Porter’s Five Forces
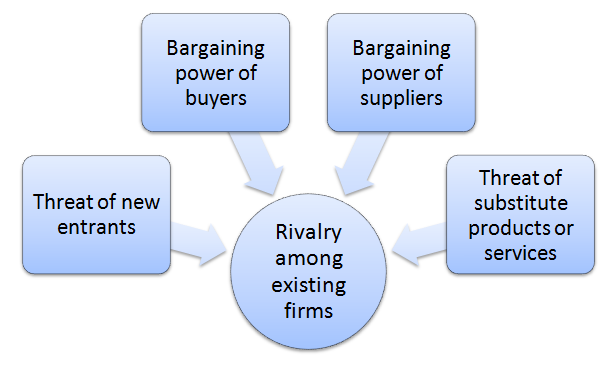
Porter’s Five Forces analytical framework developed by Michael Porter (1979)[1] represents five individual forces that shape the overall extent of competition in the industry. These forces are represented below: Threat of new entrants to consumer electronics industry is not significant due to cost and financial, knowledge and technological barriers. However, it is important to note that new businesses may overcome these barriers if they are able to introduce new products to the market based on innovative concepts. Large players such as Dell, Apple, HP, Samsung and Acer derive extensive benefits from the economies of scale and this fact represents an additional entry barrier to the consumer electronics industry. Bargaining power of buyers is immense due to the abundancy of offer and little differentiation amongst products. Moreover, there are usually no additional costs for Dell customers to switch to the competition and the majority of customers are well educated about products and services offered by Dell, another important factor that fuels buyer bargaining power. High level of price sensitivity for the type of products and services offered by Dell also increases the bargaining power of buyers. However, inability of backward integration, i.e. producing products offered by Dell by customers, can be specified as an important factor that diminishes buyer bargaining power. Bargaining power of suppliers is significant. Dell is extensively dependent on suppliers because it does not manufacture, but simply assembles its products from parts delivered by external vendors. Although there is a large number of companies that can potentially supply parts for Dell, there are only few reputable suppliers located close to Dell’s assembling units and this fact increases supplier bargaining power. Presence of supplier switching costs also contributes to their bargaining power. For Dell, the cost of supplies relative to selling price of products is high and it increases…
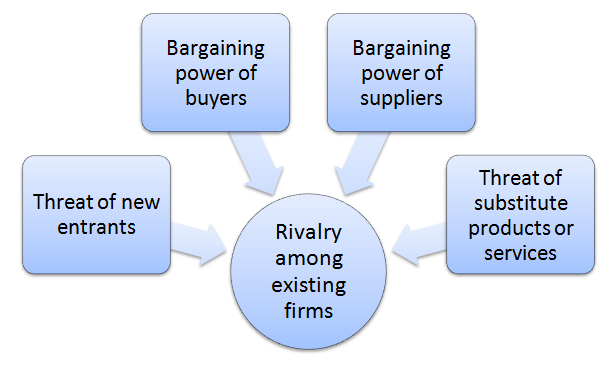
Porter’s Five Forces analytical framework developed by Michael Porter (1979)[1] represents five individual forces that shape the overall extent of competition in the industry. These forces are represented in figure below: Threat of new entrants in the industry is insignificant. This is because the global market of carbonated drinks is highly saturated and new entrants cannot benefits from the economies of scale extensively exploited by existing market players. Moreover, there is a substantial knowledge barrier in terms of being able to develop soft drinks that could successfully compete with industry leaders such as Coca Cola and Pepsi and the relevance of technological barrier can be assessed as substantial as well. Bargaining power of buyers is great and this power is fuelled by the availability of great choice of cola beverages. Moreover, there is no switching costs for customers and the price elasticity of products further increases buyer purchasing power. At the same time, the issue of Coca Cola addiction has surfaced in the media a number of times, addiction of Peter Lawrie, a professional golfer being a noteworthy exampe[2]. Accordingly, it can be argued that bargaining power of small segment of buyers who can be classified as ‘Coke addicts’ is not significant. Bargaining power of suppliers varies according to the type of supplier. There are few suppliers with great bargaining power such as Ajinomoto Co., Inc. and SinoSweet Co., Ltd suppliers of spartame, a non-nutritive sweetener and Nutrinova Nutrition Specialties & Food Ingredients GmbH, supplier of acesulfame potassium. Coca Cola operates Supplier Diversity Program that promotes diversity among suppliers for reportedly noble reasons, at the same time decreasing the bargaining power of each individual supplier. As it is illustrated in figure below, the volume of investment on supplier diversity has been consistently increasing for the last four years…. Coca Cola…

