Search results for: Ansoff Matrix

Xiaomi marketing mix (Xiaomi 7Ps of marketing) comprises elements of the marketing mix that consists of product, place, price, promotion, process, people and physical evidence. Product Xiaomi mainly focuses on hardware, software and internet services. The company’s product range is vast and includes laptops, mobile phones, tablets, smart TVs, power banks, smartwatches etc. Xiaomi also manufactures and drones, sells water purifiers, vacuum cleaners and even rice cookers. Xiaomi products such as cellphones, TVs, TV boxes, and speakers have received more than 145 industrial design awards altogether.[1] Continuous expansion of ecosystem of products and services is placed at the core of company’s business strategy. Place Xiaomi is headquartered in Beijing, China and has offices in Asia-Pacific, India, and Brazil. The mobile internet company has established its presence in 70 countries and regions and it is among the top 5 in 16 markets. These markets include Turkey, Malaysia, Mexico, Thailand, Philippines, Russia, Singapore, Indonesia, Brazil, India, and Vietnam. The mobile internet company opened its first offline retail store in February 2016 and by the end of 2017 had more than 155 stores.[2] In March 2017, the company established a new sales channel called Xiaomi kiosks to reach districts without Mi Home Stores and towns and villages with limited e-commerce access[3] Price Xiaomi pricing strategy can be described as economy pricing. Accordingly, the internet technology company sets its prices low, keeping marketing and promotional costs to a minimum. Flash sales are integral component of Xiaomi pricing strategy. The electronics and software company uses the flash sales to announce the sales of its smartphones at a greatly reduced price. Xiaomi flash sales last only for a short duration of time. For example, in India “a flash sale for the Redmi 1S model in September 2014, around 40,000 pieces were sold out in just…

Xiaomi marketing strategy has been traditionally minimalistic due to the cost leadership business strategy pursued by the company. Accordingly, the mobile internet company only engaged in social media marketing, saving on advertising costs and passing this cost advantage to customers in the forms of products with low price tags. However, “Oppo and Vivo have grown in China by using the exact tactics that Xiaomi once avoided. Both companies spend heavily on offline advertisements and celebrity endorsements, plastering billboards on subways and bus stops across China’s second- and third-tier cities.”[1] This has caused a shift in Xiaomi marketing strategy and starting from lately the internet technology company has started to use traditional marketing communications channels as well. Moreover, Xiaomi marketing strategy nowadays also includes product placements and Xiaomi holograms in fiction triller Anon (2018) can be mentioned as an example. As s privately-owned company, Xiaomi does not disclose its annual marketing budget. Xiaomi 7ps of marketing focuses on price element of the marketing mix to a greater extent compared to other elements. Accordingly, the brand’s target customer segment represents price-conscious consumers who want to own the latest smartphones with advanced functions and capabilities for affordable cost. Hunger marketing strategy is one of the integral components of Xiaomi marketing strategy. The electronics and software company appeals to emotional needs of their target customer segment by selling only limited amount of products for a limited duration of time. In other words, the company creates the shortage of supply in purpose, creating a buzz in the market and evoking desire in customers to own a MI brand smartphone. Xiaomi Inc. Report contains a full analysis of Xiaomi marketing strategy. The report illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces, Value Chain analysis, Ansoff Matrix…

PESTEL is a strategic analytical tool and the acronym stands for political, economic, social, technological, environmental and legal factors. Xiaomi PESTEL analysis involves the analysis of potential impact of these external factors on the profitability and long-term growth prospects of the mobile internet company. Political Factors in Xiaomi PESTEL Analysis There is a wide range of political factors that can affect the internet technology company. These include government stability, bureaucracy, corruption, freedom of press and others. On one hand, Xiaomi has benefited from political factors in China in general and protectionism policy of Chinese government in particular. The government of China protects local technology companies such as Tencent, Baidu and Xiaomi by imposing barriers to operate in the country to their international rivals such as Facebook, Twitter, Snapchat, YouTube and Google. The head of Xiaomi, along with the heads of Tencent and Baidu advice the government on international business policies.[1] This grants technology companies enviable opportunities to influence local political factors that affect their businesses to a certain extent. Xiaomi has even set up its Communist Party Committee in 2015[2] as a display of its support for the ruling government. On the other hand, while political factors benefit Xiaomi in its home market in China, the company is usually negatively affected from political factors outside of China. For example, the Taiwanese government has investigated Xiaomi on a cyber security threat in 2014 causing certain damage to the brand image of the company. There is a popular concern that the investigation was politically motivated because “China and Taiwan have been historical foes since defeated Nationalists fled to the island after losing a civil war to China’s Communists in 1949”.[3] Economic Factors in Xiaomi PESTEL Analysis Economic factors affecting the internet technology company are diverse. These include macroeconomic climate in the country,…

