Strategy
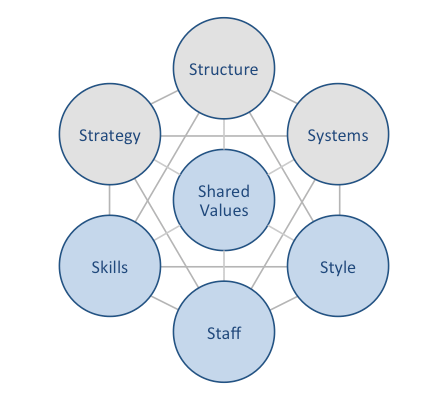
eBay McKinsey 7S framework attempts to explain the ways in which seven elements of businesses can be aligned to achieve higher effectiveness. According to McKinsey 7S strategy, structure and systems represent hard elements, whereas shared values, skills, style and staff are soft elements. The framework stresses that there are strong links between elements in a way that a change in one element causes changes in others. As it is illustrated in figure below, shared values are positioned at the core of eBay McKinsey 7S framework, since shared values guide employee behaviour with implications in their performance. eBay McKinsey 7S Framework Hard Elements Strategy. eBay has traditionally pursued first mover business strategy since the e-commerce site has been set up by Pierre Omidyar in 1995. Accordingly, the business has enjoyed from the first mover advantage in becoming the first and the largest online auction website with the widest range of products. However, the latest changes in eBay business strategy are associated with the shift from a primarily auction website to becoming an online retailer in general, a segment which is traditionally dominated by Amazon. It can be argued that if eBay fails to find new solid sources of competitive advantage as an online retailer, the e-commerce company will find it increasingly difficult to compete with Amazon in the new area. Structure. eBay business strategy can be characterised as a hierarchical reflecting the massive size of the business that employs 12,000 people worldwide and has more than 160 million customers.[1] Separation of PayPal from eBay in 2015 resulted in a major structural change for the business, at the same time depriving eBay a solid source of cash. The Board of Directors and the Senior Leadership Team comprise 11 members each and each member is responsible for a specific aspect or a geographical…
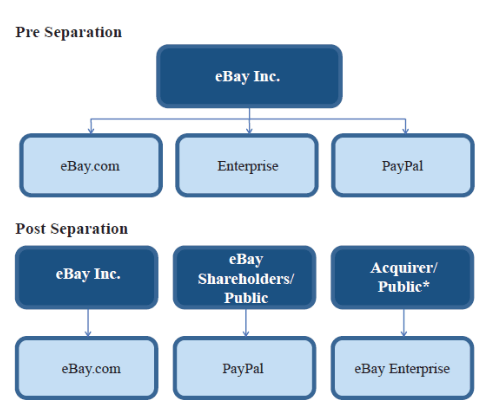
eBay organizational structure is hierarchical due to the massive size of the company that employs nearly 12,000 people worldwide. In 2015, a major restructuring was introduced to the company by separating PayPal from eBay Inc. The figure below illustrates changes to eBay organizational structure as a result of PayPal’s separation. eBay Organizational Structure eBay Board of Directors comprises 11 members and Thomas J. Tierney is the Chairman of the Board. David Wenig leads eBay executive team as President and CEO and is closely assisted by other leaders in the following positions: President, StubHub SVP, Chief Technology Officer SVP, General Counsel VP of Global Operations SVP, eBay North America SVP, eBay Asia Pacific SVP, Chief Product Officer SVP, Chief Financial Officer SVP, Chief Communications Officer SVP, eBay Europe SVP, Chief People Officer eBay Inc. Report comprises a comprehensive analysis of eBay. The report illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces, Value Chain analysis and McKinsey 7S Model on eBay. Moreover, the report contains analyses of eBay’s marketing strategy and discusses the issues of corporate social responsibility.

