Search results for: Ansoff Matrix
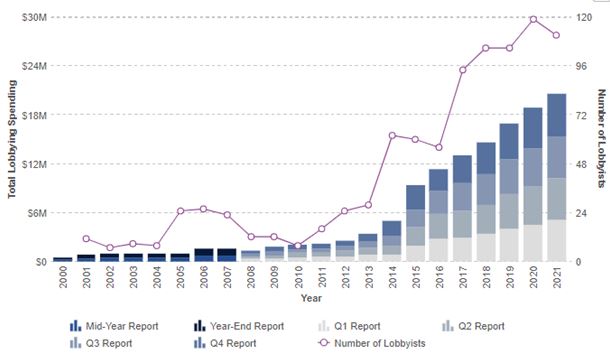
PESTEL is a strategic analytical tool and the acronym stands for political, economic, social, technological, environmental and legal factors. Amazon PESTEL analysis involves the analysis of potential impact of these factors on the bottom line and long-term growth prospects of the e-commerce giant. Political Factors in Amazon PESTEL Analysis The range of political factors that affect Amazon include but not limited to the political stability or instability in the country, the influence of home market lobbying and pressure groups and the attitude of the government towards e-commerce and retail industries in particular. Additionally, the freedom of press, trade unions and their activities and the extent of corruption belong to the list of political factors with potential implications on Amazon business practices. Due to the scope and scale of its business operations, Amazon plays an indirect role in politics in USA, Europe and some other regions. In other words, in markets where Amazon has a strong presence, the ruling government usually has a certain stance towards the e-commerce giant in particular among internet retailers. Stance of governments towards Amazon Most people either love or hate Amazon and this extends to politicians and government officials as well. Former US President Donald Trump was vocal in his dislike of the tech giant and sometimes criticised the company and its then CEO Jeff Bezos on Twitter. The current President Joe Biden also criticizes Amazon for paying low taxes and its opposition towards formation of labour unions. In February 2021 Biden “released the 2 ½-minute video. While he omitted the name of the powerful e-commerce giant, his remarks were seen as an unmistakable show of solidarity with a labour movement that failed to secure anything similar from his recent predecessors.”[1] The company has hired the former press secretary of the US President, Jay…

Amazon marketing strategy relies on the following four pillars: 1. Offering the widest range of products. The largest internet retailer in the world by revenue offers hundreds of millions of products. The wide range of product it offers has earned the online retailer the moniker The Everything Store. 2. Using customer-friendly interface. The tech giant has an advanced interface that integrates personalized recommendations and recent browsing history, among others. Ever-improving user interface is the result of the company’s focus to become Earth’s most customer-centric company. 3. Scaling easily from small to large. The e-commerce and cloud computing company has experience and competence in scaling from small to large. This factor plays in instrumental role exploring new business segments. Scaling from small to large has allowed the online retail behemoth do disrupt increasing ranges of industries such as retail, transportation, entertainment and now industrial distribution. 4. Exploiting affiliate products and resources. Up to date, the tech giant has taken a full advantage of affiliate programs, products and resources to contribute to the bottom line of the business. Amazon marketing strategy integrates a number of targeted online marketing channels, such as Associates program, sponsored search, social and online advertising, television advertising, and other initiatives. Generally, Amazon marketing strategy is based on the following principles: Amazon 7ps of marketing mainly focuses on product and place elements of the marketing mix. Offering hundreds of millions of products in the USA alone, Amazon product range is the widest among online and offline retailers. Moreover, the company is able to offer its products for competitive prices due to massive cost savings based on online nature of business operations. Amazon segmentation targeting and positioning practices are associated with targeting the widest customer segment. The retail giant does this with the application of multi-segment, adaptive, anticipatory and stop-gap…

