Posts Tagged ‘Retail’

Amazon leadership style has been classified as pragmatist. Pragmatist leaders “set high standards and unapologetically expect those standards to be met by themselves and by their employees”[1] The company’s founder and first CEO, Jeff Bezos is an exceptional and proven business leader. Bezos efficiently exercises visionary and servant leadership styles and places exceptional customer service at the core of Amazon’s business practice. Moreover, Jeff Bezos leadership style is unique in several ways. For example, it has been noted that “while you might find other internet firms focusing on a fun, relaxed atmosphere for their employees, no-frills Bezos is proving the potency of another model: coddling his 164 million customers, not his 56,000 employees.”[2] Jeff Bezos’ leadership style can be analysed through the prism of contingency leadership theory. According to contingency leadership theory, “leader’s effectiveness is contingent upon with how his or her leadership style matches to the situation.”[3] Jeff Bezos leadership style has been characterized as harsh, cutthroat and demanding.[4] It can be argued that such a leadership style fitted the situation on the onset of the business, when the company had to strengthen its position on rapidly expanding industry. In July 2021 Jeff Bezos stepped down as CEO and assumed the role of company’s executive chairman. Andy Jassy CEO of Amazon Web Services became the new CEO of the online retail behemoth. At has been noted that although Andy Jassy values Bezos leadership style the new CEO is “more mild-mannered, soft-spoken and less prone to angry outbursts compared to Bezos”[5] Nevertheless, Mr. Bezos will continue to yield an immense influence on the business and Amazon leadership style for the foreseeable future. This is because his new role executive chairman grants his involvement in strategic decision making and Mr. Bezos remains as the largest shareholder of the e-commerce giant. Amazon…
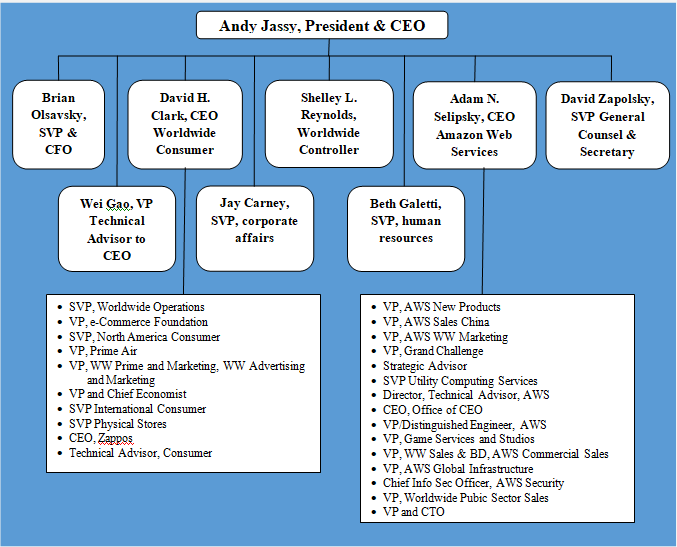
Amazon organizational structure can be classified as hierarchical. Senior management team include three CEOs and three senior vice presidents responsible for various vital aspects of the business reporting directly to CEO Andy Jassy. Amazon organizational structure has the following four key features: 1. Hierarchical corporate structure. Hierarchical structure at Amazon has developed due to the immense size of the business. The largest internet retailer in the world by revenue employs more than 1,3 million people worldwide.[1] 2. Hybrid project groups. Amazon corporate structure integrates hybrid project groups when developing new products and services. Specialists from various departments are attracted according to their skills and competencies required for the project. These employees can be attracted part-time reporting to both, the head of their departments and project leaders, or they can engage in the project full-time reporting to project manager only for the duration of the project. 3. Flexibility of the business. It is important to note that despite its large size, unlike many other companies with hierarchical organizational structure, Amazon remains highly flexible to adapt to frequent changes in the external marketplace. Moreover, the online retail giant leads changes in external business environment; it has caused disruptive innovation in e-commerce and currently it is about to cause a disruptive innovation in global logistics industry. Successful organization of hybrid project groups plays an instrumental role in maintaining flexibility of the business. Amazon organizational structure integrates many small teams that deal with various aspects of the business. Amazon founder and former CEO Jeff Bezos is credited with the introduction of ‘two pizza rule”. According to this rule, meetings should be held in teams small enough that could be all fed with only two pizzas. “Two pizza rule” continues to this day under the new CEO Andy Jassy. 4. Stability in the top management.…

