Search results for: Ansoff Matrix
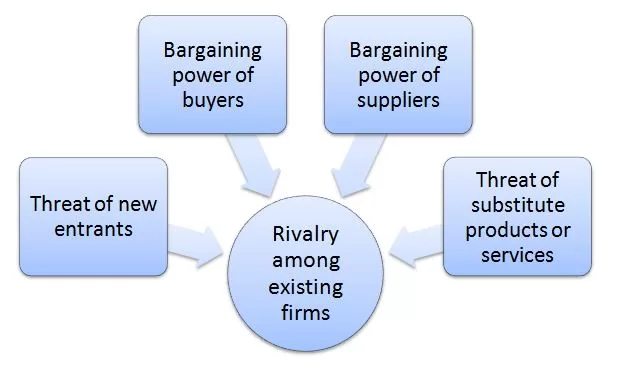
Porter’s Five Forces analytical framework developed by Michael Porter (1979)[1] represents five individual forces that shape an overall extent of competition in the industry. Square Porters Five Forces are illustrated in figure 1 below: Figure 1 Porter’s Five Forces Threat of new entrants in Square Porter’s Five Forces Analysis Threat of new entrants into the fintech sector is considerable. The following points affect the formation of the threat of new entrants into Square’s industry. 1. Time of entry. Banking and finance is already being disrupted globally and Square has been at the forefront of changes. Nowadays it has become evident that the old ways of conducting financial affairs where businesses had to wait for days, if not weeks to get their loan applications reviewed and employees have to wait for several days to get their cheques cashed will become history soon. Accordingly, some entrepreneurs, as well as, many established financial institutions are currently realizing their own projects to claim their piece of pie in the formation of the new global financial landscape. 2. Expected retaliation from current market players. While there are many entities interested in participating in the formation of new financial systems, any new market entrant will face retaliation from Square. It has to be noted that Square even stood up against deep-pocketed behemoth called Amazon. In 2014 Amazon copied Square’s main product, card reader, undercut its price by 30% and offered free two-day shipping and live customer support.[2] In response Square increased its focus on the quality of its products and customer services. By the end of 2015, Amazon had to discontinue its Register card reader. 3. Legal and regulatory barriers. Finance and banking is one of the most heavily regulated industries worldwide. There are consumer protection laws, anti-money laundering laws, broker-dealer regulations, virtual currency regulations,…

Square marketing communication mix comprises communication channels to communicate the marketing message to the target customer segment. These channels are print and media advertising, sales promotions, events and experiences, public relations and direct marketing. Square Print and Media Advertising Despite being an internet-based financial services platform, Square uses traditional forms of advertising such as TV and radio ads occasionally. The financial services and mobile payments company also uses billboards and posters to communicate its marketing message to the target customer segment. Social media is the main platform that is extensively used by Square as an effective communication channel with perspective customers. Specifically, the financial services platform uses content marketing to inform about the cases of small businesses that were able to increase their sales using Square card readers and other products and services. These success stories are meant to inspire other small businesses worldwide to try using Square products and services. Square Sales Promotions Square uses the following sales promotion techniques. 1. Square Affiliate Program. The program offers various bonuses for the use of different types of products and services by referrals. For example, the payments the company offers USD5 per new sign-up, plus a USD15 bonus when an activation starts taking payments within 45 days of signup. Moreover, there is USD5 per new sign-up, plus a USD233 bonus when an activation processes their first transaction using Square for Retail within 45 days of signup.[1] 2. Point of sale materials. Square produces and sells a wide range of point of sale products such as card readers, stands, terminals, register and wide range of related accessories. The hardware and point of sales materials are designed in simple and eye-catching attractive manners. As of September 2021, Square does not use seasonal sales promotions, money off coupons, competitions, discount vouchers,…

