Search results for: Marketing Communication Mix

Founded in 1969, Samsung Electronics is one of the leaders in consumer electronics industry in an international scale. The company employs 325,677 people in 80 countries and has more than 200 subsidiaries around the world (Sustainability Report, 2016). The business is divided into three large segments – consumer electronics, IT & mobile communications and device solutions. Samsung delivered the sales of KRW200.7 trillion and earned KRW26.4 trillion in operating profits on a consolidated basis in 2015. From the financial perspective, Samsung maintained a sound financial structure by recording a debt ratio of 35.3 percent, an equity ratio of 73.9 percent, and a return on equity ratio of 11.0 percent on a consolidated basis (Sustainability Report, 2016). Business strategy of Samsung Electronics is directed at strengthening the competitiveness and profit structures and the focus is on the development of premium products. Moreover, the international electronics company is known to benefit from product innovation and expanding its product range in a regular manner. Thanks to efficient implementation of this strategy, Samsung currently maintains the global leadership in visual display market segment with the market share of 28.3% for all flat-panel TV product lines. In the first quarter of 2015 Samsung surpassed Apple to regain its position as the largest smartphone manufacturer in the world (Sustainability Report, 2016). Currently, the multinational electronics company has certain weaknesses such as the absence of own operating system (OS) and software, damaged brand image due to product safety issues and recent corruption scandal and low profit margin. Moreover, Samsung is finding increasingly difficult to sustain its competitive advantage. Samsung Group Report contains the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces, Value Chain analysis and McKinsey 7S Model on Samsung. Moreover, the report contains analyses of Samsung’s business…
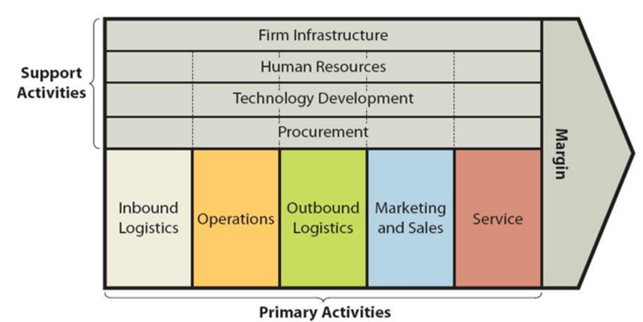
Google value-chain analysis is an analytical framework that assists in identifying business activities that can create value and competitive advantage to the business. Figure 1 below illustrates the essence of Google value chain analysis. Figure 1 Google value chain analysis Google Primary Activities Google Inbound logistics It can be argued that Google generates the greatest value in inbound logistics activities compared to other activities. Google’s core business is search. Internet users use Google’s search to find information they need, therefore the list of content generated as search results can be specified as ‘product’ provided by Google. The content Google generates as search result is created by private and organizational internet users and it comes to Google free of charge. Therefore, due to unique aspects of Google’s business model there is no inbound logistics costs for its core search business. Google also uses an extensive range of hardware, technological equipments and tools to conduct its business operations. The internet giant does not reveal the details of its supply-chain management and inbound logistics to the public. Google maintains a dedicated supplier site, where suppliers can submit invoice for payment, check invoice status and deal with a range of other administrative aspects of their cooperation with the company in a convenient manner. Google Operations Google operates via more than 70 offices in more than 40 countries internationally. Google offices are famous for their creative design and the presence of distinctive features such as sharing cubes, video games, pool tables, pianos, cafes and others. Google headquarters in Mountain View, California consists of about 4.8 million square feet of office and building space, along with about 15 acres of land that can be ground for more office space in the future. The major source of value in Google’s operations can be specified as the company’s…

Founded by Stanford University students Larry Page and Sergey Brin in 1998, Google dominates almost all of its markets and the company is well-known for its culture of creativity and innovative approach to develop new products and services. Google offers a wide range of interrelated internet-based products and services that are aimed at satisfying personal and professional needs in terms of communication, recreation, organization and increasing the level of performance and effectiveness. Google Inc. was restructured in 2015 to become Alphabet Inc. “Google’s search product became a wholly owned subsidiary of a new parent company, Alphabet, with other Google projects and teams spun out into separate “Alphabet companies,” each with its own CEO.”(Price and Nudelman, 2016, online). Alphabet Inc. is a holding company with no business operations of its own. Google is the largest business within Alphabet Inc. product portfolio. The company’s product portfolio also comprises Access, Calico, CapitalG, GV, Nest, Verily, Waymo, and X. The company classifies it’s all non-Google businesses as Other Bets. In fiscal year 2016, Alphabet Inc. generated revenues of USD90.3 billion and revenue growth of 20% year over year, with constant currency revenue growth of 24% year over year. Google segment generated revenues of USD89.5 billion, with revenue growth of 20% year over year. Other Bets revenues of USD0.8 billion with revenue growth of 82% year over year. Revenues from the United States, the United Kingdom, and Rest of the world were USD42.8 billion, USD7.8 billion, and USD39.7 billion, respectively (Annual Report,2016). The company has more than 72,000 full-time employees worldwide. Google core business strategy is business diversification and introduction of new products and services in a regular manner. Google business strategy is also based on the development of a closed eco-system to motivate customers to use greater range of products and services. Customers usually…

