Search results for: Ansoff Matrix
SWOT is an acronym for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats related to organizations. The following table illustrates Apple SWOT analysis: Strengths 1. High quality, design and performance of Apple products and services 2. Brand value of more than USD 3 trillion 3. High profit margin 4. Solid financial position of the business 5. Sophisticated supply-chain infrastructure Weaknesses 1. Lack of innovation 2. Decreasing sales of iPhones 3. Higher prices than competition 4. Incompatibility of Apple products and services with other products and services for users 5. Limited customazation options of products Opportunities 1. Further increasing concentration on Services business segment 2. Increasing focus in research and development 3. Product diversification 4. Formation of strategic partnerships 5. Increasing focus on green technology Threats 1. Quality problems with negative effects on sales and Apple brand image 2. Intensifying competition from China and India 3. Being found to have infringed on intellectual property rights 4. Reputation damage due to the tax scandal 5. Disruptive innovation by competitors Apple SWOT analysis Strengths in Apple SWOT Analysis 1. High quality of Apple products and services in terms of design and performance is the main strength of the company. Co-founder and late CEO Steve Jobs never compromised design and functionality because of the cost of raw materials and manufacturing. The same principle persists to this day. The tech giant pursues differentiation business strategy and effectively differentiates its products and services with high quality, design and performance. Moreover, highly sophisticated Apple ecosystem plays an instrumental role in maintaining brand loyalty and consequently sustaining market share in the global scale. Specifically, third-party products are not usually compatible with Apple products and all products belonging to Apple portfolio work well with each-other. Thanks to services such as iCloud, airplay, and airdrop, you can start a task in on…
PESTEL is a strategic analytical tool and the acronym stands for political, economic, social, technological, environmental and legal factors. Apple PESTEL analysis (or Apple PESTLE analysis) involves the analysis of potential impact of these factors on the bottom line and long-term growth prospects for the tech giant. Political Factors in Apple PESTEL Analysis The extent to which Apple is able to achieve its primary objective of profit maximization depends on a wide range of political factors. These include government stability, level of bureaucracy, corruption, freedom of press, home market lobbying groups etc. Additionally, activities of trade unions can be mentioned as important external political factors for Apple. Tax Payments The payment of taxes is a noteworthy political factor affecting Apple. The multinational technology company uses complex legal means to keep its tax payments as low as possible globally, especially in the US and Ireland. In the US, the tech giant holds the majority of its cash offshore so that it can avoid paying corporate income taxes in the US.[1] Any changes in government taxation policies may affect the bottom line for the iPhone maker. In Europe, European Commission concluded that Apple should have paid the Irish state at least €14 billion (USD 16.2 billion) in corporate tax for 2004-2014. However, in 2020 the General Court of the European Union ruled that European Commission was wrong, a decision that was welcomed by the Irish government.[2] Changes in taxation policies in general and the stance of governments and government agencies towards the iPhone maker in particular are external political factors that have implications for the business. Dispute with US Federal Bureau of Investigations The most significant case that illustrates the potential impact of a political factor relates to Apple’s battle with US Federal Bureau of Investigations (FBI). Specifically, the…