eBay has been continuously reinventing itself since its founding in 1995 and its strategy places a great emphasis on the first mover advantage. eBay business strategy can be described as service differentiation with the focus on user experience of both, buyers and sellers. Specifically, the most recent changes include “improving the site’s search capabilities making finding items more structured. Instead of listing all available items when a product is searched, there will now be categories such as “best value,” “brand new” and others.”[1] Generally, for the past few years eBay business strategy has been marked with a shift from a listings-based format toward a product-based format. The pursuit of this business strategy has involved a collection of product-related data from sellers to enhance user experience with the ultimate aim of building machine learning capabilities to process a global, accessible catalogue of things. In other words, eBay business strategy is attempting to shift the role and image of the company from e-commerce facilitator to an online retailer. While this decision by CEO and President Devin Wenig may reflect the overall tendency in the global market, eBay may find it increasingly difficult to compete with Amazon, taking into account Amazon’s high level of cost-effectiveness and competence in the delivery of goods. eBay business strategy for a medium term perspective also includes improving its ranking in Google search results via employing a structured data. It is important to note that the business strategy of service differentiation requires systematic financial investments in research and development. From this point of view, it can be argued that eBay may find it difficult to pursue this strategy in the future, since after the separation from PayPal in 2015, eBay lost a solid source of cash flow and a powerful growth engine. eBay Inc. Report contains more detailed…
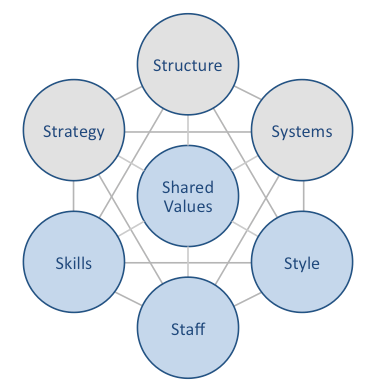
Hilton McKinsey 7S framework focuses on seven elements of a business practice that can be aligned to improve effectiveness of the company. According to the framework strategy, structure and systems represent hard elements, whereas shared values, skills, style and staff are soft elements. McKinsey 7S framework stresses the presence of strong links between elements in a way that a change in one element causes changes in others. As it is illustrated in figure below, shared values are positioned at the core of Hilton McKinsey 7S framework, since shared values guide employee behaviour with implications in their performance. Hilton McKinsey 7S Model Hard Elements Strategy. Hilton business strategy can be classified as service differentiation. The major points of differences of Hilton hotels from the competition include high quality of services and advanced integration of information and communication technologies into various aspects of hotel experience. Moreover, Hilton business strategy attempts to associate the experience of staying in Hilton Hotels with customer perceptions of status, achievement and recognition. Structure. Hilton organizational structure is hierarchical due to the massive size of the business that comprises 13 brands serving 140 million guests in 2015 alone (Annual Report, 2015). Moreover, Hilton organizational structure can also be described as divisional and the business is divided into three divisions: ownership, management and franchise, timeshare. Systems. Hilton Worldwide business operations rely on a wide range of systems such as customer reservations system, quality control system, employee recruitment and selection system, employee performance evaluation system and others. Since his appointment as the President and CEO in 2007, Christopher Nassetta simplified a wide range of Hilton systems to a great extent. For example, an introduction of a single company-wide system for employee performance evaluations simplified relevant processes to a great extent. Hilton Worldwide Holdings Inc. Report contains a detailed discussion of Hilton…
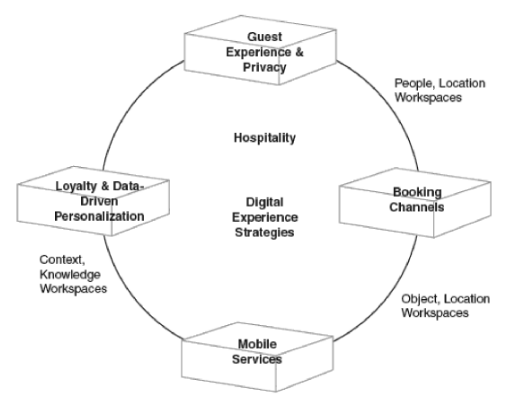
Service differentiation can be specified as the cornerstone of Hilton Hotels business strategy. Specifically, the company differentiates its services on the basis of quality, maintaining the highest level of standards and integrating IT systems into various aspects of service provision. Digital hospitality is one of the main sources of Hilton Hotels competitive advantage. As it is illustrated in Figure 1 below, the company’s digitalization efforts relate to booking channels, mobile services, loyalty and data driven-personalization, guest experience and privacy. Moreover, effective integration of these digitalization points creates additional synergetic impact for the business. Hilton Hotels and Resorts digital experience strategies capabilities[1] Hilton’s business strategy also relies on an extensive international expansion and the Hilton Worldwide added more than 100,000 rooms to its portfolio in 2015 alone, including 14,500 rooms converted from competitors’ brands and independent hotels.[2] It has to be noted that Hilton’s business strategy of an aggressive international business strategy and service differentiation with the focus on quality has resulted in the accumulation of USD10.5 billion debt, including USD726 million of non-recourse debt by the end of 2015.[3] This is because in order to sustain its business strategy, Hilton has to commit to substantial financial investments in a regular manner, despite the volatility of revenues caused by seasonal and cyclical nature of the business and a range of other factors. Hilton Hotels and Resorts may find it challenging to sustain its competitive advantages in short-term and long-term perspectives, since it can be copied by existing or new market players to threaten Hilton’s market share. Hilton Worldwide Holdings Inc. Report contains more detailed discussion of Hilton Hotels business strategy. The report also illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces, Value Chain analysis and McKinsey 7S Model on Hilton.…