In business context, SWOT acronym stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats associated with the company. The following table illustrates Xiaomi SWOT analysis Strengths 1. Efficient leadership by Lei Jun 2. Impressive growth rate 3. Cost advantage 4. Brand value estimated at USD 100 billion[1] Weaknesses 1. Low profit margin 2. Lower smartphone capabilities and functionalities compared to major competitors such as Apple and Samsung 3. Competitive advantage difficult to sustain 4. Lack of experience in the global marketplace Opportunities 1. Increasing presence in cloud segment 2. Formation of strategic collaborations 3. Focusing on marketing strategy 4. Achieving a disruptive innovation in the industry as a result of research and development Threats 1. Market saturation in smartphone industry 2. Increase in the costs of resources 3. Issues with product functionality 4. Emergence of CSR-related scandals Xiaomi SWOT analysis Strengths in Xiaomi SWOT Analysis `1. Xiaomi co-founder and CEO Lei Jun is an effective business leader named “Businessman of the Year” 2014 by Forbes Asia. Dubbed the ‘new Steve Jobs’, Lei Jun is perceived as the face of China Inc, along with Alibaba Founder Jack Ma.[2] Moreover, it is said that Lei has never yelled at his staff. When he encounters a problem, he just smiles and gets down to business, and tries to find a solution. In social gatherings, Lei is always a good listener.[3] Efficient and visionary leadership style is one of the major factors behind the phenomenal growth of the internet technology company. 2. The electronics and software company has enjoyed an impressive growth rate since its foundation in 2011. In Q4 2017, Xiaomi became the world’s No.4 in terms of quantity of shipments. Despite the decline of 6,3% in the global smartphone market, Xiaomi managed to maintain a year-on-year growth of 96.9%, the only brand demonstrating continuous…

According to Harrison’s model of culture, Xiaomi organizational culture can be classified as power culture. Specifically, powers of decision making at the internet technology company are concentrated in the hands of founder and CEO Lei Jun. Inspirational and effective leadership style of Lei Jun justifies the necessity of power culture for Xiaomi. Xiaomi organizational culture integrates the following three key elements: 1. “Just for Funs” concept. The tagline “Just for fans” is placed at the core of Xiaomi organizational culture. Founder and CEO Lei Jun explains that “the culture of fandom is about becoming friends with our consumers.”[1] There is a story of a master’s student who spends free time doing MiUI testing and moderating a Xiaomi fan forum that nets 200,000 posts every day as a volunteer.[2] 2. Innovation and creativity. Company’s official website claims that “we are incredibly flat, open, and innovative. No never-ending meetings. No lengthy processes. We provide a friendly and collaborative environment where creativity is encouraged to flourish.”[3] In other words, Xiaomi aims to promote informal organizational culture at all levels with positive implications on employee creativity. 3. Intense working culture. Xiaomi organizational culture can be characterized as intense. This is due to cost leadership business strategy followed by the company in a way that effective application of this strategy involves deriving the maximum benefit from resources, including human resources. Departure of former Google executive Hugo Barra from the key post of Xiaomi international vice president has been said to be linked to negative elements of Xiaomi organizational culture. Specifically, Barra said he was leaving because difficulties of living in “such a singular environment” had “taken a huge toll” on his life.[4] Xiaomi Inc. Report contains a full analysis of Xiaomi organizational culture. The report illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business…