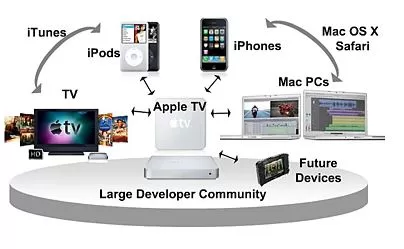
Ecosystem in its essence is “a biological community of interacting organisms”[1]. In technology terms, ecosystem refers to a group of devices and software that represent a single collaborative network. In other words, it is how well each product or service belonging to a company work individually and if end-users will get better experience when all of these products and services work together. It is the question if the whole is greater than sum of all parts. Apple ecosystem is one of the main competitive advantages associated with the brand. In fact, the iPhone maker is one of the earliest technology companies globally to purposefully form an ecosystem. Third-party products are not usually compatible with Apple products and all products belonging to Apple portfolio work well with each-other. At the same time, the ecosystem of Apple is much more than just a collection of more than 2 billion active devices[2] or services that work seamlessly. Apple ecosystem integrates the following key elements: Company image of creativity that motivates customers to upgrade their devices frequently. Perception of status and effectiveness that is associated with using Apple products Efficient devices and services that perform best with other Apple products and services Apple ID is the cornerstone of the ecosystem. It is used to register all Apple devices. Advantages of Apple Ecosystem Thanks to services such as iCloud, airplay, and airdrop, one can start a task in on one Apple device and continue it on another and there is no need to download or install anything. Moreover, Apple ecosystem offers features like AirDrop, iMessage, and FaceTime on macOS; unlocking a Mac laptop with an Apple Watch; or auto-pairing and finding lost AirPods, and the list goes on. Today, Apple ecosystem is widely considered to be the best in the industry, and arguably in…

Corporate culture of Apple plays an important role in efficiently maintaining its operations in the global scale with 164,000 full-time equivalent employees.[1] Apple organizational culture used to have a reputation of being harsh, demanding and intimidating under the leadership of founder and late CEO Steve Jobs. However, it can be argued that since assuming the top leadership in 2011, Tim Cook has invested considerable efforts towards ‘humanising’ the brand. Specifically, unlike his predecessor, Tim Cook has spoken out about human rights, privacy, immigration reform and environmental issues.[2] Apple corporate culture integrates the following important features: 1. Creativity and innovativeness. Apple pursues the business strategy of product differentiation with the focus on the design and functionality of products and services. An effective implementation of this strategy in practice requires a high level of creativity and innovativeness from employees at all levels. Accordingly, in order to encourage their employees to be more creative and innovative, the company attempts to develop relevant working environment. Creative design of Apple Campus, informal dress codes and creatively designed working space can be mentioned to illustrate this point. 2. Working under pressure. Ability to work under pressure is a must-have skill for Apple employees at all levels. In fact, it is challenging to work for the first company ever to be valued at $3 trillion. Most projects have strict and short deadlines and working long hours is a norm in the company. CEO Tim Cook sets example in terms of his loyalty to the company and working long hours. He is known for sending emails to employees at 4:30 am. Moreover, Sunday is a work night for many managers at Apple because of the executive meeting the next day. Not everyone can sustain to work at such an intense rate. But employees who survive within the first…

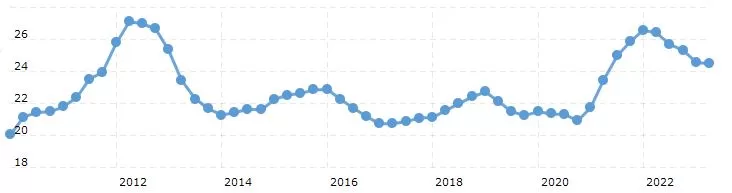