Amazon business strategy can be described as cost leadership taken to the extreme. Range, price and convenience are placed at the core of Amazon competitive advantage. The global online retailer operates with a razor thin profit margin and succeeds due to a combination of economies of scale, innovation of various business processes and a constant business diversification. Founder and first CEO Jeff Bezos believes in focusing as a business strategy on things that do not change. At the outset of the business he reasoned that people always want low prices, selection and fast delivery. Exceeding customer expectations on these points has remained as the core of Amazon business strategy. Innovation and technology the online retail behemoth uses are simply instruments to pursue this core strategy. Moreover, Amazon business strategy is guided by four principles: customer obsession rather than competitor focus, passion for invention, commitment to operational excellence, and long-term thinking.[1] The following four points constitute the cornerstones of Amazon business strategy: 1. Regularly entering into new niches and segments. Started only as an online shop for selling physical books in 1997, today Amazon sells anything that can be sold online in the global scale. Sophisticated global logistics represents one of the solid bases of Amazon competitive advantage. The tech giant has used this advantage extensively to engage in successful business diversification. Recently, the company launched Amazon Home Services, a simple way to buy and schedule local professional services as a continuation of its diversification strategy.[2] Currently, the tech giant operates in increasing range of industries including e-commerce, cloud computing, artificial intelligence, consumer electronics, entertainment, digital distribution, B2B distribution, self-driving cars and supermarkets. As the largest internet company by revenue in the world, Amazon frequently disrupts the industries it chooses to enter. The e-commerce giant occasionally finds new niches and segments accidentally, while…
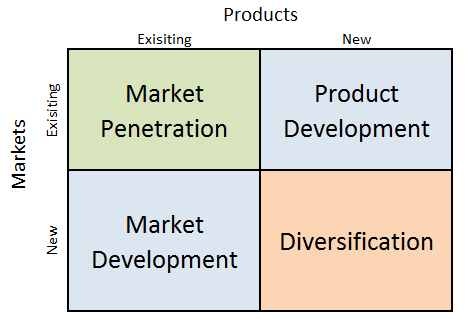
Amazon Ansoff Matrix is a marketing planning model that helps the e-commerce and cloud computing company to determine its product and market strategy. Ansoff Matrix illustrates four different strategy options available for businesses. These are market penetration, product development, market development and diversification. Amazon Ansoff Matrix Within the scope of Ansoff Matrix, Amazon uses all four growth strategies in an integrated manner: 1. Market penetration. Market penetration refers to selling existing products to existing markets. Amazon uses market penetration strategy aggressively. Sophisticated user experience features in general and recommendations feature on e-retailer’s website in particular play an important role in the application of market penetration strategy. Specifically, Amazon focuses on user experience personalization thanks to efficient application of data science and machine learning. The e-commerce giant collects and possesses a vast amount of data related to customers such as age, sex, lifestyle, habits and preferences. The company uses artificial intelligence (AI) to analyse this data and suggest products that a particular customer is highly likely to buy. 2. Product development. This involves developing new products to sell to existing markets. Product development is one of the core strategies used by Amazon. Started by Jeff Bezos selling only physical books online in 1997, today Amazon sells anything that can be sold online. The largest internet retailer in the world by revenue sells more than 500 million products, including products sold by third parties on Amazon platform. Top product categories include clothing, shoes, jewellery, home and kitchen appliances, books, electronic devices, sports and outdoor items and others. The e-commerce and cloud computing company produces increasing number of products under the private label as well. 3. Market development. Market development strategy is associated with finding new markets for existing products. Amazon is engaged in market development in a systematic manner. Started only in…

