Posts Tagged ‘Retail’

W.W. Grainger segmentation, targeting and positioning refers to ways in which the global industrial supply company chooses specific companies among large base of potential customers and develops its product and service offering to appeal to the needs of a few chosen customers. Segmentation involves dividing population into groups according to certain characteristics. Grainger uses a set of segmentation criteria such as region, size of the company, turnover and potential annual MRO spending. Moreover, complexity of customer needs is an important segmentation criteria extensively employed by the industrial supply company. Targeting is the next stage after segmentation and it is associated with selecting specific groups to sell products to. Positioning refers to the selection of the marketing mix that appeals to the needs and wants of the target customer segment to the maximum extent. Grainger uses multi-segment type of positioning and accordingly, the B2B distributor exploits more than one segment at the same time. Specifically, Grainger positions its Zoro and MonotaRO websites to appeal to the needs of small and medium-sized customer segment with simple needs for MRO products. Different customer segment with more complex needs on the other hand, are targeted via High-Touch Solutions value proposition, which involves sales and service representatives, KeepStock inventory management system and collection of orders from branches. There are important differences between B2C (business-to-customer) and B2B (business-to-business) segmentation. These differences include the following: 1. More complex and rational decision making. Decision making process by Grainger target customer segment is complex and rational. It is opposite to B2C segment, where appeal can be made to customers’ needs on emotional level to influence the purchasing behaviour. This fact has direct implications on Grainger positioning in a way that the global industrial supply company has to base its value proposition on measurable and tangible advantages. 2. Complexity of…
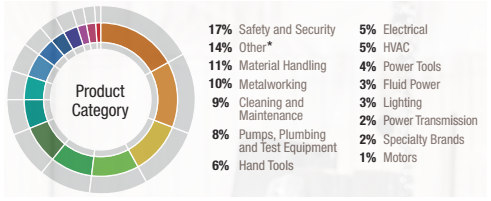
W.W. Grainger marketing mix (Grainger 7Ps of marketing) comprises elements of the marketing mix that consists of product, place, price, promotion, process, people and physical evidence. Product Element in W.W. Grainger Marketing Mix Grainger offers about 1,7 million types of products supplied by about 5000 suppliers worldwide. In 2019 no single product category comprised more than 17% of the global sales.[1] The figure below illustrates product categories of the global industrial supply company. Moreover, the B2B distributor offers certain services such as inventory management and technical support. Grainger Product Categories Place Element in W.W. Grainger Marketing Mix Grainger primarily operates in North America, Japan and Europe. The industrial supply company utilizes a wide range of sales channels such as online, mobile devices, sales representatives, local branches and product vending machines on customer sites. In 2018, 62 percent of Grainger’s revenue in the U.S. came from online channels, making it the 10th largest e-retailer in North America, according to Internet Retailer.1 Through Grainger.com, eProcurement connections, KeepStock solutions and mobile applications, the company continues to develop online capabilities that promote a personalized, relevant, effortless experience for each customer.[1] Price Element in W.W. Grainger Marketing Mix Traditionally, Grainger pricing strategy was premium pricing strategy. The worldwide distributor of industrial products was able to charge premium costs from its customer thanks to wide range of its products, convenience of purchasing and technical expertise. However, increasing popularity of Amazon Business posed a considerable threat to industrial distributors in general and Grainger in particular due to Amazon’s extensive experience and competence in e-commerce, customer service and timely product delivery. In response to growing threat from Amazon, Grainger changed its pricing strategy in 2017 to make prices more affordable. Moreover, the global industrial supply company placed greater emphasis on its Zoro brand in U.S.…

PESTEL is a strategic analytical tool used to analyse external factors affecting organizations. The acronym stands for political, economic, social, technological, environmental and legal factors. W.W. Grainger PESTEL analysis comprises the analysis of potential impact of these factors on profitability and long-term growth prospects of the global industrial supply company. Political Factors in W.W. Grainger PESTEL Analysis There is a wide range of political factors that can affect Grainger directly, as well as, indirectly. For example, government stability in international markets is one of the key political factors that can impact the performance of Grainger. Specifically, the global industrial supply company may face difficulties to grow the business in countries where there is a lack of government stability. Furthermore, if any government where company operates faces stability issues due to strikes, war or any other reasons, this