Generally, Amazon organizational culture integrates the following five key elements: 1. Immense performance pressure. Amazon organizational culture has been described as “breakneck-paced, and notoriously cost-conscious, as befits a company that has run only a small profit, or a loss, under generally accepted accounting principles for most of its life as a public company.[1] Amazon organizational culture was fiercely criticized in 2015 in The New York Times article titled “Inside Amazon: Wrestling Big Ideas in a Bruising Workplace”. Specific flaws mentioned in the article include unrealistic performance standards, the work culture based on fear and the lack of recognition of employee contribution. The article caused debates in the media and even prompted a response from Amazon CEO at the time Jeff Bezos. Furthermore, work culture at Amazon has been described as “purposeful Darwinism” approach for employee management.[2] Generally, pushy, combative and ‘bruising’ organizational culture is perceived as outdated. Nowadays, the popular belief is that workplaces need to be nurturing and encouraging, and managers need to be nice and friendly and treat their employees like family in order for a company to succeed. The largest internet retailer in the world by revenue proves this belief wrong. Amazon has a very intense corporate culture with an extensive emotional and even physical pressure to some employees. Nevertheless, Amazon along with Alphabet has been recognized by LinkedIn as the best place to work in US in 2021.[3] This can be explained in a way that Amazon has a unique organizational culture that is not for everyone. Only employees who can thrive under immense pressure and fast-paced environment can survive in this company. 2. Constant reinvention and optimization of organizational culture. Amazon founder and CEO Jeff Bezos “emphasizes the importance of constantly assessing and adjusting Amazon’s culture so it never loses the agility, nimbleness, and hunger for…

Amazon leadership style has been classified as pragmatist. Pragmatist leaders “set high standards and unapologetically expect those standards to be met by themselves and by their employees”[1] The company’s founder and first CEO, Jeff Bezos is an exceptional and proven business leader. Bezos efficiently exercises visionary and servant leadership styles and places exceptional customer service at the core of Amazon’s business practice. Moreover, Jeff Bezos leadership style is unique in several ways. For example, it has been noted that “while you might find other internet firms focusing on a fun, relaxed atmosphere for their employees, no-frills Bezos is proving the potency of another model: coddling his 164 million customers, not his 56,000 employees.”[2] Jeff Bezos’ leadership style can be analysed through the prism of contingency leadership theory. According to contingency leadership theory, “leader’s effectiveness is contingent upon with how his or her leadership style matches to the situation.”[3] Jeff Bezos leadership style has been characterized as harsh, cutthroat and demanding.[4] It can be argued that such a leadership style fitted the situation on the onset of the business, when the company had to strengthen its position on rapidly expanding industry. In July 2021 Jeff Bezos stepped down as CEO and assumed the role of company’s executive chairman. Andy Jassy CEO of Amazon Web Services became the new CEO of the online retail behemoth. At has been noted that although Andy Jassy values Bezos leadership style the new CEO is “more mild-mannered, soft-spoken and less prone to angry outbursts compared to Bezos”[5] Nevertheless, Mr. Bezos will continue to yield an immense influence on the business and Amazon leadership style for the foreseeable future. This is because his new role executive chairman grants his involvement in strategic decision making and Mr. Bezos remains as the largest shareholder of the e-commerce giant. Amazon…
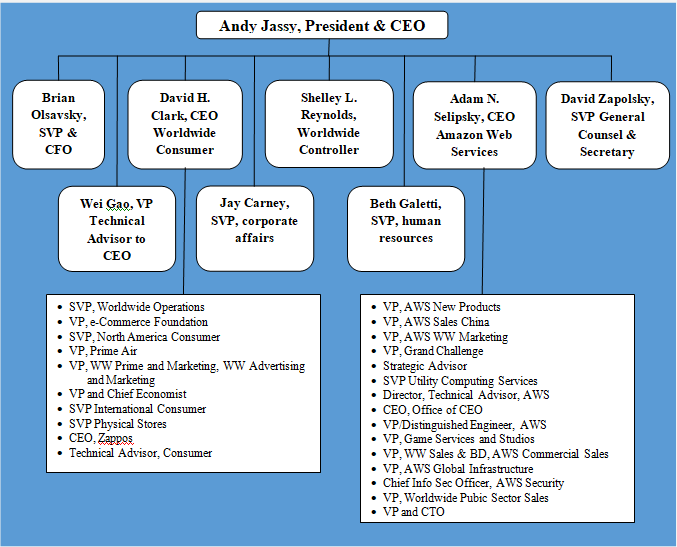