Five forces framework introduced by Porter (1980) has been acknowledged as an effective tool used in strategy formulation. Application of the framework is associated with analysis of five separate factors determine the overall level of competitiveness in the industry. Warner Bros. Porter’s Five Forces Analysis can be illustrated in the following manner: Threat of new entrants in film, television, and music entertainment industry has been traditionally moderate due to high levels of cost barriers. However, internet and rapid developments in information technology have increased the threat of new entrants to the industry through providing opportunities to lower cost barriers. Bargaining power of buyers is immense as there are no switching costs for the customers of Warner Bros. Buyer bargaining power is also fuelled by abundance of offers in films and manufacturing industry. Threat of substitute products for products offered by Warner Bros. is significant. Substitutions for Warner Bros. products include a wide range of video games, as well as, increasing popularity of major social networking websites such as Facebook, YouTube and Twitter. Bargaining power of suppliers is greater in films and entertainment industry compared to many other industries. Due to the unique nature of this industry famous actors can be classified as suppliers at the same time as serving as human resources. According to this approach, the success of sequels of famous Warner Bros. franchises such as Lord of the Rings, Batman, Harry Potter and Hangover is possible only through attracting A-list actors and actresses who have great bargaining power. Rivalry among existing competitors in global entertainment industry is intense and major companies competing in the industry along with Warner Bros. include Paramount Pictures Corporation, The Walt Disney Studios, Fox Filmed Industries and others. This portal also contains SWOT and PESTEL analyses for Warner Bros. References Porter, M. (1980) “Competitive…
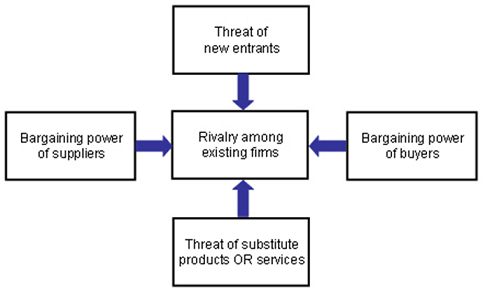
Porter’s Five Forces analysis framework comprises five individual forces that shape the overall level of competition in the industry. These forces are threat of new entrants, threat of substitute products, bargaining power of buyers, bargaining power of suppliers, and the extent of rivalry among existing competitors Threat of new entrants to the industry depends on a range of factors such as the level of capital requirements, the extent of profitability of the industry, possible barriers to enter the industry etc. Threat of substitute products for the company depend on the level of standardisation of products, the level of depreciation, direct and indirect substitution and a range of other factors Bargaining power of buyers as a factor impacting the level of competition within an industry depend on the levels of switching costs for buyers, the extent of customer sensitivity to changes in prices, the nature of the product etc. Bargaining power of suppliers along a wide range of factors depend on the variety of substitute raw materials, the costs associated with changing the supplier, the type of supply-chain management and other factors Extent of rivalry among existing competitors depend on sustainability of competitive edge, the efficiency of advertising, the level of utilisation of critical success factors for the industry etc.