Apple business strategy can be classified as product differentiation. Specifically, the multinational technology company differentiates its products and services on the basis of simple, yet attractive design and advanced functionality. Apple business strategy consists of the following four elements: 1. Focus on design and functionality of products. According to its business strategy, Apple has adapted advanced features and capabilities of its products and services as bases of its competitive advantage. The list of innovations introduced by Apple include, but not limited to the introduction of iPad, the first device of its kind that stored thousands of songs with a simple shuffle capabilities through songs, development Macintosh, the first computer to use a graphical user interface and the launch of iMac that “ripped up the computer design rule book, doing away with dull beige boxes and instead replacing them with fun, translucent machines in shades such as “Bondi Blue” that hinted at the aesthetic Apple would become so well-known for.”[1] The first company ever to be valued at $1 trillion systematically improves features and capabilities of its products, setting new standards for the industry at the same time. Take photos for example. Apple single-handedly advanced global photography industry with a range of innovations illustrated in table below. Innovation Year High dynamic range imaging 2010 Panorama photos 2012 True Tone flash 2013 Optical image stabilization 2015 Dual-lens camera 2016 portrait mode 2016 portrait lighting 2017 night mode 2019 LiDar scanning 2020 Photography innovations by Apple Inc. First mover advantage is another element of Apple competitive advantage. It has to be stated that Apple competitive advantage may be challenging to be sustained for long-term perspective. Specifically, the management may fail in terms of ensuring the addition of innovative features and capabilities in new versions of its products, thus compromising…
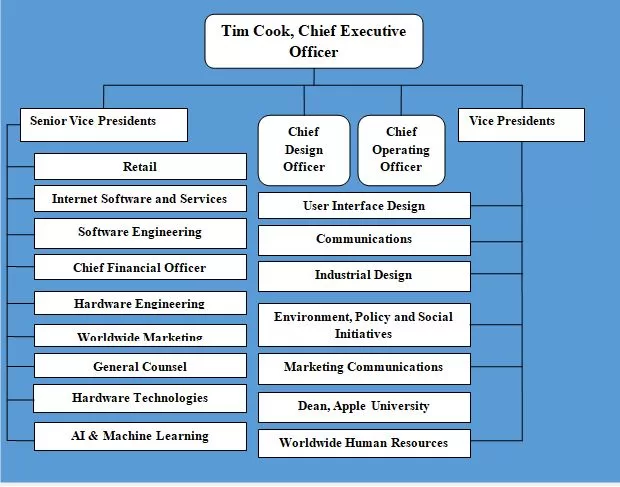
Apple organizational structure can be described as hierarchical and functional. Such a structure has been developed by its founder and former CEO late Steve Jobs in order to ensure focused realization of his innovative ideas and clear vision for the business. When Steve Jobs returned to turnaround failing Apple in 1997 the company had a typical organizational structure with many business units with their own profit and loss (P&L) responsibilities. In order to increase the coherence and fuel innovation, Jobs fired general managers of all business units (within one day) and put in place one P&L for the entire business. Apple organizational structure has been subjected to certain modifications since the leadership role was assumed by Tim Cook on August 2011. Specifically, Mr. Cook embraced the decentralization of decision making to a certain extent in order to encourage innovation and creativity at various levels. Also, Cook divided hardware function into hardware engineering and hardware technologies. As the most recent change to the corporate structure Cook added artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning as separate function areas due the increasing importance of AI and machine learning. Currently, Apple organizational structure has the format illustrated in figure below: Apple Organizational Structure Generally, Apple corporate structure has the following characteristics: 1. Hierarchical organizational structure. Although Tim Cook introduced considerable changes to Apple corporate structure since assuming the top job in 2011, the structure still remains to be highly hierarchical with many layers of management. Massive size of the company that comprises 164,000 full-time equivalent employees globally necessitates the adherence to the hierarchical organisational structure. Advantages of Apple hierarchical organizational structure include tight control possessed by senior management over all aspects of the business. Moreover, promotion opportunities motivate employees to perform well and there are clear levels of authority and responsibility. On the negative…