Amazon organizational structure can be classified as hierarchical. Senior management team include three CEOs and three senior vice presidents responsible for various vital aspects of the business reporting directly to CEO Andy Jassy. Amazon organizational structure has the following four key features: 1. Hierarchical corporate structure. Hierarchical structure at Amazon has developed due to the immense size of the business. The largest internet retailer in the world by revenue employs more than 1,3 million people worldwide.[1] 2. Hybrid project groups. Amazon corporate structure integrates hybrid project groups when developing new products and services. Specialists from various departments are attracted according to their skills and competencies required for the project. These employees can be attracted part-time reporting to both, the head of their departments and project leaders, or they can engage in the project full-time reporting to project manager only for the duration of the project. 3. Flexibility of the business. It is important to note that despite its large size, unlike many other companies with hierarchical organizational structure, Amazon remains highly flexible to adapt to frequent changes in the external marketplace. Moreover, the online retail giant leads changes in external business environment; it has caused disruptive innovation in e-commerce and currently it is about to cause a disruptive innovation in global logistics industry. Successful organization of hybrid project groups plays an instrumental role in maintaining flexibility of the business. Amazon organizational structure integrates many small teams that deal with various aspects of the business. Amazon founder and former CEO Jeff Bezos is credited with the introduction of ‘two pizza rule”. According to this rule, meetings should be held in teams small enough that could be all fed with only two pizzas. “Two pizza rule” continues to this day under the new CEO Andy Jassy. 4. Stability in the top management.…

Amazon business strategy can be described as cost leadership taken to the extreme. Range, price and convenience are placed at the core of Amazon competitive advantage. The global online retailer operates with a razor thin profit margin and succeeds due to a combination of economies of scale, innovation of various business processes and a constant business diversification. Founder and first CEO Jeff Bezos believes in focusing as a business strategy on things that do not change. At the outset of the business he reasoned that people always want low prices, selection and fast delivery. Exceeding customer expectations on these points has remained as the core of Amazon business strategy. Innovation and technology the online retail behemoth uses are simply instruments to pursue this core strategy. Moreover, Amazon business strategy is guided by four principles: customer obsession rather than competitor focus, passion for invention, commitment to operational excellence, and long-term thinking.[1] The following four points constitute the cornerstones of Amazon business strategy: 1. Regularly entering into new niches and segments. Started only as an online shop for selling physical books in 1997, today Amazon sells anything that can be sold online in the global scale. Sophisticated global logistics represents one of the solid bases of Amazon competitive advantage. The tech giant has used this advantage extensively to engage in successful business diversification. Recently, the company launched Amazon Home Services, a simple way to buy and schedule local professional services as a continuation of its diversification strategy.[2] Currently, the tech giant operates in increasing range of industries including e-commerce, cloud computing, artificial intelligence, consumer electronics, entertainment, digital distribution, B2B distribution, self-driving cars and supermarkets. As the largest internet company by revenue in the world, Amazon frequently disrupts the industries it chooses to enter. The e-commerce giant occasionally finds new niches and segments accidentally, while…
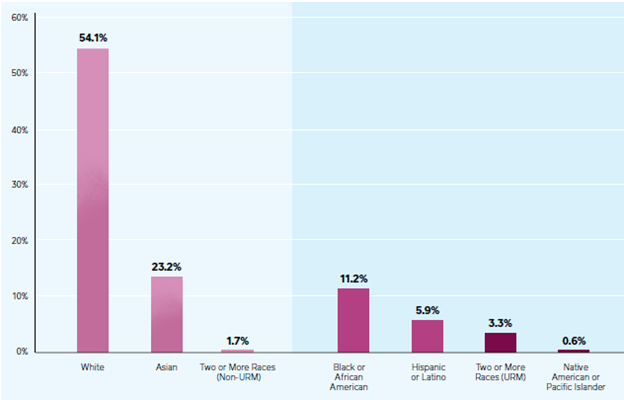