Square segmentation, targeting and positioning refers to a series of consecutive marketing efforts. It comprises the following stages: 1. Segmenting the market. Generally, market segmentation involves dividing population into certain characteristics. For Square, segmentation also involves private entities taking into account B2B, as well as, B2C nature of its business. The most popular types of segmentation are geographic, demographic, behavioural and psychographic. 2. Targeting the selected segment(s). Choosing specific groups among those formed as a result of segmentation to sell products and/or services. In B2B front Square selected as target customer segment small businesses facing difficulties accepting credit cards. In B2C business, the target customer segment for Square is broad. The financial unicorn decided to target the individuals in developed countries who engage in financial transactions with other individuals and this segment of population is large. 3. Positioning the offering. Choosing and applying the elements of the marketing mix that appeal best to the needs and wants of the selected target customer segment. Square developed a card reader and positioned this product as an effective solution for small businesses that were facing difficulties in accepting credit cards. The payments company is making an important shift from mono-segment towards multi-segment type of positioning. Specifically, the financial services platform started with selling card readers to small business segment only. Nowadays, Square’s expanding range of financial products and services are attracting increasing numbers of medium business segment as well. For B2C customer segment the financial services platform positioned its products and services as simplified versions of products and services already available on the market. For example, Cash App offers individuals hassle-free possibilities of investing in stock and bitcoin without any commission. Square Inc. Report contains the above analysis of Square segmentation, targeting and positioning and Square marketing strategy in general. The report illustrates…
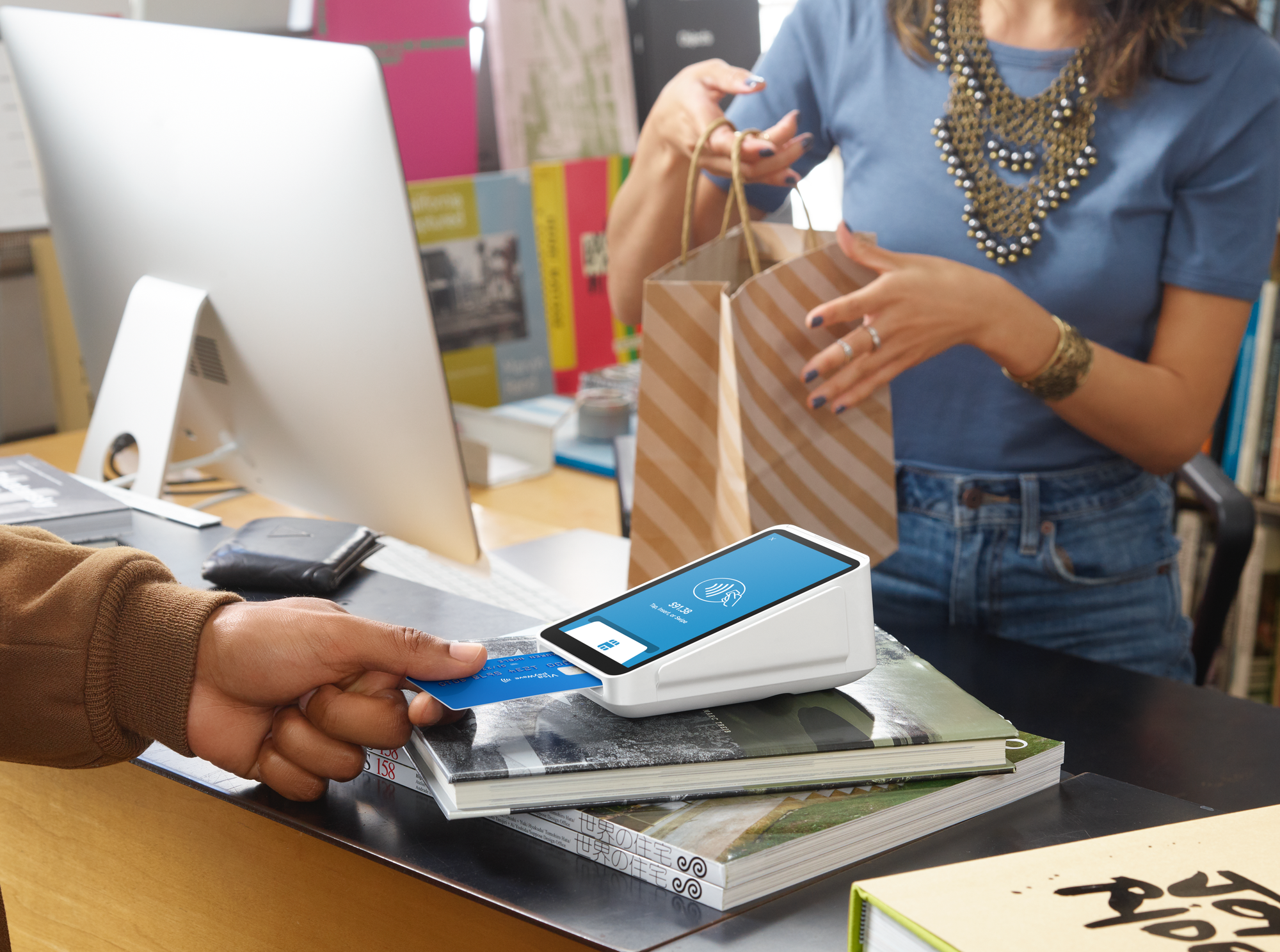

Square marketing mix (Square 7Ps of marketing) comprises elements of the marketing mix that managers can review and optimise in order to increase their revenues. The original 4Ps of the concept introduced by E. Jerome McCarthy in 1960 consisted of product, price, place and promotion. Later, additional 3Ps – process, people and physical evidence were added to further expand the model. Product Element in Square Marketing Mix (Square 7Ps of Marketing) Square offers financial products and services for small businesses, as well as, consumers. The company offers more than 30 distinct products and services to sellers that help them manage and grow their business. These include but not limited to Point of Sale (POS) systems, bank card readers, terminals, register and others. Cash App, on the other hand is an ecosystem of financial services that allows individuals to store, send, receive, spend, and invest their money. As of December 2019, Cash App had approximately 24 million monthly active customers who had at least one cash inflow or outflow during a given month.[1] The financial services and digital payments company is engaged extensively in development of new products and services to strengthen its ecosystem. Product development expenses for the year ended December 31, 2019, increased by USD173.1 million, or 35%, compared to the year ended December 31, 2018.[2] Place Element in Square Marketing Mix (Square 7Ps of Marketing) Place element of marketing mix refers to distribution strategies of products and services. Square distributes its products and services through the following channels: Online store in official website of the company Direct sales and account management teams to acquire large sellers Third-party developers and partners who offer Square solutions to their own customers. Price Element in Square Marketing Mix (Square 7Ps of Marketing) Square monetizes its products through a combination…
