Literature Review

Systematic literature review can be defined as “a review with a clear stated purpose, a question, a defined search approach, stating inclusion and exclusion criteria, producing a qualitative appraisal of articles” (Jesson et al., 2011, p.12). References Jesson, J., Matheson, L. & Lacey, F.M. (2011) “Doing Your Literature Review: Traditional and Systematic Techniques” SAGE Publications
By John Dudovskiy
Category: Literature Review

Literature review can be divided into two categories: exemplary and exhaustive. It has been noted that “in the exemplary review, the writer assumes the reader knows about the subject and so presents only key references to reacquaint the reader with representative work that relate to the research study” (Rubin et al, 2009, p.236). An exhaustive literature review, on the other hand, is considered to be comprehensive with the author researching and presenting all the information related to the research area. References Rubin, R.B., Rubin, A.M., Haridakis, P.M. & Piele, L.J. (2009) “Communication Research: Strategies and Sources” Cengage Learning
By John Dudovskiy
Category: Literature Review

The role of women in media advertising has been discussed by many authors from various angles. According to Ross and Byerly (2008) traditionally media advertisements have positioned women as passive and submissive. At the same time, Ross and Byerly (2008) state that this prescribed role for women in media is being changed at the moment, however certain limitations still exist. Cheng and Chang (2009) relate to the role of women in media advertising to sex appeal. Moreover, Cheng and Chang (2009) argue that this situation is not likely to change for a foreseeable future and authors attempt to justify this viewpoint by referring the basic human nature. Accoring to Abel et al. (2010) the integration of female body images in advertisement in various forms has increased significantly during the last two decades. It has been noted that women in advertisements are represented thinner and well below their average weight. Mogel (2010) addresses the issues of media stereotyping in relation to woman. Specifically, according to Mogel (2010) media stereotyping perceives the role of women as intimate objects with submissive characters. Biermann (2011) addresses the same issue and argues that the role of women in many parts of the world is stereotyped by the media as housewives with the main concerns for house cleaning. According to Saad (2012) the significance of the nature of female representation in TV and radios are greater compared to the print media. Saad (2012) explains his stand in a way that while TV media and radio force their advertising on their viewers, in print media generally advertisement are less interruptive, in a way that people can skip them if they want to do so. McAllister and West (2013), on the other hand, relate the reasons of images of women being used more frequently than images of men…

It is acknowledged by secondary data authors that online retailing in its various forms, including retailing of food and grocery products is considered to be a component of e-commerce. E-Commerce can be defined as “conducting business transactions – generally financial transactions – via communications technology” (Morley and Parker, 2010, p.431) Laudon and Traver (2009) inform that internet boom in general, and e-commerce in particular that has started towards the end of the last century had transformed the various aspects of lives of people significantly in a global scale. Authors offer different viewpoints about the nature of that affect but agree on the idea that “with the introduction of e-commerce, we have come to expect 24-hour delivery of products from across the world, and home delivery of groceries from the local Tesco at a time of our choosing” (Gustafsson, 2006, p.39) Hall (2008) mentions a survey conducted in 2008, which revealed that sixty-five percent of food companies were engaged in selling specialty food via internet. The following table illustrates the findings of the survey in a more detailed way: Internet Sales as Percent of Gross Sales Internet Sales as Percent of Total Sales in 2007 Internet Sales as Percent of Total Sales in 2008 Less than 10% 40.0 37.5 11-20% 10.0 10.0 21-30% 1.0 10.0 31-40% 2.0 2.5 41-50% 0.0 0.0 51-60% 2.5 0.0 More than 60% 2.5 2.5 No response 22.5 27.5 However, some authors (May, 2000, Kozami, 2002, Ashley, 2004, and others) dismiss the idea that purchasing food and grocery products through internet is an entirely new thing. They justify their stand by stating that “we should be suspicious of claims that internet provisioning is something entirely new. There are obvious continuities with existing telephone and television shopping, even if the service has become widespread and notionally democratized”…