Facebook Inc. is a social media giant that owns Facebook, Instagram, WhatsApp, Oculus and a range of other e-commerce businesses. Founded in 2004 in Harvard University dormitory by Mark Zuckerberg and several of his classmates, Facebook emerged to become the most popular social media site in the world attracting more than 1.13 billion daily active users and 1.03 billion mobile daily active users (Stats, 2016). Facebook’s mission statement is “to give people the power to share and make the world more open and connected” (Annual Report, 2015) and the company generates revenues from selling advertising placements to marketers. Facebook business strategy is associated with an extensive and continuous focus on user experience, growth via acquisitions, new product development and continuously exploring the new ways of monetization. The social media company employs more than 12600 people globally and in 2015 the company generated revenues of USD17.93 billion, which is an increase of 44% year-over-year and ad revenue was of USD17.08 billion, which is an increase of 49% compared to the previous year (Annual Report, 2015). Facebook has been successful in efficient capitalization on mobile advertising and its evolving role as a news source for increasing numbers of its users has positive implications on the long-term growth prospects of the business. At the same time, the social media company is not free of weaknesses and its major weaknesses include the dependence of revenues only on advertising, challenges in sustaining the growth rate of revenues and the dependence of the business on a few key personnel such as Mark Zuckerberg and Sheryl Sandberg. Facebook Inc. Report contains the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces, Value Chain analysis and McKinsey 7S Model on Facebook. Moreover, the report contains analyses of Facebook’s business strategy,…
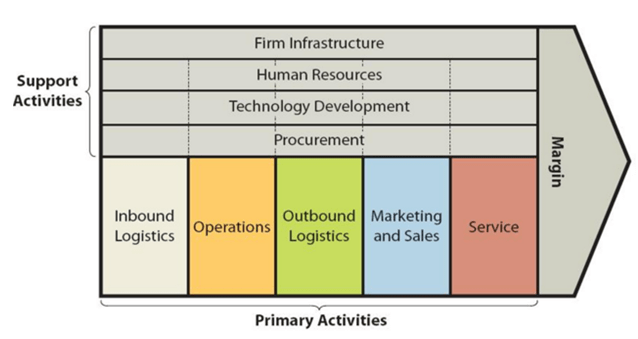
Value chain analysis is a strategic analytical tool that analyses the sources of value creation for businesses. Gap Inc. value chain analysis presented below critically analyses the most important primary and support activities that contribute to the competitive advantage of the apparel and accessories retailer. The figure below illustrates the essence of value chain analysis. Gap Inc. Value chain analysis Primary Activities Inbound logistics Gap Inc. inbound logistics involves purchasing from about 1,000 vendors that have factories in about 40 countries. During the fiscal year of 2015, approximately 99 percent of purchases, by dollar value, were from factories outside the United States, while the remaining 1 percent of all purchases were from domestic factories. Moreover, about 24 per cent of total purchases by dollar value during the same period were made from factories based in China.[1] Due to the massive purchase volumes, economies of scale can be specified as the main sources of value creation for Gap Inc. Moreover, the company benefits from strategic, long-term relationships with its suppliers. In 2016, the company embraced supplier transparency practices disclosing the list of factories that produce its clothes around the world.[2] Operations GAP Inc. business operations are conducted in two formats[3]: Gap Inc. has company-operated stores in the United States, Canada, the United Kingdom, France, Ireland, Japan, Italy, China, Hong Kong, Taiwan, and beginning in October 2015, Mexico. The company also has franchise agreements with unaffiliated franchisees to operate Gap, Banana Republic, and Old Navy stores throughout Asia, Australia, Europe, Latin America, the Middle East, and Africa. Gap Inc. has 3,721 company-operated and franchise store locations throughout the world. The company derives value in operations primary activities mainly through opening its stores in locations and shopping centers frequently attended by the representatives of the target customer segment. Outbound logistics Gap Inc.…

Gap Inc. is a global apparel retail company that owns Gap, Banana Republic, Old Navy, Athleta, and Intermix clothing, fashion and accessories brands. The first GAP store was opened in 1969 by Doris and Don Fisher and today Gap Inc. is the largest specialty apparel retailer in the North America with 3,721 company-operated and franchise store locations around the globe. The company has more than 140,000 employees worldwide (Annual Report, 2015) and its organizational structure can be characterized as hybrid integrating certain elements of divisional and hierarchical organizational structures. Gap Inc. uses cost leadership business strategy for all five brands within its portfolio offering fashion, apparel and accessories products for much cheaper prices compared to the prices of premium fashion brands. Apart from cost leadership, competitive advantages possessed by the company include a strong portfolio of distinct brands across multiple channels, a global presence of the brand and strategic relationships with its suppliers. At the same time, Gap Inc. has certain weaknesses such as declining sales and profits, failure to utilize online sales channels in an efficient manner, dependency on external manufacturers and others. The company has been struggling with declining sales and profits during the last two years. Net sales for fiscal 2015 decreased 4 percent to USD 15.8 billion compared with USD 16.4 billion for fiscal 2014. Gross profit for fiscal 2015 was USD 5.7 billion compared with USD 6.3 billion for fiscal 2014 (Annual Report, 2015). The range of initiatives introduced by CEO Art Peck to deal with this problem includes focusing on core products that contributed to the global success of the company, start selling on Amazon and engaging in international market expansion. Gap Inc. Report contains the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces, Value…

