Simple Random Sampling
Simple random sampling (also referred to as random sampling or method of chances) is the purest and the most straightforward probability sampling strategy. It is also the most popular method for choosing a sample among population for a wide range of purposes. This method is considered to be the most unbiased representation of population. Nevertheless, sampling error persists with this method, similar to other sampling methods.
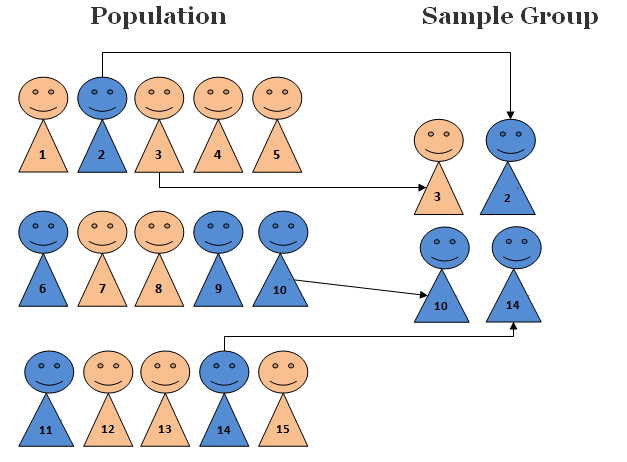
In simple random sampling each member of population is equally likely to be chosen as part of the sample. It has been stated that “the logic behind simple random sampling is that it removes bias from the selection procedure and should result in representative samples”[1].
Ideally, the sample size of more than a few hundred is required in order to be able to apply simple random method in an appropriate manner.[2] It can be argued that this method is easy to understand in theory, but difficult to perform in practice. This is because working with a large sample size is not easy and it can be a challenge to get a realistic sampling frame.
Many dissertation supervisors advice the choice of random sampling methods due to the representativeness of sample group and less room for researcher bias compared to non-random sampling techniques. However, application of these methods in practice can be quite difficult due to the need for the complete list of relevant population members and a large sample size.
Other variations of random sampling include the following:
There are two popular approaches that are aimed to minimize the relevance of bias in the process of random sampling selection: method of lottery and the use of random numbers.
The method of lottery is the most primitive and mechanical example of random sampling. In this method you will have to number each member of population in a consequent manner, writing numbers in separate pieces of paper. These pieces of papers are to be folded and mixed into a box. Lastly, samples are to be taken randomly from the box by choosing folded pieces of papers in a random manner.
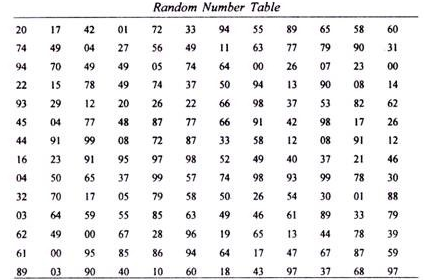
The use of random numbers, an alternative method also involves numbering of population members from 1 to N. Then, the sample size of N has to be determined by selecting numbers randomly. The use of random number table similar to one below can help greatly with the application of this sampling technique.
Application of Simple Random Sampling: an Example
Let’s assume that as part of your dissertation you are assessing leadership practices on work-life balance in ABC Limited that has 600 employees. You have chosen survey as primary data collection method for this research. In this scenario you can apply simple random sampling method involves the following manner:
- Prepare the list of all 600 employees working for ABC Limited
- Assign a sequential number for each employee from 1 to N (in your case from 1 to 600).
- Determine the sample size. In your case the sample size of 150 respondents might be sufficient to achieve research objectives.
- Use random number generator and generate 150 numbers from 1 to 600. You can do it using software such as Research Randomizer, Stat Trek or any other. Once random numbers are generated, in total 150 employees assigned with respective generated numbers are going to represent sample group members for your research.
Advantages of Simple Random Sampling
- If applied appropriately, simple random sampling is associated with the minimum amount of sampling bias compared to other sampling methods.
- Given the large sample frame is available, the ease of forming the sample group i.e. selecting samples is one of the main advantages of this method.
- Research findings can be generalized due to representativeness of this sampling technique and a little relevance of bias.
- It is straightforward sampling method that requires no advanced technical knowledge
Disadvantages of Simple Random Sampling
- It is important to note that application of random sampling method requires a list of all potential respondents (sampling frame) to be available beforehand and this can be costly and time-consuming for large studies.
- The necessity to have a large sample size can be a major disadvantage in practical levels.
- This sampling method is not suitable for studies that involve face-to-face interviews covering a large geographical area due to cost and time considerations.
My e-book, The Ultimate Guide to Writing a Dissertation in Business Studies: a step by step approach contains a detailed, yet simple explanation of sampling methods. The e-book explains all stages of the research process starting from the selection of the research area to writing personal reflection. Important elements of dissertations such as research philosophy, research approach, research design, methods of data collection and data analysis are explained in this e-book in simple words.
John Dudovskiy
[1] Gravetter, F.J & Forzano, L.B. (2011) “Research Methods for the Behavioural Sciences” Cengage Learning p.146
[2] Saunders, M., Lewis, P. & Thornhill, A. (2012) “Research Methods for Business Students” 6th edition, Pearson Education Limited