John Lewis Porter’s Five Forces Analysis. The level of competitive environment in Chinese market of department stores is best analysed with the application of Porter’s five forces model which specifies five individual forces that form the competitive environment in a marketplace. The level of existing competition is intense in Chinese department store market with the largest market share divided between such companies as Lane Crawford, Lotte Mart, Maoye International, Mitsuokoshi, and New World Department Store China Limited. Barriers to entry into the market. Chinese government has continually relaxed rules and regulations for starting businesses during the last several decades (Han et al., 2011), which has resulted in barriers for entering department store business lowered. Customer bargaining power is high in Chinese department store market. This is caused by the high level of competition in the marketplace. Threat of substitute products and services in China in relation to John Lewis department store is highly limited and this situation increases the level of attractiveness of the market. Supplier bargaining power. Interestingly, “in China, the bargaining power of suppliers was once very large due to the shortages and the planned price system” (Zhuang et al., 2003, p.40). However, as the principles of free market economy are increasingly being adopted in China, supplier bargaining power is diminishing. References Han, J., Liu, R. & Zhang, J. (2011) “Globalisation and Wage Inequality: Evidence from Urban China” Zhuang, G., Herndon, N.C. & Zhou, J.N. (2003) “The Transforming Structure of Cometition in China’s Retail Industry” Journal of Marketing Channels, Vol. 11(1)

Porter’s competitive five force’s model as provides a useful stepping stone for an organization to identify its competitive position. Consumers are at the stage where they mane valid requests and are definite key stakeholders in companies. Acme appears to have taking this on board from the start by ensuring that it provides its customers with varied products and different designs. Acme Whistles exists on a global scale and it sufficiently able to defend its position against new entrants. The forces will allow Acme to determine where the company stands versus its buyers, suppliers, entrants, rivals and substitutes. Anticipating and exploiting shifts in the forces; and shaping the balance of forces to create a new industry structure that is more favourable to the company. Ease of Entry by competitors into the market As previously stated in the afore-mentioned Acme Whistles has an advantage over its competitors as it has not only gained a level of popularity but has had a level of longevity in its particular industry which makes it that bit more difficult for its competitors. Equally having patented designs which are individually tested as well as various designs, research and development and set up costs make it that more difficult for a potential competitor. The bargaining power of customers Customers in Acme’s market do not have as much buyer power as other industries. With the engraved whistle, there are other manufactures but Acme is able to offer it at a cheaper price as it has the existing foundation to do so. Equally the uniqueness of each design does not easily allow the buyer to switch to another producer and the large of buyers reduces any potential power. The bargaining power of suppliers Evidently Acme is at a stage where it has an established relationship with its suppliers. With…

Ryanair Porter’s Five Forces Analysis. Porter’s Five Forces analytical tool assists in analysing competitive environment for Ryanair Bargaining power of suppliers Boeing has been traditionally Ryanair’s main supplier, however, there are reports that “Ryanir is interested in Comac’s planned C919 aircraft, which is being developed to rival the Boeing 737 and the Airbus A320, the dominant players in the commercial aircraft market” (Milmo, 2011, online). Comac, Chinese jet manufacturer, is attracting Ryanair’s interest due to grater amounts of seats within its planes, as well as increased level of efficiency associated with energy consumption (Cliff et al, 2011). This fact signals about Ryanair’s increasing bargaining power towards its main supplier, Boeing. However, the supplier switching costs for Ryanair is extremely high due significant amount of expenses involved associated with pilot retraining needs. Moreover, “airline pilots have a strong bargaining power in the airline industry” (Pelapu et al, 2007, p.48), because there is no abundant supply of highly qualified and experienced pilots. Nevertheless, Ryanair enjoys rapidly increasing power towards a different category of its suppliers. Specifically, as Walsh (2011) confirms, highly intensified level of competition among airports has significantly increased the bargaining power of airline companies in their business relationships with the local airports. Bargaining power of customers Bargaining power of customers can be explained as “an advantage that comes from gathering together to put collective pressure on producers to lower prices or improve quality” (Business Dictionary, 2012, online). Ryanair customers enjoy high bargaining power because switching to another airline is simple and not associated with additional expenses. However, it has to be mentioned that only for Ryanair, but for airline industry in general “the bargaining power of buyers is relatively high and increasing, since most airline companies are forced to cut costs by aggressive competitors” (Szymanski, 2011, p.7) Increased level of…