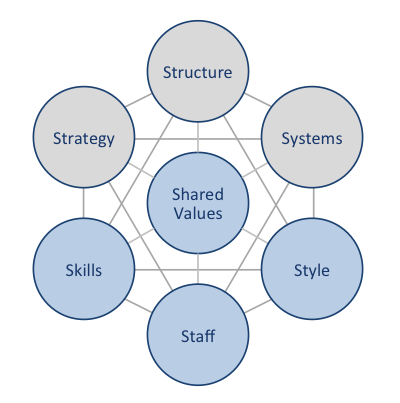
Red Bull McKinsey 7S framework explains how seven key elements of businesses can united to increase the overall effectiveness of the company. According to Red Bull McKinsey 7S framework strategy, structure and systems represent hard elements, whereas shared values, skills, style and staff are soft elements. As it is illustrated in figure below, shared values are positioned at the core of Red Bull McKinsey 7S framework, since shared values guide employee behaviour with implications in their performance. Red Bull McKinsey 7S Framework Hard Elements Strategy. Red Bull pursues the business strategy of product differentiation. The company differentiates its energy drinks according to the perception of ‘Red Bull gives you wings’. Specifically, according to the company’s marketing message, consumption of Red Bull energy drinks result in enhanced mental and physical performance. Benefiting from first mover advantage and an extensive reliance on marketing also represent important elements of Red Bull business strategy. Structure. Red Bull organizational structure can be described as divisional and company runs two business divisions: Red Bull soft drinks and other businesses. Red Bull soft drinks division comprises Red Bull Energy drinks (regular, sugar free, zero calories and Red Bull editions) and Red Bull Simply Cola. Other business division, on the other hand, comprises motor racing, media, MVNO and fashion online retailing. Systems. Main systems that run Red Bull GmbH include information system, HR system, financial system, quality management system and others. The management attempts to achieve a close integration between individual systems within the organization in order to increase the overall effectiveness of the company… Red Bull GmbH Report contains a detailed discussion of Red Bull McKinsey 7S framework. The report also illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces, Value Chain analysis and on Red Bull.…

Red Bull business strategy is to associate the brand with a lifestyle of an adventurous spirit. An extensive and aggressive marketing is placed at the core of Red Bull business strategy. The brand’s marketing communication message – ‘Red Bull gives you wings’, is constantly communicated to the target customer segment via multiple marketing communication channels in an integrated manner. Red Bull business strategy is product differentiation and Red Bull is a premium energy drink. Accordingly, Red Bull energy drinks are generally more expensive compared to other energy drinks such as Monster, Rockstar, Lucozade, NOS and Amp. Customers are charged additionally for augmented benefits of Red Bull consumption that include the perception of leading a full and active lifestyle and enhancing mental and physical performance. According to Red Bull business strategy, its competitive advantages rely on the following points: First mover advantage in the energy drink sector in developed countries. Red Bull founder Dietrich Mateschitz was the first to introduce energy drinks to the west by adjusting the taste of Thai drink Krating Daeng. Unique and sweet taste of the energy drink. The Red Bull flavouring is still produced in Bangkok and exported into manufacturing plants internationally. An appealing brand image associated with extreme sports. The company owns a number of sports teams such as RB Leipzig,FC Red Bull Salzburg, Red Bull Brasil and New York Red Bulls to reinforce the brand image. Effective marketing strategy. This integrates Red Bull TV online channel, The Red Bulleting online magazine and about 150 people employed for content marketing and media strategy[1] It has to be noted that Red Bull GmbH is increasingly becoming a media company with the launch and acquisitions of increasing numbers of media businesses. This strategy serves to further strengthen Red Bull brand image via communicating relevant marketing messages to the…
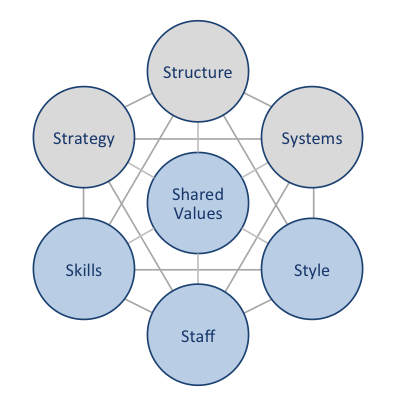
British Airways McKinsey 7S framework illustrates how seven individual elements of the airline business are aligned to increase the overall effectiveness of the business. McKinsey 7S divides elements into hard and soft groups. Strategy, structure and systems represent are considered as hard elements, whereas shared values, skills, style and staff represent soft elements. As it is illustrated in the figure below, shared values are positioned at the core of British Airways McKinsey 7S framework, since shared values guide employee behaviour with implications in their performance. British Airways McKinsey 7S Framework Hard Elements Strategy. British Airways pursues the business strategy of service differentiation. Specifically, the airline differentiates its services via an extensive reliance on digitalization and information technology and a high level of customization of service provision. An aggressive international market expansion is another important element of British Airways business strategy and in 2016 alone the airline company is expected to fly to more than a dozen new routes.