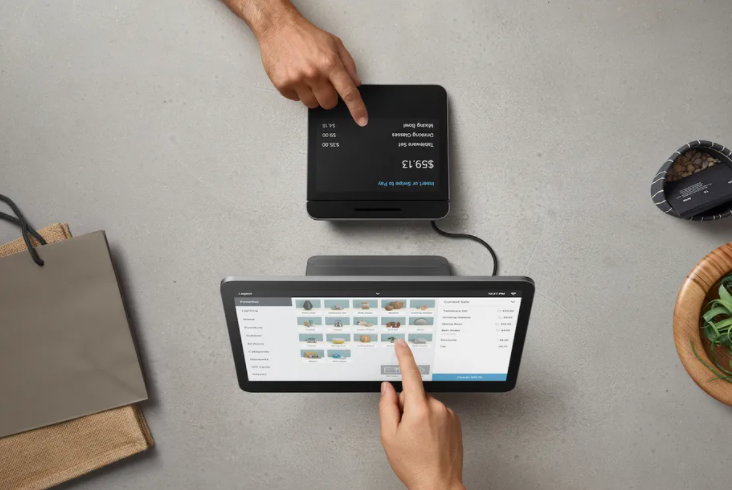

As a financial unicorn, Square was able to develop an effective ecosystem of payments products and services and gain an international acclaim. An effective marketing strategy plays an important role behind the phenomenal rise of the fintech. Sales and marketing expenses for the year ended December 31, 2019, increased by USD213.7 million, or 52%, compared to the year ended December 31, 2018. Total advertising costs for the three months ended March 31, 2021 and 2020, were USD85.9 million and USD36.2 million[1], respective. Square marketing strategy is based on the following principles: 1. Effective use of Freebies. Square offers peer-to-peer money transfer service to its Cash App customers for free as a marketing strategy. This strategy encourages extensive usage of Cash App which includes Cash Card among other features. 2. Reliance on Referrals as a marketing strategy. According to Square’s Referral Program if a customer refers her friend, both benefit from rewards. Rewards include credits on processing fees up to USD1.000 in sales over the next six months and discounts for certain type of products.[2] This program effectively contributes to the overall volume of revenues. 3. Attractive design of products. Square products are designed in a minimalistic, yet attractive manner. Designers at the B2B fintech are given a great degree of autonomy and they prioritise simplicity in their work. Square card readers, terminals, register and accessories usually attract customers’ attention due to their slick design and they effectively contribute to the overall design of small and medium business premises they are used by. 4. Content marketing. Focusing on content marketing on the basis of customer stories is one of the main pillars of Square marketing strategy. “The Square marketing team targeted tech- and social-media-savvy shop owners in the Bay Area, and these early customers helped them spread the word”[3] Nowadays,…
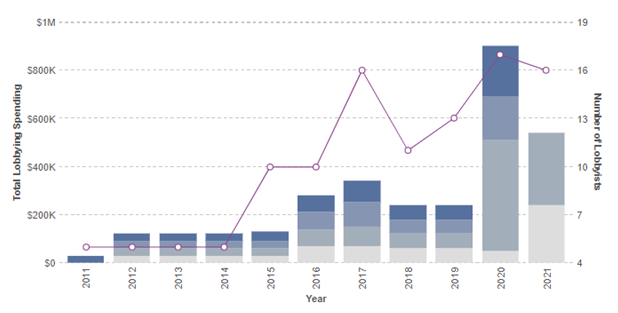
PESTEL is a strategic analytical tool. The acronym stands for political, economic, social, technological, environmental and legal factors. Square PESTEL analysis refers to the analysis of potential impact of these external factors on the performance of the financial services and digital payments company. Political Factors in Square PESTEL Analysis There are many political factors that can affect the bottom line for Square directly or indirectly. These include government stability, the level of bureaucracy, corruption, freedom of press and others. Moreover, activities of trade unions, government trade controls and tax policies, as well as, home market lobbying activities also belong to the list of political factors that can affect the business. Custom tariffs Square works with manufacturers from China to develop its hardware products. In September 2018, the United States imposed tariffs on certain imports from China, including on some Square hardware devices manufactured in China. The tariffs on these products were initially set at 10%, but were increased to 25% in May 2019. On September 1, 2019, the United States imposed new tariffs at 15% on additional imports from China, including Square’s remaining hardware products manufactured there, but rolled back these new tariffs to 7.5% effective February 14, 2020. The tariffs negatively affect the gross margin on the impacted products, which only partially has been offset by adjustments to the prices of some of the affected products. Bureaucracy Bureaucracy is one of the main political factors for Square. International market expansion for the financial services and digital payments company requires registering the business with local authorities in due manners. Business registration processes, as well as, the practice of conducting business can be highly bureaucratic, especially in developing countries and such a situation can have adverse effects on Square operations in respective markets. Particularly, bureaucracy can slow down…