Grainger CSR (corporate social responsibility) programs and initiatives aim to address the issues of social awareness, environmental factors and ethical labour practices while promoting a greener, more culturally conscious attitude to both peers and customers. Grainger CSR Advisory Council has the mission of providing strategic awareness and encouraging transparency. Moreover, the global industrial supply company has CSR Working Group that leads programs to promote CSR goals. The company began using the Global Reporting Initiative’s Sustainability Reporting Standards in 2016 and, since 2017, has been a member of the Dow Jones Sustainability Index.[1] The B2B distributor offers more than 100,000 environmentally friendly products that help customers reduce energy consumption, conserve water, reduce waste and improve indoor air quality. [2] In 2018 the company was included in the top 10 placement in Barron’s “List of 100 Most Sustainable U.S. Companies” for the second time. Grainger Supporting Local Communities Hundreds of Grainger employees volunteered 8500 hours in local communities throughout the US in 2018 Members of Grainger workforce also help communities devastated by natural disasters worldwide In 2018, the global industrial supply company donated more than USD120,000 worth of products to Team Rubicon, a veteran-led group that helps communities worldwide get back on their feet after disasters. Grainger Educating and Empowering Workers All employees have completed Business Conduct Guidelines Training In 2017 the company provided 154 Grainger Tools for Tomorrow scholarships to employees in 85 participating colleges Grainger invested more than USD 4,5 million in employee education and development since 2006 Employee Health and Safety at Grainger Lost time incident rate per 100 employees decreased from 0,4 in 2017 to 0,3 in 2018 Total recordable incident rate per 100 employees totalled to 1,4 in 2017 and 2018 Grainger and Gender Equality and Minorities In total 38% of all workforce in…
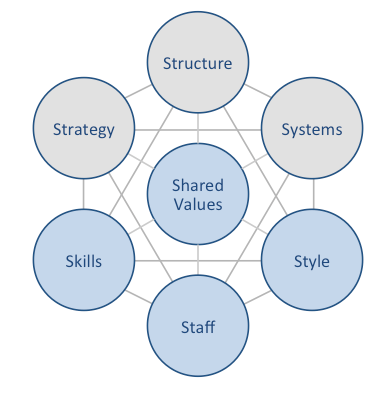
W.W. Grainger McKinsey 7S model illustrates the ways in which seven elements of industrial distribution business can be aligned to increase the overall effectiveness. The framework specifies strategy, structure and systems as hard elements, whereas shared values, skills, style and staff are considered as soft elements. According to McKinsey 7S model, there are strong links among elements in a way that a change in one element causes changes in others. As it is illustrated in Figure 7 below, shared values are positioned at the core of Grainger McKinsey 7S model. This is because shared values guide employee behaviour with implications on their performance. W.W. Grainger McKinsey 7S model Hard Elements in W.W. Grainger McKinsey 7S model Strategy Grainger pursues differentiation business strategy. The B2B distributor differentiates itself in the market by offering the widest range of MRO products. Specifically, Grainger offers about 1,7 million types of products supplied by about 5000 suppliers worldwide.[1] Moreover, the differentiation strategy pursued by the industrial supply company also relates to inventory management, technical support and differentiated sales and services. Structure Grainger has an hierarchical organizational structure with Chairman and CEO DG Macpherson sitting at the top of the hierarchy. The B2B distributor had a major restructuring in 2013 in Americas business segment. Moreover, taking into account growing competition from Amazon business, increasing integration of internet of things into industrial distribution practices and other changes in external business environment, it can be argued that Grainger organizational structure may change in the medium term perspective. It can be forecasted that changes in Grainger’s corporate structure will be directed in increasing the flexibility of the business so that it can react to changes in external marketplace more effectively. Systems There is a wide range of business systems that keep MRO products distribution at the global marketplace…