Porter’s Five Forces is a strategic analytical tool used to analyse the business environment in an industry level. Five forces are comprised of intensity of rivalry among the established firms, bargaining power of buyers, threats of substitutes, bargaining power of suppliers, and the risk of entry by potential competitors (Porter, 2004). The essence of the model is that “the stronger each of these forces is, the more limited is the ability of established companies to raise prices and earn greater profits” (Hill and Jones, 2009, p.43). Source: Tom Spencer (online) Intensity of rivalry among the established firms is high in Russian marketplace with a range of local companies such as Moscow City Telephone (MGTS), and VolgaTelecom, as well as multinational companies operating in Russia that include VimpelCom, Golden Telecom and others. Bargaining power of buyers is significant in the Russian marketplace due to the increased level of offers for private and commercial broadband services. In other words, potential and current customers of broadband companies have a wide range of companies to choose from; therefore they possess significant bargaining power in commercial interactions with broadband suppliers. Threats of substitute products and services are low for broadband companies. This is because the convenience hotels offer to their customers that involve providing access to the internet in an effective manner are difficult to substitute with alternative products and services. Bargaining power of suppliers is considered to be moderate for Guest-Tek operations in Russia. Guest-Tek suppliers mainly include global technology manufacturers like IBM MicroElectronics, Sony, PMC Consumer Electronics and others. The bargaining power of such companies is not significant due to the fact that the level of competition in technology manufacturing industry is highly intensifying and Guest-Tek can change its suppliers with minimum or no inconveniences if such necessity arises. Risk of…

Five forces strategy, introduced by Michael Porter (2004) describes five individual forces that shape the level of competition in any given industry. These forces consist of threat of new entrants, bargaining power of buyers, threat of substitute products or services, bargaining power of suppliers and the level of rivalry among existing firms within the industry. Threat of New Entrants Threat of new entrants relates to the level of difficulty associated with entering the industry. Accordingly, if there are substantial barriers to enter the industry the threat of new entrants would be low, and vice versa. The most significant industry entrance barriers are specified by Baker and Hart (2007) as brand loyalty, absolute cost advantage, economies of scale, switching cost and the level of government regulation. The threat of new entrants to the software industry in UK can be described as high. This is because the amount of financial resources required for entering the industry can raised by many businesses and individual entrepreneurs. Moreover, there is a constant risk for major software companies such as Oracle that any new business with innovative software offerings can claim Oracle’s market share within a short period of time. Bargaining Power of Buyers The essence of the bargaining power of buyers primarily relates to the level of easiness or difficulty with which buyers can change the companies. (Johnson et al, 2006). However, nowadays the buyers possess a vast amount of bargaining power almost in all industries due to the intensifying level of competition. The same applies to the UK software industry as well. Specifically, there are several other global players in UK software industry such as IBM, Microsoft and SAP, as well as, many other local companies that compete with Oracle in direct and indirect ways. Many of these companies offer the customers…

The Porter’s Five Forces model examines and analyses the competitive environment of Sharp Corporation. According to Porter (2004) there are five forces, which are discussed below in turn, that determine industry attractiveness and profitability in long-run. Threat of Entry of New Competitors Lynch (2006) states that in general threat of entry of new competitors in electronics industry is high as the new entrants can overcome entry barriers by investing in facilities, advanced technology or outsourcing the same electronic components from suppliers. However, Johnson and Scholes (2006) argue that the strong brand and large scale of economies the company built over the years with the use of advanced technologies resulted in high entry barriers such as large capital requirement, high switching costs, need for advanced technology, know-how knowledge and innovation, preventing new competitors entering into market. Threat of Substitute Products Although Sharp has strong brand equity associated with high quality and reliable products allowing the company to sell its products at premium, with increasing number of products being manufactured in China and Malaysia the company is struggling to reduce the impact of cheaper substitute products on most of its marketing segments (Datamonitor, 2010). Moreover, while certain products of Sharp such as TVs are considered to be the best in the market, many other products the company manufactures including PCs and mobile phones falls short from meeting high customer expectations indicating that it is high likely that there are direct alternative products available for these market segments. Bargaining power of Buyers Considering the nature of the electronics industry it is argued that the bargaining power of buyers is rather high. This is because electronic products are highly price sensitive as majority of them are considered to be luxury goods rather than essential and today’s consumers tend to demand high quality…