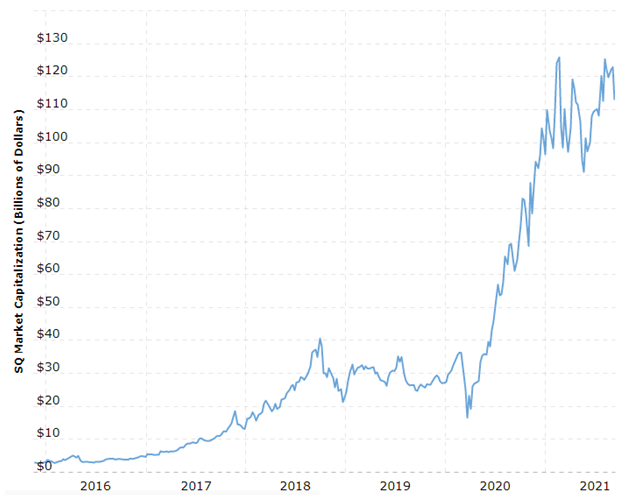
SWOT is an acronym for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats related to organizations. Strengths and weaknesses are considered as internal to the business and companies can change them. Opportunities and threats, on the other hand, are external in a way that companies cannot influence them. The following table illustrates Square SWOT analysis: Strengths 1. Strong leadership by Jack Dorsey 2. Strong brand value 3. Effective ecosystems 4. Impressive growth rate of the business Weaknesses 1. Lack of global presence 2. High employee turnover 3. Dependence on payment cards networks 4. 4. High costs of operations Opportunities 1. International market expansion 2. Developing new products and services 3. Diversification 4. Support from governments Threats 1. Jack Dorsey conflict of interest or burnout 2. Increasing complexity of the business 3. Cyberattacks 4. 4. Emergence of new competitors Square SWOT analysis Strengths in Square SWOT Analysis 1. Square co-founder and CEO Jack Dorsey is a serial entrepreneur with proven leadership skills and business acumen. Dorsey successfully exercises purpose-driven leadership and his purpose at Square is making it easier for everyone to particulate in the economy. Moreover, Jack Dorsey is also a proven innovator and he is often compared to Steve Jobs, justifiably so. Dorsey’s effective leadership and innovative potential may play an instrumental role in expanding Square portfolio with more innovative products and services with positive implications on the long-term growth of the business. 2. Square market capitalization is more than USD 113 billion as of September 2021[1] As illustrated in figure below, Square stock value has increased more than 27 times from USD 9,00 since its IPO in October 2015 to its current USD 247,90. Specifically, market capitalization of the payments company soared during the past year once user conveniences associated with Square products and services became evident to a wider customer…

Square organizational culture integrates the following 3 key elements: 1. Informal work environment. Work environment at Square is highly informal and this has a stark reflection the design of its offices worldwide. Moreover, “Square has designed its work spaces to be large, open and ripe for serendipitous collaboration”[1] In other words, Square organizational culture defies formality in the workplace through seemingly-casual, yet effective organization of workspaces. 2. Inclusion and diversity. Square organizational culture embraces and promotes diversity among employees at all levels. There are various employee communities in the company that cater for the interests of its members. These include Black Squares Association, Latinx, Asian Pacific Islander Squares, Veterans at Square and others. These communities are employee-run resource groups that promote universal inclusivity through networking, development opportunities, and social events.[2] In other words, people belonging to minority groups do not feel alienated when they join Square with positive implications on their work performance and overall happiness. 3. Social and economic impact. Square positions itself as a challenger to traditional banks. Specifically, the company attempts to democratise a wide range of financial services to simplify them and make these services available for small businesses for a little cost. From this point of view, the financial services and digital payments company is set to disrupt banking sector in a global scale. Such a challenger position attracts specific type of workforce, who are motivated by the perception of participating in and contributing to the worldwide change of banking services for the better. These types of highly motivated employees contribute to the formation of an advanced organizational culture at Square. Square Inc. Report contains the above analysis of Square organizational culture. The report illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces,…