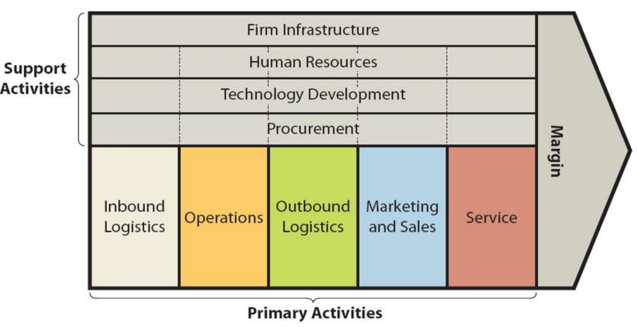
W.W. Grainger value chain analysis is an analytical framework that assists in identifying business activities that can create value and competitive advantage for global MRO products distributor. Figure below illustrates the essence of Grainger value chain analysis. W.W. Grainger Value chain analysis Grainger Primary Activities Grainger Inbound logistics Grainger inbound logistics involves receiving and storing MRO products by the global industrial supply company in its distribution centres for subsequent shipment to customers. The worldwide distributor of industrial products purchases approximately 1,7 million types of MRO products from approximately 5000 suppliers worldwide and stores them in distribution centres. Economies of scale is a major source of value creation in inbound logistics for the global industrial supply company. Additionally, the B2B distributor benefits from its strategic relationships with its suppliers in general and key suppliers in particular. Grainger Operations Grainger operations are divided into the following three segments: 1. United States segment. This segment generated sales of USD 8,6 billion in 2018, 72% of total revenue of the company.[1] The industrial supply company divides its customers in US segment into two categories according to complexity of their needs. a) Large customers in the US. Customers in this segment have complex needs and require services at their place of business. Grainger source of value creation in dealing with large customers in the US include adoption of partnership approach and assisting customers to reduce total cost of ownership in MRO spend by helping them to manage their labour, product and inventory costs. b) Medium customers in the US. This customer segment has less complex needs compared to large customers. Moreover, medium or mid-size customers in the US are mainly concerned with the solutions of their immediate business problems. Ranges and prices of products can be specified as major source of value creation…
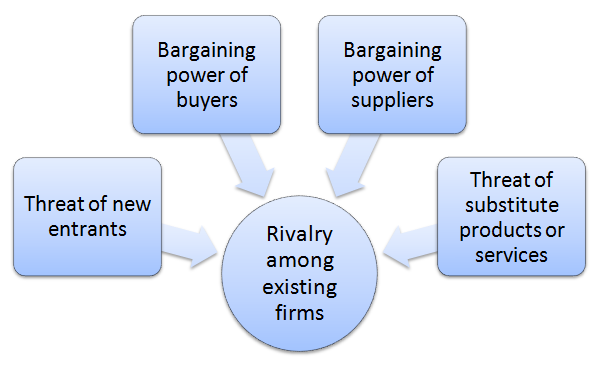
Porter’s Five Forces is a strategic analytical framework developed by Michael Porter (1979)[1]. The framework consists of five individual forces that shape an overall extent of competition in an industry. W.W. Grainger Porter’s Five Forces are illustrated in figure below: Porter’s Five Forces Threat of new entrants in W.W. Grainger Porter’s Five Forces Threat of new entrants into traditional B2B distribution is not significant. Inter-relationships of the following factors determine the extent of threat of new entrants into industrial distribution: 1. Economies of scale. Economies of scale is a critical success factor in B2B distribution. Grainger purchases more than 1,7 million types of products from approximately 5000 suppliers worldwide.[2] Accordingly, Grainger benefits from the economies of scale to a great extent with positive implications on the cost structure of the business. However, new market entrants are not able to benefit from the economies of scale to a similar extent and therefore, economies of scale emerges as an important entry barrier to the B2B distribution industry. 2. Capital requirements. Industrial distribution is a highly capital-intensive business. In order to be successful and challenge established market players, new entrants need to have wide range of products stored in warehouses and distribution centres. Substantial capital investments are needed to achieve all of these and unless new market entrants do not come up with innovative business models to disrupt the industry, capital requirements are likely to persist as an important entry barrier to the industry. 3. Expected retaliation from existing businesses. Current market players in B2B distribution are likely to retaliate against any new entrants that possess a considerable threat to their market share. This is a noteworthy entry barrier for potential new entrants to the industry. For example, once Amazon Business started to become a formidable player in the global market of…

