supply chain management system can be applied to create value in inbound logistics by businesses using cost leadership strategy, as well as, businesses using differentiation strategy with an equal level of efficiency.
Below you can find some of the most popular value creation strategies used by businesses following cost leadership and differentiation business strategies:
Primary activities
| Activities | Value adding strategies | Costleadership | Differen-tiation |
| Inbound logistics | Economies of scale | Relevant | Relevant |
| Just-in-Time supply chain management | Relevant | Relevant | |
| Development of strategic relationships with suppliers | – | Relevant | |
|
Operations |
Sophisticated operational systems | Relevant | Relevant |
| Benefiting from technological innovations | Relevant | Relevant | |
| Use of the most advanced technologies to increase the quality | – | Relevant | |
| Locating operations units in developing countries | Relevant | Relevant | |
| Outbound logistics | Delivering to consumers directly without intermediaries | Relevant | Relevant |
| Cooperation with other businesses to share distribution costs | Relevant | – | |
| Extensive integration of information and communication technologies | Relevant | Relevant | |
| Marketing & sales | Effective utilization of social media and viral marketing | Relevant | Relevant |
| Sophisticated online sales system | Relevant | Relevant | |
| Direct marketing to save costs | Relevant | ||
| Service | Superior customer services | – | Relevant |
| Efficient product return and refund practices | – | Relevant | |
| Follow-up by the company after the sales | – | Relevant |
Support activities
| Activities | Value adding strategies | Cost leadership | Differen-tiation |
| Firm infrastructure | Flat organizational structure | Relevant | Relevant |
| Innovative organizational culture | Relevant | Relevant | |
| Advanced quality control system | – | Relevant | |
|
Human resources management |
Employee motivation via application of intangible employee motivation tools | Relevant | Relevant |
| Extensive employee support and development programs | – | Relevant | |
| Attracting highly qualified and competent employees for all levels | – | Relevant | |
| Reducing operational expenses via paying minimum wages | Relevant | Relevant | |
|
Technology development |
Effective integration of technology into a wide range of organizational processes and procedures | Relevant | Relevant |
| Breakthroughs via investments in new technology development | – | Relevant | |
| Sharing of technology with other firms to save costs | Relevant | – | |
| Procurement | Procurement of unique inputs | – | Relevant |
| Negotiating the cheapest price | Relevant | – | |
| Gaining cost advantage due to high volume | Relevant | Relevant |
You can find many examples for the application of value chain analysis using the case studies of famous global brands here.
[1] Porter, M.E. (1985) Competitive Advantage: Creating and Sustaining Superior Performance, Simon & Schuster