Search results for: Mckinsey 7s
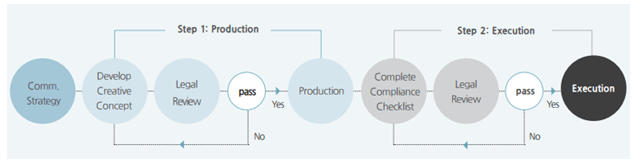
Samsung’s has the largest marketing budget in the competition and this fact partially explains the leadership position of the business in terms of market share. Samsung spent a total of USD10.2 billion (11.5 trillion won) on marketing in 2016 alone. This included USD3.9 billion (4.4 trillion won) toward advertisements, a 15% increase from 2015[1]. Samsung marketing strategy integrates various forms of advertising, events and experiences, public relations, direct marketing and personal selling as discussed further below in more details. The multinational electronics company has 53 global sales bases worldwide. Samsung marketing strategy is based on the following principles: Samsung 7ps of marketing places greater emphasis on product element of the marketing mix, compared to other elements such as process, people and physical evidence. Specifically, with 34 R&D centres worldwide and 53 global production bases, the multinational electronics company attempts to ensure the continuous pipeline of new products with innovative features and capabilities. Samsung segmentation targeting and positioning strategy integrates multi-segment, imitative and anticipatory positioning techniques. Samsung marketing communications strategy, as it is illustrated in figure below, comprises two steps and each step involves a set of separate activities. It has to be noted that legal review as an important element of marketing communication process is present in both steps – production and execution. This is because neglecting legal implications associated with the development and delivery of marketing communication messages can cause considerable damage to the brand image with severe financial implications. Samsung Electronics marketing communication process[2 Samsung Group Report contains a full analysis of Samsung marketing strategy. The report illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces, Value Chain analysis and McKinsey 7S Model on Samsung. Moreover, the report contains analyses of Samsung leadership, organizational structure and…
PESTEL is a strategic analytical tool used to assess the impact of external factors on businesses. Samsung PESTEL analysis involves critical analysis of political, economic, social, technological, environmental and legal factors affecting the multinational electronics company. Political Factors in Samsung PESTEL Analysis A set of political factors such as political stability in the country, government attitude towards the industry and the company, home market lobbying and pressure groups, international pressure groups, risk of military invasion of the country and others affect revenue and long-term growth prospects of Samsung Electronics in direct and indirect ways. Samsung Electronics is found to be involved in a number of political scandals in its home market in South Korea. Lee Kwang-jae, Uri Party representative working for South Korean President Roh Moo-hyun officially admitted the receipt of 50 to 60 billion KRW from Samsung Group in the forms of bonds to be used in the presidential campaign in 2002. Moreover, the prosecution found that the company has also funded the opposition, Grand National Party via 2.47 billion KRW before the election.[1] The instance mentioned above represents an attempt by the company to achieve positive impact of political factors via illegal means and methods with potentially severe detrimental impact on Samsung brand image. In August 2017, Jay Y. Lee, the former de facto head of the Samsung conglomerate, was given 5-year jail term for his role in bribery and embezzlement, part of a series of scandals that led to the ouster of Park Geun-hye, South Korea’s first female president.[2] As it is illustrated in figure below, Samsung has increased the amount of its political lobbying significantly starting from 2012. It can be argued that these spending included controversial payments as discussed above. Annual lobbying by Samsung Group[3] Economic Factors in Samsung PESTEL Analysis Strong Korean currency is one of…
SWOT is an acronym for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats related to organizations. The following table illustrates Samsung SWOT analysis: Strengths 1. Leadership in visual display market segment 2. Strong patent portfolio 3. High brand value 4. Global leadership across all mobile and smartphone markets 5. Solid financial position of the company Weaknesses 1. Absence of own OS and software 2. Damage to brand image due to product safety issues 3. Low profit margin 4. Extensive product portfolio 5. Competitive advantage hard to sustain Opportunities 1. Further increasing investment in R&D 2. Focusing on mobile advertisements 3. Entering cloud business segment 4. Increasing presence in emerging markets 5. Entering into strategic collaboration with affiliated businesses Threats 1. Changes in currency exchange rate 2. Intensification of competition due to the slowing growth in the industry 3. Disruption in the pipeline of new products 4. Patent infringement lawsuits 5. Disruptive innovation by competitors Samsung SWOT analysis Strengths 1. Samsung has maintained the largest market share in the global market of visual display since 2006. Samsung Display Solutions has advanced the field of digital signage by introducing leading-edge new hardware, including new video walls featuring the world’s narrowest bezel and the world’s first TIZEN-powered premium signage.