Square CSR programs and initiatives mainly focus on four key priority areas – Climate Action, Social Impact, Employees and Culture, and Corporate Governance. These initiatives are led by Neil Jorgensen, Global Environmental, Social, and Governance Lead at Square. Square Supporting Local Communities Square has invested USD 100 million in minority and underserved communities The financial unicorn assists some local communities in the US to preserve their local culture and deal with other most pressing issues. In many offices there are active volunteer communities, referred to volunteams that undertake various projects to support local communities Square and Gender Equality and Minorities Square invests in employee resource groups such as Black Squares Association, LatinX Community, LGBTQ group, and others in order to create an inclusive environment The majority 54,1% of US employees of The fintech are white people, as illustrated in Figure 1 below: Figure 1 Race and ethnicity of Square Inc. employees in US[1] Energy Consumption by Square Square launched Bitcoin Clean Energy Investment Initiative, USD 10 million investment to help accelerate renewable energy adoption in bitcoin mining. The payments company is planning to evaluate and explore clean energy options, working closely with its key provider partners. Carbon Emissions by Square In 2020 the total carbon footprint for Square totalled to 247,900 tCO2e. The Figure 2 below illustrates the share of carbon emissions by operations: Figure 2 Square Inc. total carbon emissions in 2020[2] The financial services and digital payments company has aimed to be zero carbon for operations by 2030. Other CSR Initiatives and Charitable Donations by Square Leads Program offered to managers at all levels is designed to develop leadership skills and competencies The finance sector disruptor fully pays parental leave globally, caregiving leave to US employees In UK Square partnered with The Entrepreneurial…
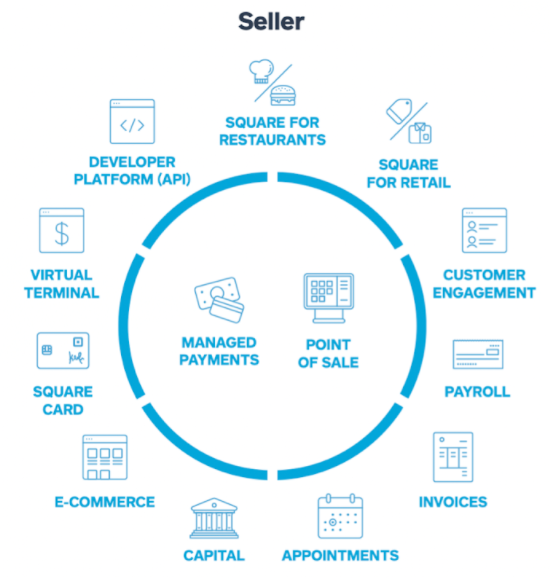
Square ecosystem represents a growing ecosystem of financial services. Ecosystem of Square can be divided into two groups: seller ecosystem and cash ecosystem. Square seller ecosystem is a cohesive commerce ecosystem that helps its sellers start, run, and grow their businesses. As illustrated in Figure 1 below, the core services for sellers are managed payments and points of sales products and services. Specific functionalities that contribute to these services include customer engagement platform, payroll invoices services, functionality to make appointments and capital management tools. Moreover, e-commerce and developer platforms, as well as, virtual terminal are important components of Square ecosystem on the Seller front. Figure 1 Square Seller products and services Square cash ecosystem, represented by Cash App comprises a wide range of financial products and services that are designed to help individuals manage their money. These include a cash card, instant discounts tool Boost. The strongest feature of Cash App that has no analogue in the market is the functionality to purchase Bitcoints and stocks in a simple, secure and hassle-free manner. Figure 2 Square Cash App functionalities The financial services and digital payments company is increasing the linkage between its seller and cash ecosystem in order to from strengthen its position in the market. For example, employers with seller account can pay their employees from seller revenues the next business day using Instant Payments feature when employees use Cash App. There is still room for growth of Square ecosystem on both fronts – Seller and Cash App. Apart from connecting the both ecosystems. The finance sector disruptor can also scale each of them, as well as, engage in optimised cross-selling. Moreover, the developer platform can play an instrumental role in expanding the ecosystem for Square, through exposing Application Program Interface (API) to third party developers to adjust it…
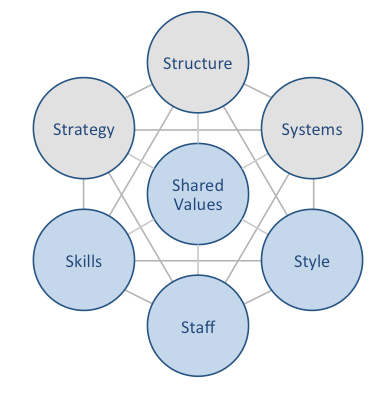