During Steve Jobs era that covers the period 1997 – 2011, Apple leadership was autocratic with Steve Jobs micro-managing a wide range of business operations. It has been noted that “when Steve Jobs was in charge, everything flowed through him.”[1] Apple leadership practices have changed dramatically under Tim Cook. Acknowledged as the World’s Greatest Leader by Fortune Magazine[2], Tim Cook proved to be effective from various perspectives. Moreover, Tim Cook has been praised by employees for inspirational leadership and helping his subordinates to become a better human being.[3] The multinational technology company is parting with perfectionism and autocracy elements of leadership that had prevailed under Steve Jobs. Apple leadership style integrates the following elements: 1. Democratic leadership style. In contrast to highly autocratic leadership style of Apple co-founder and late CEO Steve Jobs, the current CEO Tim Cook exercises and promotes democratic leadership. For Cook, it is important to build consensus among senior management regarding strategic decisions for the ebusiness. Moreover, since assuming the top role, Cook granted greater autonomy to new product development team, decreasing the direct participation of the CEO in new product development process. 2. “Quiet” leadership. Tim Cook has been praised for his quiet, yet effective leadership style. Nicknamed as “quiet leader” by some industry analysts[4], Cook is totally different from his charismatic predecessor, Steve Jobs. At the same time, Tim Cook is occasionally criticized by analysts and industry watchers for the lack of ambition and vigour, his predecessor Steve Jobs had. For example, according to a report by BGC financial services firm, “under Cook, Apple has been cautious about entering new product categories. The Apple Watch, launched in April 2015, is the No. 1 smartwatch, but overall sales have disappointed. Apple Music, which debuted in June 2015, has grown rapidly to 15 million subscribers, but…
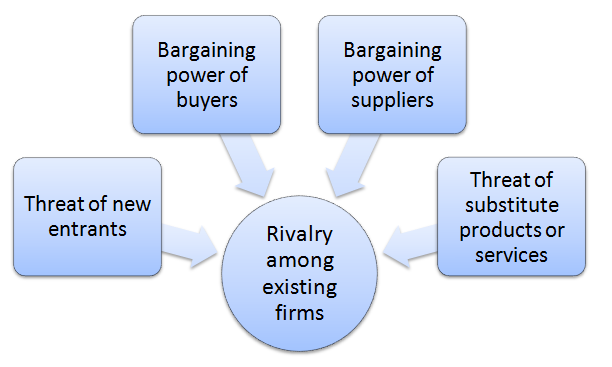
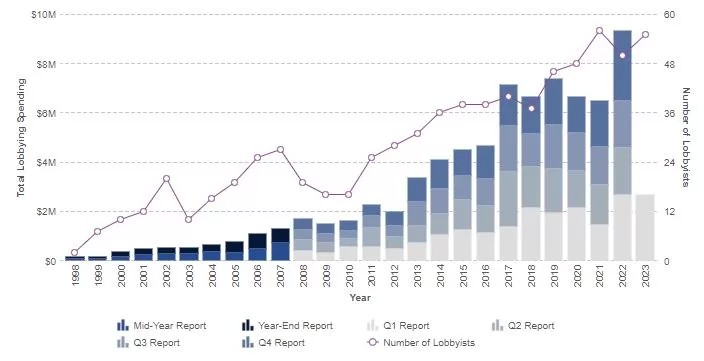
Porter’s Five Forces analytical framework developed by Michael Porter (1979)[1] represents five individual forces that shape the overall extent of competition in the industry. Apple Porter’s Five Forces are represented in Figure 1 below: Figure 1 Porter’s Five Forces Threat of new entrants in Apple Porter’s Five Forces Analysis Threat of new entrants into consumer electronics industry is not substantial. The following factors, among others, determine the threat of new entrants into the industry to compete with Apple: 1. Massive capital requirements. Manufacturing technological devices and producing operating systems require massive capital investments. As illustrated in Table 1 below, the top players in the market invest billions of dollars in R&D in order to keep the pipeline of new products and services active. New market entrants will have to produce new products and services that will have to compete with products and services of top players that invest billions of dollars every year in R&D. Rank Company R&D spending (USD) 1 Amazon 70.3 billion 2 Alphabet 38.1 billion 3 Meta Platforms 34.0 billion 4 Apple 25.3 billion 5 Microsoft 23.0 billion 6 Samsung Electronics 18.2 billion 7 Intel 17.5 billion 8 Roche 16.0 billion 9 Volkswagen 14.0 billion 10 Johnson & Johnson 14.0 billion Table 1 Top R&D spenders among technology companies in 2022 Moreover, capital is needed to obtain resources in general and to attract human resources and talented employees in particular. Accordingly, it is safe to argue that access to capital can prove to be a substantial entry barrier for new businesses. 2. Economies of scale. Economies of scale are substantial entry barrier into consumer electronics and tech industry. New players will find it difficult to compete with established global brands such as Apple, Samsung, Google and HTC that are able to gain cost advantage…