Effectiveness of Xiaomi leadership can be considered as one of the main competitive advantages for the business. Xiaomi CEO Lei Jun is a respected businessman in China who previously led Kingsoft and founded Joyo.com that was sold to Amazon in 2014. It is said that Lei has never yelled at his staff. When he encounters a problem, he just smiles and gets down to business, and tries to find a solution. In social gatherings, Lei is always a good listener.[1] Named businessmen of the Year by Forbes in 2014 and along with Alibaba Founder Jack Ma, Lei Jun is rightly considered as the face of China Inc.[2] Xiaomi CEO is recognized as an effective charismatic leader worldwide. Along with Lei Jun, seven co-founders of the company have senior leadership roles with the titles of president and vice-presidents. Having co-founders in the senior management team is an important factor due to increased sense of ownership with positive implications on the performance of executives. Xiaomi has been dubbed as “Apple of China” for its emulation of design of Apple’s products, as well as, Lei Jun style of product announcements and his general image that resembles late Apple founder and CEO Steve Jobs. However, Lei Jun leadership style is fundamentally different from Steve Jobs leadership. Specifically, while Steve Jobs was known for his centralized and micro-managing leadership style, Xiaomi CEO has a reputation for being a good listener and takes into account views of other members of his senior management team. Xiaomi leadership challenges at present include maintaining cost leadership position amid intensifying competition from other budget internet technology brands such as Oppo and Vivo. Xiaomi Inc. Report contains a full analysis of Xiaomi leadership. The report illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL,…
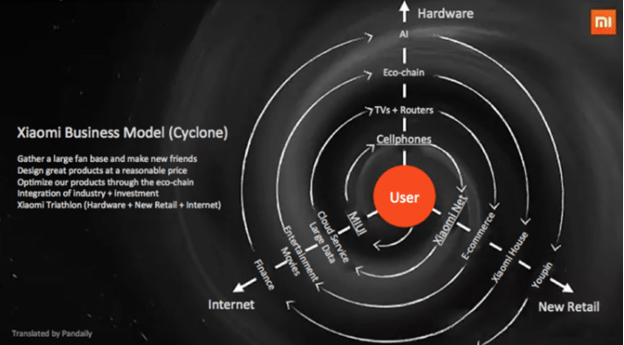
Xiaomi business strategy can be classified as cost leadership. According to its founder and CEO Lei Jun, Xiaomi was founded on the belief that “high-quality technology doesn’t need to cost a fortune.”[1] Accordingly, the company offers smartphones and other internet-technology products and services for affordable prices. On a wider perspective, Xiaomi business strategy is based on the following four pillars: 1. Gathering and utilising a large fan base. Xiaomi has a large fan base involving millions of people across the globe. Fans spend countless hours online discussing Xiaomi products on various forums, thus increasing the level of brand awareness with no extra cost for the company. The mobile internet company enjoys cult-like following, the same way as its major competitor Apple. According to its business strategy, Xiaomi fosters, develops and encourages its fans via Mi Fan Festivals that involves discounts and gifts. The motto of the company is “Just for Fans” and the company is also known to recruit its new employees among Mi Fans. 2. Designing great products at a reasonable price. Xiaomi practices ‘design as you built’ philosophy, incorporating Mi Fans feedback in a constant manner at all stages of new product development. Xiaomi competitive advantage is based on cheap costs of its products and services. In simple terms, cheap costs of Xiaomi products and services is the main reason for consumers buying those products and services. 3. Constant optimization of products through eco-chain. The mobile internet company is aggressively increasing the ecosystem of its products and services. This is another important aspect of Xiaomi business strategy. Currently, Xiaomi ecosystem comprises 55 companies including 29 companies which were incubated from the ground up by Xiaomi.[2] The ecosystem produces ever-increasing range of products ranging from smartphones to rice cookers. 4. Xiaomi Triathlon: Hardware+New Retail+Internet. As it is illustrated in…