W.W. Grainger marketing strategy was traditionally limited to its famous product catalogues and print and media advertisement. The company CEO D.G. Macpherson admitted in 2019 that marketing was a new skill for the global industrial supply company, but the company was learning very quickly.[1] The necessity for improvement of Grainger marketing strategy is fuelled by intensifying competition in general, and competition from Amazon business in particular. Grainger’s total advertisement expense totalled to USD316million, USD241 million and USD187 million for 2019, 2018 and 2017, respectively.[2] Grainger unique selling proposition is associated with extensive range of MRO products and deep knowledge of company’s sales force regarding main product categories. Moreover, competitive advantages of industrial products distributor include advanced customer services and omni-channel sales strategy. Grainger 7ps of marketing has traditionally focused on product element of the marketing mix to a greater extent compared to other elements. The B2B distributor boasts an extensive product range that includes about 1,7 million types of products supplied by about 5000 suppliers worldwide. [3] Starting from a few years ago, however, Grainger marketing strategy had to change to a certain extent to increase its focus on the price element of the marketing mix. Specifically, due to the increasing threat from Amazon Business, Grainger had to cut profit margin in 2017 to decrease the prices of many products. Segmentation, targeting and positioning practices is an integral part of Grainger marketing strategy and the B2B distributor pursues multi-segment type of positioning. Specifically, the industrial supply company appeals to MRO products needs of all types of customers – small, large and medium. The company targets small and medium businesses through Zoro and MonotaRO websites, whereas large customers with more complex needs are targeted via maintaining face-to-face direct relationships with numerous Grainger sales force representatives. W.W. Grainger Report contains the above analysis…

W.W. Grainger marketing communication mix is a framework that explains the application of individual elements of communication by the global industrial supply company. Individual elements of the marketing communication mix consist of print and media advertising, sales promotions, events and experiences, public relations, direct marketing and personal selling. W.W. Grainger Print and Media Advertising W.W. Grainger and its portfolio brands such as Zoro, MonotaRO and Cromwell use print and media advertising in an occasional manner. Specifically, the global industrial supply company uses TV commercials such as “Keeping America Running” and “We’ve got Your Back”, as well as, radio commercials. Additionally, the B2B distributor uses magazines, newspapers, billboards and posters forms of print and media advertising. It is important to note that despite increasing popularity of social media, up to date extensive potentials of viral marketing remain unutilised by Grainger. Lack of usage of viral marketing can be specified as one of the main shortcomings of Grainger marketing strategy. W.W. Grainger Sales Promotions W.W. Grainger uses the following forms of sales promotions: Clearance Centre on company website. The global industrial supply company offers discounts of up to 70% for some items purchased online. Money off coupons. Grainger does not offer coupons directly, but there are dozens of third-party companies such as Groupon, RetailMeNot and SlickDeals that offer money-saving coupons that can be used with the B2B distributor. Point of sale materials. The industrial supply company uses posers and display stands in its 457 branches worldwide[1] to increase the visibility of popular products and product categories. Customer Loyalty Program. Global MRO products distributor has Red Pass Plus Program that offers customer a set of advantages such as free next day delivery and savings of up to 15% on thousands of products.[2] W.W. Grainger Report contains a full…