[1] Structure. British Airways is owned by International Airline Group (IAG), the largest airline group in Europe that also owns Iberia, Vueling and Aer Lingus. British Airways organizational structure is hierarchical reflecting the large size of the business. The new CEO Alex Cruz is expected to introduce de-layering initiatives into British Airways organizational structure as a part of his wide-scale cost-cutting measures. Systems. Apart from the standard set of organizational systems such as employee recruitment and selection system, performance appraisals system, quality control system, complaint handling system and others, British Airways also maintains a number of industry-specific systems. These include, but not limited to passenger check-in system, baggage handling system, in-flight entertainment system and others. British Airways Report contains a detailed discussion of British Airways McKinsey 7S framework. The report also illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such…

British Airways is a premium segment airline and accordingly British Airways business strategy can be specified as service differentiation. The airline aims to generate a return on capital of a minimum 15 per cent with an operating profit margin of 12 – 15 per cent.[1] British Airways business strategy focused on service differentiation is planned to be continued in the following directions[2]: Replacement or refurbishment of 99 per cent of wide-body aircraft by 2020 Improvement of in-flight entertainment in-seat power and the rollout of on-board WIFI Further investments in digital technologies to provide personalised, seamless service British Airways business strategy also relies in international market expansion strategy in an aggressive manner. In 2016 alone the airline company is expected to fly to more than a dozen new routes, including Biarritz in France, Mahon in Menorca and Palermo in Sicily. The airline also announced additional services from Heathrow and Gatwick to Krakow in Poland, Stockholm in Sweden, Split in Croatia, Berlin in Germany, Olbia in Sardinia and Gibraltar. British Airways competitive advantage is based on the following points: The highest standards of service with a focus on service personalization. The variety of choice is another important aspect of British Airways competitive advantage. For example, in the World Traveller cabin, customers can choose from a wide range of Taste of the Far East’, ‘Gourmet Dining’, ‘Taste of Britain’, ‘Great British Breakfast’, ‘Healthy Choice’ and ‘Vegetarian Kitchen’.[3] Focus on digitalization and increasing integration of information technology into various aspects of service provision and business processes. British Airways Report contains more detailed discussion of British Airways business strategy. The report also illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces, Value Chain analysis and McKinsey 7S Model on British Airways. Moreover, the report…

Introduction Modern businesses are granted with vast opportunities in terms of revenue maximisation through entering new markets. Implementation of international market expansion strategy involves strategic-level decision making in relation to global branding strategies, the choice of market entry strategies such as wholly-owned subsidiaries, exporting, licensing, or forming joint-ventures, as well as, deciding on the level of standardisation or adaptation of products and service in new markets. Market entry strategies, branding strategies and the levels of standardisation or adaptation of each single element of marketing mix can be rightly specified as critical success factors directly impacting the success of business in the new market. This essay represents a critical analysis of standardisation vs. adaptation in international marketing in the twenty first century. The essay starts with discussing advantages and disadvantages of standardisation. This is followed by critical analysis of adaptation strategy as an effective customer-orientation strategy by referring to relevant real-life business case studies. The essay is completed by drawing conclusions on standardisation vs. adaptation debate and its relevance to the modern marketplace. Standardisation as a cost saving strategy Standardisation involves using “the same range of products, the same pricing, promotional and location strategies” (Gupta and Randhawa, 2008, p.77). Rationale behind standardisation practices relate to homogenisation of consumer wants and needs due to intensifying forces of globalisation (Winer, 2009). Standardisation can focus on core competitive advantage of the brand and it “allows for a consistent and strong brand to be developed across all markets” (Donelly, 2009, p.150). A Conceptual Model of International Marketing Strategy in relation to standardisation vs. adaptation has been introduced by Theodosiou and Leonidou (2003). According to the model, the degree of standardisation or adaptation is impacted by antecedent factors which have external and internal characteristics. External characteristics of antecedent factors consist of environmental factors, market characteristics, customer issues,…
