Samsung SWOT Analysis: Strong Financial Position and Leadership in Global Display Market
SWOT is an acronym for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats related to organizations. The following table illustrates Samsung SWOT analysis:
| Strengths
1. Leadership in visual display market segment 2. Strong patent portfolio 3. High brand value 4. Global leadership across all mobile and smartphone markets 5. Solid financial position of the company |
| Weaknesses
1. Absence of own OS and software 2. Damage to brand image due to product safety issues 3. Low profit margin 4. Extensive product portfolio 5. Competitive advantage hard to sustain |
| Opportunities
1. Further increasing investment in R&D 2. Focusing on mobile advertisements 3. Entering cloud business segment 4. Increasing presence in emerging markets 5. Entering into strategic collaboration with affiliated businesses |
| Threats
1. Changes in currency exchange rate 2. Intensification of competition due to the slowing growth in the industry 3. Disruption in the pipeline of new products 4. Patent infringement lawsuits 5. Disruptive innovation by competitors |
Samsung SWOT analysis
Strengths
1. Samsung has maintained the largest market share in the global market of visual display since 2006. Samsung Display Solutions has advanced the field of digital signage by introducing leading-edge new hardware, including new video walls featuring the world’s narrowest bezel and the world’s first TIZEN-powered premium signage.[1] Samsung had a global TV market share of 27.6% in 2015. The global market share for UHD TV market share amounted to 34.1% for the same year.[2] Moreover, in 2015 Samsung Electronics had mobile phone market share of 21.1%, smartphone market share of 22.2% and tablet market share of 15.0%.[3]
2. Strong patent portfolio is one of the solid bases of Samsung competitive advantage. In 2015 alone, the multinational electronics company registered 5072 global patents in the US Patent and Trade Office. Samsung is the 2nd largest patent holder in the US since 2006.[4] The multinational electronics company has 36 R&D centres across the world to secure core technology for the future and invested KRW 14.8488 trillion in R&D in 2015. An uncompromised stance towards R&D can allow the company to continue with the pipeline of new products such as the Galaxy S5,Galaxy Note 4 and Galaxy Note edge.
3. Interbrand’s The Best 100 Global Brands 2015 ranked Samsung No.7 with an estimated brand value of KRW 45.3 billion, the same level of the previous year’s figure. According to “Brand Finance Global 500 Report”, by the British evaluation consultancy Brand Finance, Samsung’s brand value amounts to USD66.2 billion in 2017, a 13% increase from USD58.6 billion in 2016, and is the sixth highest in the world[5]. Forbes, on the other hand, estimates Samsung brand value USD 38.2 billion, the 10th most valuable brand in the world.[6] High brand value can be interpreted as a solid sign of consumer loyalty and it has immense positive effects on the long-term growth prospects of the business.
4. Samsung Electronics maintains leadership position by the volume of sales in the global market of smartphones. Samsung shipped more than 300 million smartphones in 2016 alone. At the end of 2016, Samsung led the smartphone market with a share of 21.2%. In 2017, Samsung sold more smartphones than any other device maker in the first quarter, earning the company 26.1% market share worldwide.[7] Thanks to its leadership position in this market, Samsung is able to generate substantial revenues to fund its R&D initiatives so that the position of the company can be further strengthened.
5. Solid financial position of the business is one of the most notable strengths possessed by Samsung Electronics. The multinational electronics company delivered sales of KRW200.7 trillion and earned KRW26.4 trillion in operating profits on a consolidated basis in 2015. From the financial perspective, Samsung maintained a sound financial structure by recording a debt ratio of 35.3 percent, an equity ratio of 73.9 percent, and a return on equity ratio of 11.0 percent on a consolidated basis[8]. Moreover, as it is illustrated in figure below, Samsung generated the record operating income of KRW14 trillion in quarter 2 of 2017 alone.
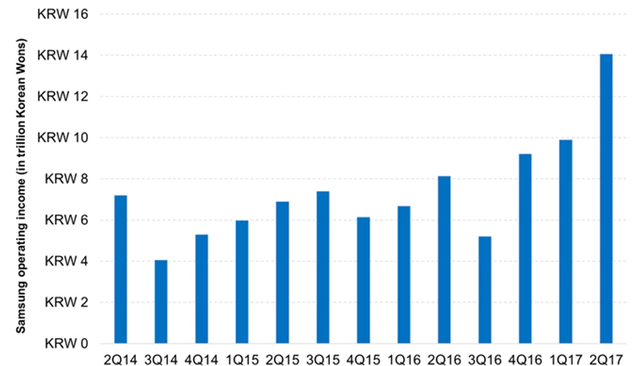
Samsung Electronics quarterly operating income
Weaknesses
1. Samsung does not have its own operating system (OS) and software and therefore, it is dependent on external OS, notably Android, owned by Google. The absence of Samsung’s own OS and software has negative implications on the level of consumer loyalty and the company also misses an attractive potential for increasing the volume of revenues. It is critically important for Samsung to address this weakness in short or medium term perspective.
2. Samsung brand image has been damaged to a considerable extent due to a number of product safety issues. Samsung Galaxy Note 7 smartphone is the most notable case, where the company received at least 92 reports of Note 7 batteries overheating in the United States, with 26 reports of burns and 55 reports of property damage due to the explosion of the phone.[1] These incidents led to Galaxy Note 7 smartphone model being abandoned by Samsung.
Moreover, the multinational electronics company has to recall 144,000 Samsung washing machines worldwide due to being prone to causing fires. There were similar smaller incidents in the past with the recall of 184,000 microwave ovens in the United States in 2003 and the recall of 210,000 refrigerators in South Korea in 2009.[2]…
Samsung Group Report contains a full version of Samsung SWOT Analysis. The report illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces, Value Chain analysis and McKinsey 7S Model on Samsung. Moreover, the report contains analyses of Samsung leadership, organizational structure, business strategy and organizational culture. The report also comprises discussions of Samsung marketing strategy and addresses issues of corporate social responsibility.
[1] About Us (2017) Samsung Electronics, Available at: http://displaysolutions.samsung.com/about-us/our-vision
[2] Samsung Sustainability Report (2016)
[3] Samsung Sustainability Report (2016)
[4] Samsung Sustainability Report (2016) Samsung Electronics
[5] Suk-yee, J. (2017) “Samsung’s Brand Value Ranks 6th in the World” Business Korea, Available at: http://www.businesskorea.co.kr/english/news/industry/17184-brand-value-samsung%E2%80%99s-brand-value-ranks-6th-world
[6] The World’s Most Valuable Brands (2017) Forbes, Available at: https://www.forbes.com/powerful-brands/list/#tab:rank
[7] Reisinger, D. (2017) “Samsung Is Back Atop the Smartphone Market” Fortune, Available at: http://fortune.com/2017/04/11/samsung-apple-market-share/
[8] Samsung Sustainability Report (2016) Samsung Electronics
[9] Chen, B.X. & Sang-Hun, C. (2016) “Why Samsung Abandoned Its Galaxy Note 7 Flagship Phone”, The New York Times, Available at: https://www.nytimes.com/2016/10/12/business/international/samsung-galaxy-note7-terminated.html?ribbon-ad-idx=2&rref=business&module=Ribbon&version=context®ion=Header&action=click&contentCollection=Business%20Day&pgtype=article
[10] Chen, B.X. & Sang-Hun, C. (2016) “Galaxy Note 7 Is Not Samsung’s Only Problematic Product” The New York Times, Available at: https://www.nytimes.com/2016/10/13/business/international/samsung-galaxy-note7-profit-battery-fires.html?mcubz=0