For the last two or three decades, the principal target of economy has been the control of inflation (Delong, 2002). Both politicians and economists say that this is the first economic duty of any government. And they tend to assume that other economic goals such as economic growth and low unemployment will be achieved only if the inflation is held under control. According to Frank and Bernanke (2001), as economic growth and low unemployment is achieved through successful controlling of inflation, then there is a relationship between inflation and economic growth. There were many researches and investigations to identify and analyse the relationship between inflation and economic growth which were carried out by Barro (1995) Li (2000), Gokal and Hanif (2004), and they all identified the relationship between two variables. They all tend to conclude that a consistent economic growth can be achieved with low consistent inflation rates; however, higher inflation rates distort the economic growth consistency of any country. Like many other developing and emerging groups, CIS countries also aim to achieve low sustainable inflation together with high economic growth which is of great importance for any country. Malik, (2005), indicates that one of the determinants of macro-economic stability is inflation, and long term economic growth requires macroeconomic stability which will be achieved through low inflation along with sustainable budget deficits, realistic exchange rates and appropriate real interest rates. He points out that the stability of inflation rates has an enormous impact on the economic growth of the country. Khan and Senhadji (2001) state that first researchers to study and detect the nonlinear inflation and economic growth relationship were Fischer (1993). Later, Sarel (1996) examined the data of 87 countries and covered the period of 1970-1990. He actually found structural break point of the relationship between inflation and economic…
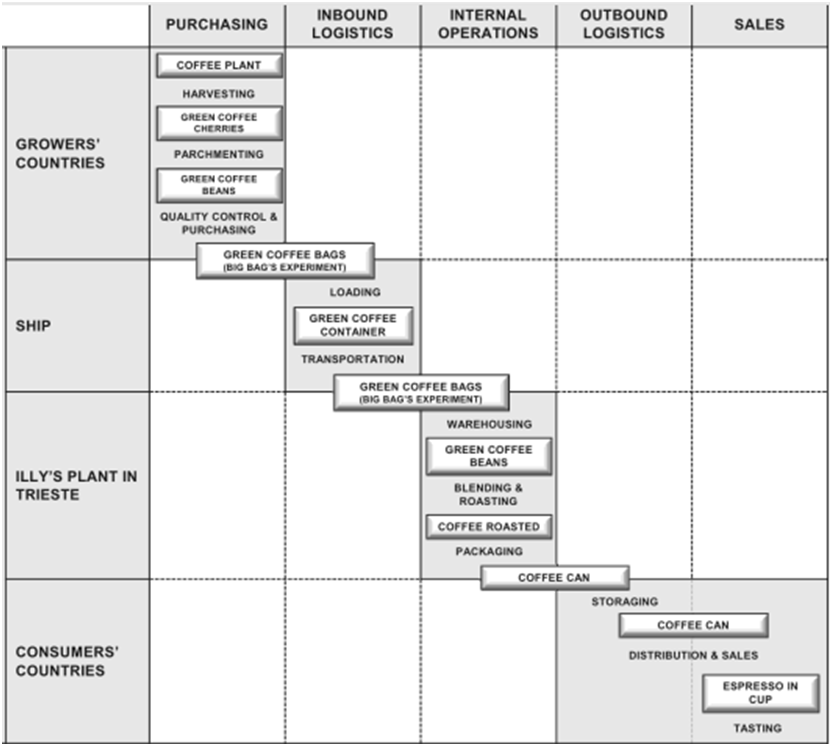
Illy is a global coffee brand that is sold in 140 countries and employs more than 800 people globally (Illy: By the Numbers, 2013). The main difference between traditional logistics and supply chain has been drawn by Agrawal and Smith (2009) in a way that supply chain is a much broader concept than logistics and it focuses on the quality of relationships between various elements within the supply chain with the aims of achieving improvements Elements of supply-chain management (SCM) have been specified by Wisner et al. (2008) as purchasing, operations, distribution, and integration. Wisner (2008) argues that effectiveness in one particular element does not compensate shortcomings in other elements, and thus businesses need to strive to strive to obtain competitive advantages each of these elements. Three major tendencies impacting SCM have been specified by (Muller, 2011). Firstly, increasing numbers of businesses are acquiring their resources from other countries. Secondly, timeframe associated with the delivery of resources and the quality of resources is playing increasing role for firms in terms of obtaining competitive advantage. Thirdly, rapid technological developments among a range of other factors are causing uncertainties in the market with direct implication on SCM practices Ruston et al. (2010) advocate the adoption of strategic approach in dealing with suppliers. This viewpoint has been supported by a wide range of other authors as well, and the benefits of adopting a strategic approach with suppliers have been listed as more effective quality control based on trust (Leeman, 2010) and achieving greater level of supplier cooperation in times of economic difficulties (Agrawal and Smith, 2009). Basu and Wright (2012) further expand this point and argue that adoption of strategic approach in dealing with suppliers based on ethical practices can have highly positive implications on business brand image if these relationships are communicated…

The nature of leadership in private sector organisations is directly impacted by the primary purpose of such organisations and this primary purpose is profit maximisation (DuBrin, 2012). This opinion is confirmed by Goldsmith et al. (2010), who perceive profit maximisation as the main assessment criteria for private sector organisational leaders. According to Gold et al. (2010) constant search for competitive advantage can be justly specified as one of the most fundamental characteristics of leadership in private sector organisations. According to this stance, competitive advantage can be derived from a wide range of sources and business processes, and it is the responsibility of a business leader to be able to formulate the most appropriate competitive advantage, and ensure its efficient utilisation. Stanfield (2009) explore the issues of ethics for modern business leaders and conclude that the level of ethical requirements have increased for business leaders in the last several decades contributed by increasing level of scrutiny business leaders are being subjected to. Stanfield (2009) offers justification for this claim by stating that increasing role of viral media in the society makes any evidence of unethical behaviour hard to escape from. Maintaining high level of flexibility and implementing changes in relation to various business processes in a constant manner is pointed to as a significant challenge to business leaders by Kezar et al. (2011) and Kreitner and Cassidy (2012). Moreover, Kezar et al. (2011) stress the role of assertiveness and communication skills for business leaders in order to be able to implement changes in an efficient manner. The issue of talent management by business leaders comprehensively addressed by Bertocci and Bertocci (2009) reveals another important aspect of successful leadership practice. Specifically, according to Bertocci and Bertocci (2009) human resources need to be perceived as the most valuable business asset in the 21st…