can impose risks to Grainger properties located in the country. Activities of trade unions can be mentioned as another type of political factor that can affect the bottom line for the B2B distributor. Trade unions can demand and achieve higher wages for Grainger employees with negative implications on profitability of the business. Additional range of external political factors for Grainger includes level of bureaucracy and corruption, the extent of freedom of press, government trade controls and others. Economic Factors in W.W. Grainger PESTEL Analysis Grainger profitability and growth prospects are subject to a range of external economic factors. Changes in currency exchange rate is one of the main economic factors for the industrial supply company, because in 2019 the company generated 28% of its total revenues from international markets outside of its home market US.[1] Inflation rate can be highlighted as another significant economic factor for the worldwide distributor of industrial products, as increasing level of inflation erodes buyer purchasing power…
SWOT is an acronym for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats related to organizations. The following table illustrates W.W. Grainger SWOT analysis Strengths 1. Experience, competence and knowledge in selling MRO products 2. Economies of scale 3. An extensive product range 4. Increasing share of sales via e-commerce Weaknesses 1. Substantial indebtness 2. Overdependence on home market in the US 3. Vulnerability to Amazon Business 4. Ineffective marketing strategy Opportunities 1. Increasing integration of Artificial Intelligence into various business processes 2. Engaging in value added activities for customers 3. Pursuing international market expansion strategy into developing countries 4. Emergence of competitor vulnerabilities Threats 1. Increasing strength of local distributors due to COVID-19 pandemic 2. Further loss of market share to Amazon Business 3. Inability to sustain competitive advantage 4. Changes in currency exchange rates. W.W. Grainger SWOT Analysis Strengths in W.W. Grainger SWOT Analysis 1. Established in 1925 by William W. Grainger – motor designer, salesman, and electrical engineer as a wholesale electrical sales company, by now the B2B distributor has an extensive experience of more than 90 years in industrial distribution. In-depth technical knowledge due to experience and know-how serves as a competitive advantage for the business and it plays an instrumental role in further expansion of product categories. 2. Grainger derives massive benefits from the economies of scale. The industrial products distributor sells about 1,7 million types of products supplied by about 5000 suppliers worldwide to more than 3,5 million customers internationally.[1] Immense scale of business operations allows Grainger to source products in bulk, negotiating low purchasing prices. Moreover, economies of scale benefit the business in terms of inbound logistics, warehousing and outbound logistics of products to end-users. 3. Arguably, Grainger covers the greatest range of MRO products among distributors worldwide. Unlike B2C business, in B2B distribution inclusion…
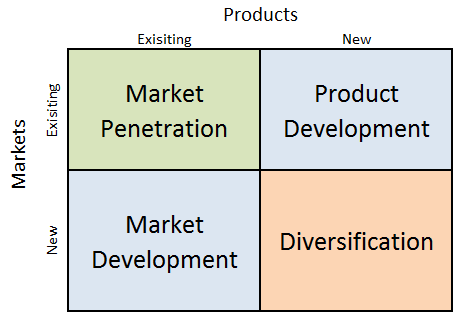
W.W. Grainger Ansoff Matrix is a marketing planning model that helps the global industrial supply company to determine its product and market strategy. Ansoff Matrix illustrates four different strategy options available for businesses. These are market penetration, product development, market development and diversification. W.W. Grainger Ansoff Matrix Within the scope of Ansoff Matrix, Grainger uses all growth strategies except diversification growth strategy in the following manner: 1. Market penetration. Market penetration involves selling existing products to existing markets. Grainger sells about 1,7 million types of MRO products covering a wide range of product categories.[1] The industrial supply company sustains market penetration business strategy via developing and maintaining relationships with customers through sales and service representatives and digital solutions. 2. Product development. This growth strategy is associated with developing new products to sell to existing markets. Grainger does not produce any product in-house, but continually expands its supplier base for new MRO products. Particularly, the worldwide distributor of industrial products is focused on expanding SKUs in its Zoro and MonotaRO subsidiaries to offset increasing competition from Amazon Business. In 2019 the company added about 1,5 million SKUs to its Zoro US assortment to increase it to approximately 3,5 million products.[2] 3. Market development. Market development strategy is associated with finding new markets for existing products. Currently, the B2B distributor has 456 branches and 30 distribution centres in US, Canada, Latin America, Japan and Europe. The worldwide distributor of industrial products may enter market in Asia in the foreseeable future[3]. Grainger enters new markets with Endless Assortment business model with a single online sales channel. Later, MRO products distributor may shift to High-Touch Solutions model in any given market if there is growing demand from large customers with more complex needs. 4. Diversification. Diversification involves developing new products to sell to new…