[1] Samsung had a global TV market share of 27.6% in 2015. The global market share for UHD TV market share amounted to 34.1% for the same year.[2] Moreover, in 2015 Samsung Electronics had mobile phone market share of 21.1%, smartphone market share of 22.2% and tablet market share of 15.0%.[3] 2. Strong patent portfolio is one of the solid bases of Samsung competitive advantage. In 2015 alone, the multinational electronics company registered 5072 global patents in the US Patent and Trade Office. Samsung is the 2nd largest patent holder in the US since 2006.[4] The multinational…

Founded in 1969, Samsung Electronics is one of the leaders in consumer electronics industry in an international scale. The company employs 325,677 people in 80 countries and has more than 200 subsidiaries around the world (Sustainability Report, 2016). The business is divided into three large segments – consumer electronics, IT & mobile communications and device solutions. Samsung delivered the sales of KRW200.7 trillion and earned KRW26.4 trillion in operating profits on a consolidated basis in 2015. From the financial perspective, Samsung maintained a sound financial structure by recording a debt ratio of 35.3 percent, an equity ratio of 73.9 percent, and a return on equity ratio of 11.0 percent on a consolidated basis (Sustainability Report, 2016). Business strategy of Samsung Electronics is directed at strengthening the competitiveness and profit structures and the focus is on the development of premium products. Moreover, the international electronics company is known to benefit from product innovation and expanding its product range in a regular manner. Thanks to efficient implementation of this strategy, Samsung currently maintains the global leadership in visual display market segment with the market share of 28.3% for all flat-panel TV product lines. In the first quarter of 2015 Samsung surpassed Apple to regain its position as the largest smartphone manufacturer in the world (Sustainability Report, 2016). Currently, the multinational electronics company has certain weaknesses such as the absence of own operating system (OS) and software, damaged brand image due to product safety issues and recent corruption scandal and low profit margin. Moreover, Samsung is finding increasingly difficult to sustain its competitive advantage. Samsung Group Report contains the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces, Value Chain analysis and McKinsey 7S Model on Samsung. Moreover, the report contains analyses of Samsung’s business…
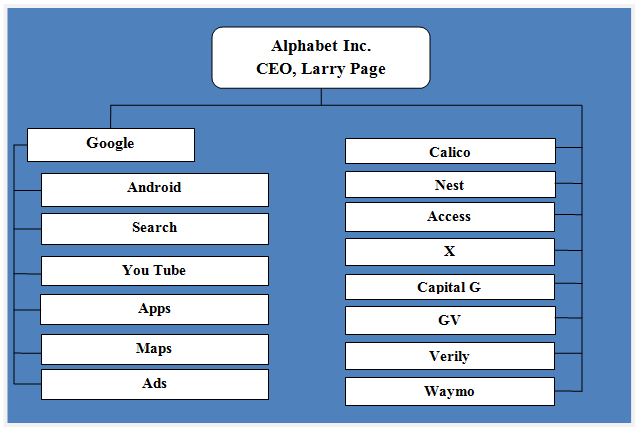
Alphabet Inc. organizational structure is divisional. Each division is positioned as a separate brand such as Google, Calico, Nest, Access (Fiber) and others. Alphabet’s individual divisions have flat organizational structure and this gives business a range of benefits such as lack of bureaucracy, high level of flexibility and effective two-way communication between senior management and other employees. Google Inc. was restructured in 2015 to become Alphabet Inc. “Google’s search product became a wholly owned subsidiary of a new parent company, Alphabet, with other Google projects and teams spun out into separate “Alphabet companies,” each with its own CEO.”[1]. Alphabet Inc. is a holding company with no business operations of its own. The main aim behind this restructuring was to help entrepreneurs build and run companies with the autonomy and speed they need. In other words, the company was restructured to move beyond search engine business and to engage in diversification strategy to a greater extent. Introduction of new businesses such as Waymo, a self-driving car company and Debug project, which aims to stop mosquitoes in their tracks have been enabled by this restructuring initiative. Figure below illustrates Alphabet Inc. organizational structure: Alphabet Inc. organizational structure The current pattern of Alphabet Inc. organizational structure gives CEO Larry page and the senior leadership greater freedom to explore new projects and acquisitions — regardless of how they fit into Google’s mission “to organize the world’s information and make it universally accessible and useful.” Alphabet Inc. (Google) Report contains a full analysis of Alphabet Inc. organizational structure. The report illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces, Value Chain analysis and McKinsey 7S Model on Alphabet Inc. Moreover, the report contains analyses of Alphabet leadership, business strategy and organizational culture. The report also…