Major differences between public and private sector organisations have been specified and addressed by a range of management scholars. According to Wirick (2009) the main difference between public and private sector organisations relates to forms of ownership. Specifically, public sector organisations are owned and operated by government, whereas private sector organisations are not part of the government. The form of ownership as the main distinctive point between public and private sector organisations has also been mentioned by Kassel (2010), Sims (2010) and others. Linked to the point above, aims and objectives of organisations have also been specified by authors as a major point of difference between public and private sector organisations. Kassel (2010) and Starling (2010) assert that the primary objective of organisations operating in private sector is profit maximisation. Gallos (2008) advises not to be deluded by charitable acts of private sector organisations in regards to intentions and insists that all of these acts are aimed at supporting the primary objective of private sector organisations which is profit maximisation. The aims of public sector organisations, on the other hand, involve serving the interests of taxpayers through various manners according to the type of the organisation (Sims, 2010). For example, public schools aim to provide education to citizens within a country, whereas the objectives of public health organisations involve providing quality healthcare. Importantly, the source of funding of organisations represents another point of difference between public and private sector organisations (Sabatier, 2007). Namely, public sector organisations are funded by taxpayers; therefore serve the interest of taxpayers, while private sector organisations are funded by individuals and corporate investors aiming to make a profit. References Gallos, J.V. (2008) “Business Leadership: A Jossey-Bass Reader” 2nd edition, John Wiley & Sons Kassel, D.S. (2010) “Managing Public Sector Projects: A Strategic Framework for Success…

According to Grigoroudis and Siskos (2009) as taken by Oliver (1997) “satisfaction is the consumer’s fulfilment response. It is a judgement that a product or service feature, or the product or service itself, provided (or is providing) a pleasurable level of consumption-related fulfilment, including levels of under-or overfulfillment” (Grigoroudis and Siskos, 2009, p.4) The Business Dictionary (online, 2013) defines private sector as a part of national economy that consists of private enterprises including personal sector (households) and corporate sector (companies). The definition of the public sector is suggested by The Free Dictionary (2011) as “the part of an economy that consists of state-owned institutions, including nationalised industries and services provided by local authorities” (The Free Dictionary, online, 2011). Although the term ‘quality’ on its own is widely known and does not require further elaboration, some authors have offered their viewpoints regarding the definition of the term within the context of customer services. Specifically, it has been stated that, “quality of the delivered products or services is essential to achieving customer satisfaction. The quality concept embraces how to meet all customers’ requirements, including how they are greeted on the telephone or at the counter, the speed with which a query is responded, providing new services when required, and ensuring the delivered services satisfy the community needs” (Nagel, 2000, p.47). Introduction According to Grigoroudis and Siskos (2009) the advantages of private sector organisations over the public sector organisations include better level of the service, more information about various aspects of customer services, better management, market testing and rewarding performance. Secondary data authors (Murley, 1997) argue that a part of the issue of effective customer service provision within public sector relates to the identification of customers in public sector in the first place. Discussing police services specifically, the author reasons that “their customers…

Intensifying forces of economic globalisation have facilitated the shift of production from highly developed countries such as the US and European countries to emerging superpowers like China, India, and Vietnam during the last several decades (Jacques, 2012). However, there is an argument that a set of technological breakthroughs such as introduction of 3D printing may reverse this shift. This article represents a critical analysis of the boomerang effect of competitive advantage in manufacturing in relation to developed countries as discussed in The Economist Special Report entitled Manufacturing and Innovation: A Third Industrial Revolution by Paul Markillie (2012). The article starts with a brief discussion about the rise of China as a world’s largest manufacturer. This is followed by discussing the likelihood of boomerang effect, i.e. shift of production back to rich countries. Moreover, the article contains a discussion of an alternative scenario analysing the chances for China to retain its current manufacturing leadership position in the global scale. Rise of China as a World’s Largest Manufacturer Cheap costs of human resources are widely believed to be one of the main reasons behind the emergence of China as the largest manufacturer in the world. According to the US Bureau of Labour Statistics only several years ago the cost of labour in Chinese factories was as low as 64 cent per hour whereas, hourly pay rate in the US factories amounted to $21.11 (Businessweek Magazine, 2004). Accordingly, this vast difference in employee pay rates has motivated many multinational businesses based in the US and Europe to outsource and offshore their manufacturing to China in an attempt to gain cost advantages. Moreover, highly increasing level of effectiveness of human resources in China can be specified as another factor that has contributed to its status of the largest manufacturer in the world. It has been…