Square McKinsey 7S model is intended to illustrate how seven elements of business can be aligned to increase effectiveness. The framework divides business elements into two groups – hard and soft. Strategy, structure and systems are considered hard elements, whereas shared values, skills, style and staff are soft elements. According to Square McKinsey 7S model, there is a strong link between elements and a change in one element causes changes in others. Moreover, shared values are the most important of elements because they cause influence other elements to a great extent. McKinsey 7S model Hard Elements in Square McKinsey 7S Model Strategy Square business strategy is based on principles of simplifying financial transactions and developing an ecosystem of financial products and services. The financial services platform has two types of ecosystem – seller ecosystem and cash ecosystem. Square systematically expands both ecosystems with addition of new financial products and services that simplify processes and challenge the status quo. Structure Square organizational structure is highly dynamic, reflecting the rapid expansion of the range of financial products and services offered by the finance sector disruptor. Although it is difficult to frame Square organizational culture into any category due to the complexity of the business, it is closer to flat organizational structure compared to known alternatives. Specifically, co-founder and CEO Jack Dorsey has very little tolerance for bureaucracy and formality in business processes. Moreover, Dorsey believes in providing independence to teams and maintain the team sizes small. All of these are reflected in Square organizational structure. Systems Square Inc. business operations depend on a wide range of systems. These include employee recruitment and selection system, team development and orientation system, transaction processing systems and others. Moreover, customer relationship management system, business intelligence system and knowledge management system is also important…
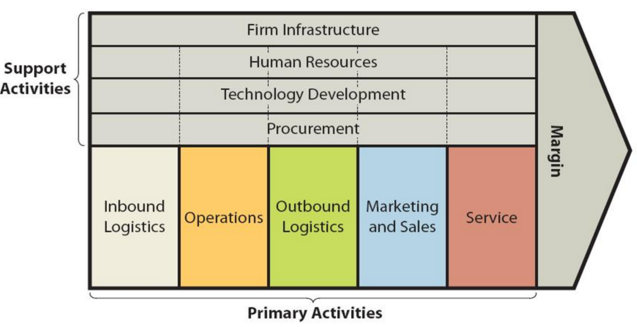
Value chain analysis is a strategic analytical tool that can be used to identify business activities that create the most value. The framework divides business activities into two categories – primary and support. The figure below illustrates the essence of Square value chain analysis. Square Value Chain Analysis Square Primary Activities Square Inbound logistics Inbound logistics refers to receiving and storing raw materials for their consequent usage in producing products and providing services. Along with a wide range of financial services, Square offers related hardware products such as card readers, stands, terminals, registers, hardware kits and accessories. The majority of hardware products are produced in China. Accordingly, cost-effectiveness of producing hardware products is the main source of value creation in inbound logistics for Square. Square Operations Square operations are divided into the following two segments: 1. Seller ecosystem. An expanding ecosystem of products and services that are designed to assist sellers to start, run and grow their businesses. In 2019 this segment processed USD106.2 billion of Gross Payment Volume (GPV), which was generated by nearly 2.3 billion card payments from 407 million payment cards.[1] 2. Cash ecosystem. This segment centred on Cash App integrates financial products and services that help individuals manage their money. As of December 2019, Cash App had approximately 24 million monthly active customers who had at least one transaction in any given month.[2] The main source of value creation in operations primary activity for Square refers to high level of speed and convenience of products and services enabled by technology. The finance sector disruptor spotted demand in both segments and developed products and services to satisfy demand with the use of the latest technology. Square Outbound Logistics Outbound logistics involve warehousing and distribution of products. Square uses the following distribution channels to distribute…