Grainger organizational culture integrates the following key elements: 1. Diversity and inclusiveness. Grainger organizational culture can be classified as inclusive. The B2B distributor places a great emphasis on diversity within the workforce and focuses on representation of minorities in the company. Grainger was named Best Company to work for Millenials by The Women’s Choice Award.[1] 2. Value for technology and innovation. The global industrial supply company duly recognizes the importance of technological innovation and attempts to adopt innovation approach to various business processes and problem solving constantly. 3. Focus on teamwork. The industrial supply company employs about 25000 people worldwide[2] and employees are organized into teams of varying sizes. The company attempts to extract maximum benefit from teamwork and promotes the values of collaboration and knowledge sharing across employees at all levels. Global MRO products distributor has the following mission statement that the company attempts to align with its corporate culture[3]: We keep the world working. As the way work gets done around the world continues to evolve, Grainger is here to serve customers like no one else can. According to framework of Harrison’s Model of Culture (1972), Grainger corporate culture can be classified as task culture. It worth to be specified that in organizations with task culture employee skills and competencies to deal with a task at hand play an integral role identification of a source of influence. In other words, the most experienced and competent team members have the highest influence in projects. W.W. Grainger Report contains the above analysis of W.W. Grainger organizational culture. The report illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces, Value Chain analysis, Ansoff Matrix and McKinsey 7S Model on W.W. Grainger. Moreover, the report contains analyses of W.W. Grainger leadership, organizational…
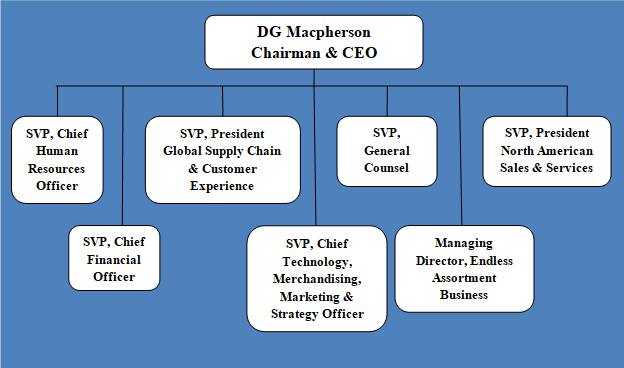
W.W. Grainger organizational structure can be classified as hierarchical. The decision making power is concentrated on the hands of Chairman and CEO DG Macpherson. The global industrial supply company maintains hierarchical type of organizational structure due to the massive size of the company that comprises about 2500 employees working in 457 branches, 31 distribution centres and offices worldwide.[1] Grainger organizational structure was subjected to major changes in 2013 “to provide greater focus and a more consistent integrated approach to pursue growth opportunities”[2]. Specifically, the B2B distributor established Americas business to include Canada, the U.S., Mexico, Panama, Puerto Rico, Dominican Republic, Costa Rica, Colombia and Peru. The figure below illustrates the top layer of Grainger organizational structure. Grainger Organizational Structure Hierarchical nature of Grainger corporate structure provides the worldwide distributor of industrial products a set of advantages. Specifically, the current pattern of Grainger corporate structure has a clear line of leadership, authority and responsibility. Moreover, hierarchical organizational structure is associated with employees having a narrow field of focus and accordingly, there is a potential for employees to become highly qualified experts in their fields. At the same time, hierarchical organizational structure is also linked to certain shortcomings that can have detrimental effects on Industrial products distributor’s long-term growth prospects. In hierarchical companies there is a risk of rivalry between different departments with negative implications for the overall profitability of the business. Moreover, centralization of power and authority at the highest level in hierarchical organizational structures may leave little room for initiatives for floor-level and medium level employees to adopt a creative and innovative approach to deal with various business processes. W.W. Grainger Report contains the above analysis of W.W. Grainger organizational structure. The report illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces, Value Chain analysis, Ansoff Matrix and…

W.W. Grainger business strategy relies on two business models depending on the type of customer: high-touch solutions and endless assortment. High-touch solutions business model focuses on large companies with complex needs mainly in North America and Europe. The endless assortment business model, on the other hand, targets customers with less complex needs with a broad range of products sold online. Endless assortment business model comprises Zoro in the US and MonotaRO in Japan. Grainger business strategy consists of the following three elements: 1. Widest range of MRO products. An extensive assortment of products is Grainger’s unique selling proposition. The global industrial supply company sells about 1,7 million types of products supplied by about 5000 suppliers worldwide[1], along with offering value-added services such as inventory management and technical support. 