Alphabet Inc. leadership team is headed by CEO Larry Page. The executive team consists of 16 members, responsible for various aspects of the business. Formerly, Eric Schmidt was CEO of Google until the business was restructured in 2015 and Alphabet Inc. was instituted as a holding company of Google, along with other businesses. Alphabet Inc. was instituted as an analogue to Warren Buffett’s Berkshire Hathaway.[1] Alphabet Board of Directors comprises 13 members, led by Executive Chairman of the Board Eric Schmidt. The Board includes successful and experienced business leaders such as Alan Mulally and Paul Otellini, as well as, distinguished economists such as Roger W. Ferguson Jr. Ph.D. and Shirley M. Tilghman Ph.D. Table below illustrates the leadership of companies within Alphabet portfolio Alphabet Inc. Company CEO Google Sundar Pichai Access Greg McCray Calico Art Levinson, former CEO of Genentech CapitalG David Drummond GV David Krane Nest Marwan Fawaz Verily Andy Conrad, founding CEO with background in X Waymo John Krafcik, background in auto industry X Astro Teller Alphabet Inc. leadership challenges in present include ensuring the profitability of business subsidiaries other than Google such as Access, Calico, CapitalG, GV, Nest, Verily, Waymo, and X. Although Larry Page has proven leadership skills, being one of the driving forces behind the emergence of Google to its current state, it is not guaranteed that he is able to replicate that same success in relation to non-Google businesses within Alphabet portfolio. Alphabet Inc. (Google) Report contains a full analysis of Alphabet Inc. leadership. The report illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces, Value Chain analysis and McKinsey 7S Model on Alphabet Inc. Moreover, the report contains analyses of Alphabet Inc. business strategy, organizational structure and organizational culture. The report also comprises…

Alphabet (Google) business strategy is based on the following three elements: 1. Business diversification and introduction of new products and services in a regular manner. This constitutes the core of Alphabet business strategy (Google business strategy). Starting from search engine business in 1998, the product portfolio of the company has been consistently expanded. Today Alphabet Inc. offers the widest ranges of products and services including self-driving cars, indoor and outdoor cameras, learning thermostats, and smoke alarms and even products to stop mosquitoes in their tracks. First mover advantage is the main Alphabet (Google) competitive advantage in relation to the majority of these products and services. 2. Business acquisitions. Alphabet (Google) business strategy involves rapid growths via acquisitions. As of December 2016, Alphabet acquired more than 200 companies and 30 acquisitions were made in 2015 and 2016 alone. The efficiency of the internet giant to effectively integrate its corporate culture to new businesses it acquires is one of the solid sources of Alphabet (Google) competitive advantage. 3. Profit maximization through creation of a closed eco-system. Google has created a collection of inter-connected services and applications. Customers usually enter this ecosystem through using Chrome browser, watching YouTube videos or using Gmail. In no time, they are prompted to use additional services such as Drive, Play, Calendar, Blogger and others. A greater range of products a customer uses, the more profit Google earns via advertising in various formats. Moreover, machine learning and Artificial Intelligence (AI) has been focus of the business for the past several years with direct implications on Alphabet business strategy (Google business strategy). Introduction of Google Assistant and its integration into a new family of hardware devices like the Pixel and Google Home in 2016 is a big step for the company towards enhancing machine learning and AI. Alphabet Inc.…
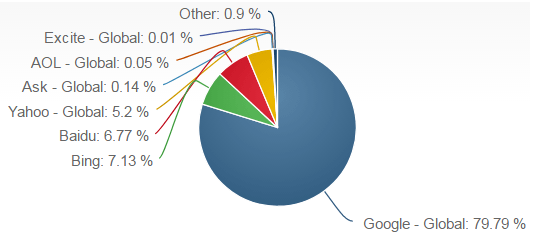
SWOT is an acronym for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats related to organizations. The following table illustrates Alphabet (Google) SWOT analysis: Strengths1. Market leadership in search engine segment 2. First mover advantage for many products and services 3. Organizational culture and spirit of creativity 4. Ecosystem of products and services 5. Strong position in online advertising segment Weaknesses 1. Reliance on advertising as primary source of revenues despite diversification 2. Many products and services in Alphabet portfolio are not profitable 3. High employee turnover rate at executive level 4. Sharing user information 5. Weak presence in social networking segment Opportunities 1. Increasing presence in consumer electronics industry 2. Acquisitions of related businesses 3. Increasing focus on cloud computing 4. Further developing Google+ 5. Benefiting from shift from desktop to mobile computing Threats 1. Failure