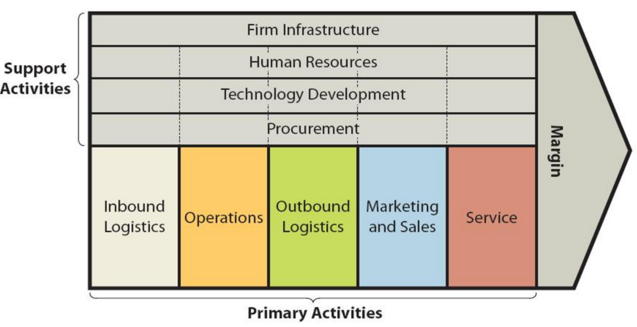
Apple value chain analysis is an analytical framework that assists in identifying business activities that can create value and competitive advantage to the business. Figure 1 below illustrates the essence of Apple value chain analysis. Figure 1 Apple Value Chain Analysis Apple Primary Activities Apple Inbound logistics Inbound logistics primary activity refers to receiving and storing of raw materials for their consecutive use in manufacturing. Apple works with hundreds of suppliers around the globe and maintains a highly sophisticated supply-chain management as illustrated in Figure 2 below. Figure 2 Apple operations roadmap[1] Apple supply chain involves more than 3 million people working for thousands of businesses in 52 countries[2] The multinational technology company’s purchase commitments typically cover its requirements for periods up to 150 days[3]. Tim Cook is an experienced word-class supply chain professional. Steve Jobs had convinced him to join Apple as head of supply chain in 1998 when the tech giant was in trouble, risking the bankruptcy. As part of massive supply chain turnover Tim Cook cut the numbers of suppliers, reduced the number of warehouses by half and established relationships with contract manufacturers. Cook has been able to reduce Apple inventory turn over from 1 month to 2-5 days. Cook further reduced the numbers of suppliers after becoming CEO in 2011. As a result of these and other initiatives, Apple supply chain practices have become a benchmark for efficiency for global businesses. The main sources of value in Apple inbound logistics relate to the economies of scale due to the massive scope and scale of business operations as discussed below and the development of strategic relationships with suppliers. Moreover, Apple Inc. exercises an immense bargaining power in dealing with its suppliers and as a result, the company is able to secure cost advantage in the purchase of…

Apple marketing mix (Apple’s 7Ps of marketing) comprises elements of the marketing mix that consists of product, place, price, promotion, process, people and physical evidence. Product Element in Apple Marketing Mix (Apple 7Ps of Marketing) In 2010, before he became chief executive officer, Tim Cook claimed that Apple’s all products could fit on a single table. At that time the multinational technology company produced only 14 products.[1] It is different now. It has been noted that “no longer do the barista and the corporate executive use the same iPhone — today, there are high-end models, consumer models, and a long line of old products the company keeps around to fill every niche and price point.”[2] Today, Apple designs, manufactures and sells technological devices such as IPhone smartphones, IPad tablets, Mac desktop and portable personal computers and iPod digital music and media players. Moreover, the company generates revenues via iTunes and the iTunes Store, Mac App Store, iCloud and Apple Pay. Apple also develops iOS and OS X operating system software and a range of application software such as iLife and iWork. Lastly, Apple Corporation designs, manufactures and sells own and third-party Mac-compatible and iOS-compatible accessories, including Apple TV, headphones, cases, displays, storage devices and various other connectivity and computing products and supplies[3]. Apple also sells third-party digital content and applications through iTunes Store®, App Store®, Mac App Store, TV App Store, iBooks Store™ and Apple Music®. Table 1 below illustrates the full range of Apple products, their brief descriptions and additions in 2023: Product Categories Description Additions in 2020 iPhone A line of smartphones based on iOS operating system iPhone SE, iPhone 12, iPhone 12 Pro, iPhone 12 Pro Max, iPhone 12 mini Mac A line of personal computers based on macOS operating system 16-inch MacBook Pro, 13-inch MacBook Pro, 27-inch iMac iPad…