2. Offering differentiated sales and services. Grainger pursues differentiation business strategy and differentiates sales and service practice on the grounds of speed and convenience. The global industrial supply company employs thousands of product segment specialists that can advice about technical aspects and specifications of products offered. Advanced onmi-channel sales practice is another ground for differentiation for Grainger. The industrial supply company utilizes a wide range of sales channels such as online, mobile devices, sales representatives, local branches and product vending machines on customer sites. 3. Many branches in strategic locations. Grainger is one of the B2B distributors with the most branches. The company has 31 distribution centres in strategic locations and 457 branches worldwide. In the US alone, the industrial supply company has 16 distribution centres, 249 stand-alone branches, 32 onsite branches and 2 will-call express locations.[2] The great numbers of branches and their strategic positioning allows Grainger to delivery MRO products to end-users in a shortest period of time. W.W. Grainger Report contains the above analysis of W.W. Grainger business…

Founded in Illinois, US in 1928, W.W. Grainger Inc. is a B2B distributor of maintenance, repair and operating (MRO) products and services. The global industrial supply company has more than 3,5 million customers and about 25000 employees worldwide. (Fact Book, 2020). The global MRO products distributor works with approximately 5000 suppliers internationally. In 2019 Grainger generated revenues of USD 11,2 billion, 3% increase compared to the previous year (Annual Report, 2019). Grainger pursues differentiation business strategy. Specifically, the B2B distributor differentiates on the basis of products, offering the widest range of MRO product categories. Grainger’s use of differentiation business strategy also extends to differentiated sales and services. The company delivers its products with high level of speed and convenience and employs highly qualified sales representatives with deep technical knowledge. Grainger has hierarchical organizational structure and its organizational culture is based on diversity and inclusiveness and value for technology and innovation. Moreover, focus on teamwork can be highlighted as one of integral components of Grainger organizational culture. Business development strategy for the B2B distributor integrates market penetration, product development and market development strategies. The industrial products distributor immensely benefits from the economies of scale and the company has an extensive experience and knowledge in selling MRO products. At the same time, Grainger has certain weaknesses that can have negative implications on long-term growth prospects of the business. High level of indebtness is a major issue for the company and as of December 2019, Grainger’s consolidated debts amounted to USD 2,4 billion. Moreover, with total 72% of revenues generated in the US in 2019 (Fact Book 2020), the B2B distributor is over-dependent on the home market in the US. W.W. Grainger Inc. Report contains the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces,…

Gap Inc. management rightly acknowledges Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) as one of the critically important aspects of the business. The company has won a number of awards for its CSR programs and initiatives, including 2016 Catalyst Award in recognition of its commitment to equality, diversity and inclusion[1]. Moreover, in 2015 Gap Inc. was named as The Most Ethical Company by The Ethisphere Institute.[2] Gap Inc. releases Global Sustainability Report annually and it includes the details of CSR programs and initiatives engaged by the company. The table below illustrates the highlights from the latest report for 2013-2014: Categories of CSR activities Gap Inc. CSR Performance Supporting local communities Gap’s employees volunteered 558,000 hours in 2014 alone Educating and empowering workers The company provided job training and store internships through its This Way Ahead program to more than 2000 teens and young adults. Labor and human rights Over the past several years the company raised the hourly wage to USD 10 for more than 60,000 employees Employee health and safety The company has a centralized online reporting system that tracks all incidents and injuries. The information is analyzed at least quarterly to assess risks and develop prevention measures Gender equality and minorities P.A.C.E. program aims to support female employees and suppliers gain the skills and confidence to advance at work and at home. The program aims to educate one million women throughout the world by 2020. Gap Inc. pays female and male employees equally for equal work In 2015, women represented more than 70 per cent of Gap’s senior leadership. The company sponsored 6 employee resource groups to promote diversity and inclusion. Environment a) energy consumption b) water consumption c) Waste reduction and recycling d) CO2 emissions The fashion retailer has…