of costly projects to generate profit 2. Competition from Facebook on search segment 3. Emergence of new competitors 4. Challenges of maintaining the current growth rate 5. Potential lawsuits Alphabet (Google) SWOT analysis Strengths 1. Initially introduced only as a search engine, Google has effectively dominated this segment due to the speed and efficiency of operations according to the mission of the company “to organize world’s information and make it universally accessible and useful”[1]. As it is illustrated in figurebelow, Google has the market share of more than 79% in desktop search engine, whereas its closest competitor Microsoft’s Bing has the less than one fifth of Google’s market share. Google’s current leadership in search engine attracts massive revenues via advertising and this position has also positive implications on the sales of its own products and services. Global market share distribution in desktop search segment as of April 2017[2] 2. Alphabet employs more than 27,100 people in research and development (R&D). The company invested USD…

Founders of the company Sergey Brin and Larry Page wrote in the original founders’ letter that “Google is not a conventional company. We do not intend to become one.”[1] Such an unconventional spirit is present in various aspects of Google organizational culture. Google organizational culture integrates the following three key elements: Encouragement of creativity. Google organizational culture embraces collaboration and creativity, and encourages the iteration of ideas to address complex technical challenges. Encouragement of creativity from employees at all levels is evident in many aspects of the business. Openness and freedom. Internal transparency is an important element of Google organizational culture. It has been noted that “on every software engineers’ first day, he or she gets access to almost all of Google’s code; every employee can view the personal goals and objectives of every other employee.”[2] Googleplex, Google’s headquarters in Mountain View, California, as well as, other Google offices around the world are open spaces and they look more like an adult playground, not a place for work.[3] Supporting employees at multiple levels. While work pressure for Google employees may be high, the internet giant offers an extensive range of tangible and intangible benefits to increase employee job satisfaction. These benefits include free breakfast, lunch, and dinner, free health and dental, free haircuts, free dry cleaning, subsidized massages, gyms and swimming pools, video games, foosball and ping pong. The company even employs a chief happiness officer whose sole job is to keep employees happy and maintain productivity.[4] Alphabet Inc. (Google) Report contains a full analysis of Google organizational culture. The report illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces, Value Chain analysis and McKinsey 7S Model on Alphabet Inc.. Moreover, the report contains analyses of Google leadership, organizational structure…
PESTEL is a strategic analytical tool and the acronym stands for political, economic, social, technological, environmental and legal factors. Alphabet (Google) PESTEL analysis involves the analysis of potential impact of these factors on the bottom line on long-term growth prospects. Political Factors in Alphabet (Google) PESTEL Analysis Google has been suspected of a political agenda a number of times with negative effects on its brand image. Particularly, Google has been accused by Chinese state media for “playing an active role in exporting culture, value and ideas”[1], thus pursuing political aims, rather than conducting appropriate business practices. Moreover, Project Loon, an initiative to provide internet in rural and remote areas via balloons and cell towels based on the ground is faced with geopolitical challenge in a way that the project is perceived as undercover by US intelligence services to conduct espionage activities[2]. Google is also criticized for interfering with politics and influencing political environment in the US and other parts of the world. It has been noted that “goggle nearly anything political and you’ll get a result that contains both legitimate news and partisan hackery, equally ready to be read. Better yet, clear out your search history, begin a search, and see what pops up to finish the search for you. Googling “Hillary” gave me “Hillary Clinton age” and “Hillary Clinton email.” So without even trying, I’ve gotten the impression of an old lady with an email problem”[3] A range of political factors that might impact Google range from political stability and government attitude towards the brand to the impact of home market lobbying and pressure group. Activities of international pressure groups such as One World Broadcasting Trust can be mentioned as an additional political factor that might affect Google in direct or indirect ways. Economic Factors in Alphabet (Google) PESTEL Analysis…