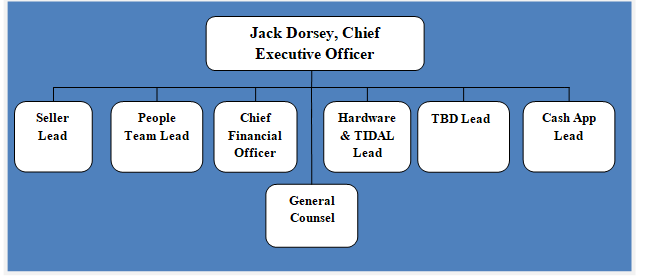
Square Inc. organizational structure can be classified as relatively flat, taking into account ever-growing size of the business. Co-founder and CEO Jack Dorsey attempts to maintain a start-up environment and culture and reduce bureaucracy in order to keep the business flexible to be able to respond to changes in the external environment. Therefore, it can be argued that Square organizational structure is designed to increase the speed of decision-making. Leads of units operate as a CEOs and they report only to Jack Dorsey. Leads oversee project leaders and project teams at Square are small groups comprising maximum 12 people of diverse backgrounds. As illustrated in figure below, Square’s cryptocurrency business unit TDB is a division separate from both, seller and cash units. One of the reasons for this separation may relate to regulatory reasons. Specifically, maintaining crypto separate from other units decreases the chances of regulatory interferences. Square organizational structure The company is increasing the range of products and services extensively. This strategy can increase complexity of the business with direct implications on Square organisational structure, despite CEOs attempts to maintain it simple. Accordingly, the senior management of the financial services platform has a challenging task of maintaining flexibility of the business amidst its exponential growth. Moreover, there are opinions among industry analysts that CEO Jack Dorsey’s ultimate plan is to make Square a holding company for autonomous fintech businesses[1]. A Tweet by Dorsey on July 2021 claiming that the payments company will create a new business line to help developers build financial services products focused on Bitcoin can be seen as a signal to support such as viewpoint. Square Inc. Report contains the above analysis of Square organizational structure. The report illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five…

Efficiency of Square leadership is one of the competitive advantages of the business. Jack Dorsey, Square co-founder, President, and Chief Executive Officer, also serves as Chief Executive Officer of Twitter, Inc. The payments company Board of Directors comprises strong business leaders such as former CFO of PayPal Roelof Botha, CEO of Shake Shack Randy Garutti and former CFO of Goldman Sachs David Viniar. Square leadership style integrates the following two principles: 1. Purpose-driven leadership. Leadership style practiced by Jack Dorsey can be classified as a purpose-driven leadership. This type of leadership can be defined as “prioritizing purpose and people over profit and greatness over growth.”[1] For Square leadership the prioritized purpose is making easier for everyone to participate in the economy. The payments company attempts to achieve this mission through developing an ecosystem of financial products and services that are greatly simplified versions of banking services. Moreover, the purpose serves as a compass for long term decision making for Square leadership team. 2. Focus on team effort and appreciation of teamwork. At Square great emphasis is placed at teamwork and decision-making at strategic level reflects inputs from teams. It has been noted that “whether he is discussing Twitter or Square, Dorsey gives most of the credit to his team.”[2] Such an approach encourages team members at all levels to feel the ownership of the company with positive implications on their work performance. Currently, Square leadership is faced with a challenge of sticking to its leadership principles and maintaining organizational culture amid an extensive growth of the business in an international scale. Taking into account successful leadership experience of Dorsey at Twitter, which is a truly global business, it can be expected that senior management at Square can deal with this challenge in an appropriate manner. Square Inc. Report contains the above…
