Research Reliability
Reliability refers to whether or not you get the same answer by using an instrument to measure something more than once. In simple terms, research reliability is the degree to which research method produces stable and consistent results.
A specific measure is considered to be reliable if its application on the same object of measurement number of times produces the same results.
Research reliability can be divided into three categories:
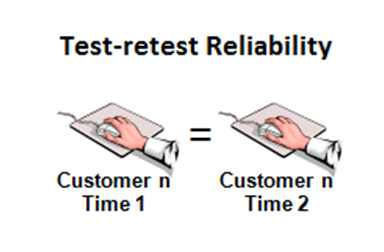
1. Test-retest reliability relates to the measure of reliability that has been obtained by conducting the same test more than one time over period of time with the participation of the same sample group.
Example: Employees of ABC Company may be asked to complete the same questionnaire about employee job satisfaction two times with an interval of one week, so that test results can be compared to assess stability of scores.
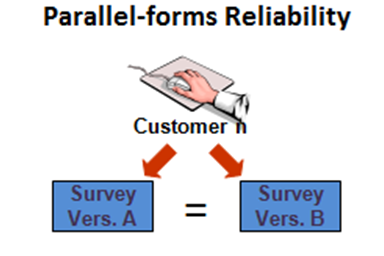
2. Parallel forms reliability relates to a measure that is obtained by conducting assessment of the same phenomena with the participation of the same sample group via more than one assessment method.
Example: The levels of employee satisfaction of ABC Company may be assessed with questionnaires, in-depth interviews and focus groups and results can be compared.
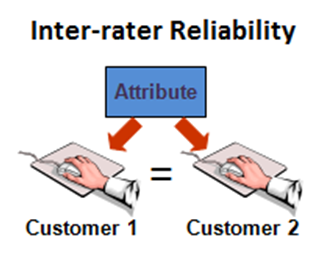
3. Inter-rater reliability as the name indicates relates to the measure of sets of results obtained by different assessors using same methods. Benefits and importance of assessing inter-rater reliability can be explained by referring to subjectivity of assessments.
Example: Levels of employee motivation at ABC Company can be assessed using observation method by two different assessors, and inter-rater reliability relates to the extent of difference between the two assessments.
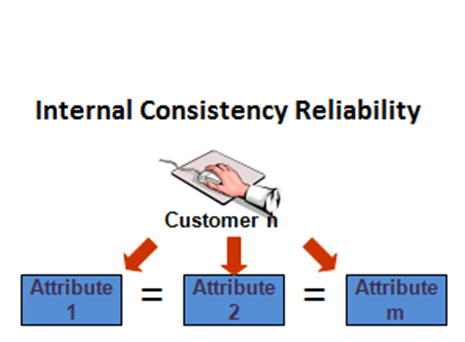
4. Internal consistency reliability is applied to assess the extent of differences within the test items that explore the same construct produce similar results. It can be represented in two main formats.
a) average inter-item correlation is a specific form of internal consistency that is obtained by applying the same construct on each item of the test
b) split-half reliability as another type of internal consistency reliability involves all items of a test to be ‘spitted in half’.
My e-book, The Ultimate Guide to Writing a Dissertation in Business Studies: a step by step assistance offers practical assistance to complete a dissertation with minimum or no stress. The e-book covers all stages of writing a dissertation starting from the selection to the research area to submitting the completed version of the work within the deadline. John Dudovskiy