Xiaomi Inc. is a privately owned electronics and software company founded in 2010 by serial entrepreneur Lei Jun, along with seven other co-founders. The mobile internet company has established its presence in 70 countries and regions and it is among the top 5 in 16 markets. Xiaomi currently employs about 18,000 people. In 2017 Xiaomi generated more than RMB 100 billion revenues and expected to get listed in the Fortune Global 500 list in foreseeable future. Xiaomi business strategy is based on cost advantage. Moreover, the company gathers and utilizes its large fan base in an efficient manner with positive implications on customer loyalty and the bottom line for the business. An aggressive expansion of ecosystem of products and services is also placed at the core of Xiaomi business strategy. The mobile internet company has matrix and flat organizational structure. According to framework of Ansoff Growth Matrix, Xiaomi uses all for strategies – market penetration, product development, market development and diversification, in an integrated manner. Efficient leadership by founder and CEO Lei Jun, impressive rate of growth and cost advantages compared to competition are considered as major strengths associated with Xiaomi. At the same time, the company has noteworthy weaknesses such as low profit margin, lower smartphone capabilities and functionalities compared to major competitors and difficulties of sustaining competitive advantage. Xiaomi Inc. Report contains the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces, Value Chain analysis and McKinsey 7S Model on Xiaomi. Moreover, the report contains analyses of Xiaomi business strategy, leadership and organizational structure and its marketing strategy. The report also discusses the issues of corporate social responsibility. 1. Executive Summary 2. Business Strategy 3. Leadership 4. Organisational Structure 5. Organizational Culture 6. Xiaomi and Ansoff Matrix 7. SWOT Analysis…

Uber Technologies Inc. is a global transportation technology company that operates in more than 10,000 cities in approximately 71 countries. The ride-hailing giant and its subsidiaries employ approximately 22,800 people globally (Annual Report, 2020). The global transportation technology company generated revenues of USD 11,1 billion in 2020, a decline of 14% compared to the previous year. Uber incurred operating losses of USD 3.0 billion, USD 8.6 billion and USD 4.9 billion in 2018, 2019 and 2020 respectively. The largest taxi company in the world has no cars of its own. Drivers are independent contractors for the company and they use their own or rented cars to drive with Uber using Uber app. The company has effectively disrupted the taxi industry in the global scale. Uber business strategy involves increasing service range to cater for the needs of great amount of customers and focusing on high levels of user convenience. Moreover, cost-saving through technological innovation is placed at the core of Uber business strategy. The company follows growth path through acquisitions, purchasing start-ups that can contribute to its ecosystem. The ride-hailing giant had a leadership crisis in 2017. Lack of leadership skills of co-founder and the first CEO Travis Kalanick had caused the formation of a poor corporate culture. As a result the company suffered from a range of serious scandals involving discrimination, sexual harassment and even mobbing. Uber CEO was even caught on video rudely arguing with driver about declining fares (Wong, 2017). Mr. Kalanick had to step down from leadership role as demanded by investors and Expedia’ CEO Dara Khosrowshahi became a new CEO for Uber. Uber possesses considerable strengths such as the first mover advantage, global market leadership and the brand value and advanced level of user convenience. At the same time, the company has serious weaknesses such…

Widely considered as a controversial genius and a charismatic leader, Steve Jobs has served as chairman and CEO of Apple for 14 years and he is credited for the global success of the company. The decease of Steve Jobs on October 5, 2011 because of cancer implications resulted in grievances for millions of people around the globe, at the same time casting concerns for the future of Apple Inc. Although, a long-term Apple executive with impressive track record – Tim Cook has been named apple CEO several months before the decease of Steve Jobs, nevertheless, there are concerns about the sustainability of Apple’s innovative corporate culture, as this culture had been closely associated with the former CEO. Apple Organisational Culture on Steve Jobs Era Late Apple chairman and CEO, Steve Jobs is widely perceived as unconventional leader who was able to rally various stakeholders of the company for his vision and at the same time “demanded excellence from his staff and was known for his blunt delivery of criticism” (McInerney, 2011). According to Harrison’s Model of Culture (1972) Apple organisational culture when Steve Jobs was in charge can be classified as a power culture. Accordingly, Steve Jobs had concentrated most of the decision making powers at his hands, constantly challenging subordinates for better performance, and criticising employees blatantly and undiplomatically if their performances did not meet his expectations (Arneson, 2011). Moreover, described as “antithesis of servant leadership model” (Katzenbach, 2012), Steve Jobs was famous for pressurising teams and individuals to better performance and creating a corporate culture of high level of performance where A list employees would thrive, however B list employees, comprising the majority of workforce, would be subjected to unnecessary level of stress. According to Harrison’s Model of Culture (1972) the power culture has both advantages, as well…