eBay Inc. is a US-based e-commerce company and global corporation that provides consumer-to-consumer and business-to-consumer online sales platform. Founded in 1995 by Pierre Omidyar, nowadays eBay employs nearly 12,000 people worldwide, including 6200 employees in the USA. More than 160 million people buy from eBay annually and the company generated the revenues of more than USD 8.6 billion in 2015 alone. eBay’s mission statement is ‘to be the world’s favourite destination for discovering great value and unique selection’. eBay business strategy focuses on benefiting from the first mover advantage via introducing innovative services and regularly adding new features and capabilities to existing services with the aim of enhancing user experience. The senior management led by CEO and President Devin Wenig has made a strategic decision to transfer the business from an online auction to become the largest online retailer, an area which is currently dominated by Amazon. The e-commerce company has certain weaknesses that include dependence of the business on a range of products and services controlled by competitors such as Google, an overall complexity of the business model and an absence of eBay’s own distribution network to compete with Amazon. eBay Inc. Report contains the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces, Value Chain analysis and McKinsey 7S Model on eBay. Moreover, the report contains analyses of eBay’s business strategy, leadership and organizational structure and its marketing strategy. The report also discusses the issues of corporate social responsibility. 1. Introduction 2. Business Strategy 3. Leadership 4. Organizational Structure 5. SWOT Analysis 5.1 Strengths 5.2 Weaknesses 5.3 Opportunities 5.4 Threats 6. PESTEL Analysis 6.1 Political Factors 6.2 Economic Factors 6.3 Social Factors 6.4 Technological Factors 6.5 Environmental Factors 6.6 Legal Factors 7. Marketing Strategy 7.1 7Ps of Marketing 7.2 Segmentation,…
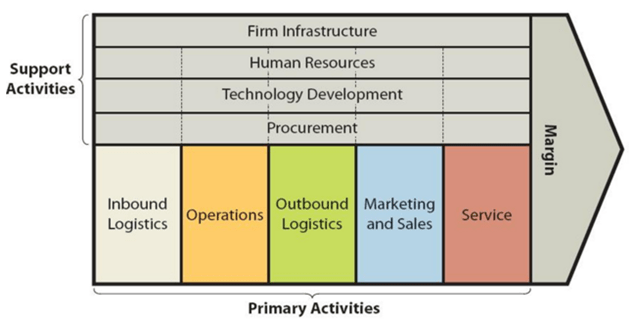
Hilton value chain analysis identifies business activities that can create value and competitive advantage to the business. The framework of value chain analysis divides business activities into two categories: primary and support activities. The figure below illustrates the essence of value chain analysis: Hilton Value Chain Analysis Primary Activities Inbound logistics Hilton inbound logistics represents a highly sophisticated system that ensures smooth operations in 572 hotels and resorts in 85 countries around the world.[1] Hilton’s “procurement group aggregates buying into national contracts for its various brands, and enables local providers where it makes sense to do so”[2] Hilton’s supply chain management and inbound logistics is unique in a way that the company makes deals directly with suppliers, then negotiates markups with the distributors that handle warehousing and delivery. This practice is an important source of value for the business since it enables the control of the whole supply chain. Operations Hilton Worldwide operates its business via the following three segments: Ownership segment. This segment consists of 146 hotels with 59,463 rooms which are owned or leased by Hilton Worldwide. Management and franchise segment consists of 4,419 hotels with 691,887 rooms. These are owned by third parties and managed by Hilton Worldwide. The company also licences its brand to franchises. As of December 2015, Hilton Worldwide franchised 3,875 hotels with 533,039 rooms. Timeshare segment consists of 45 properties comprising 7,152 units. This segment is engaged in marketing and selling timeshare intervals, operating timeshare resorts and timeshare membership clubs and providing consumer financing. Hilton operations are divided into four geographical segments: Americas Europe Middle East and Africa Asia Pacific The main sources of value in Hilton’s business operations include the highest level of standard of service, a high level of service personalization and integration of information and communication technologies into the various…

Hilton Hotels is a global flagship brand of Hilton Worldwide Holdings Inc.and it has 572 hotels and resorts in 85 countries and territories across six continents. Hilton Worldwide is the largest hotel company and the fastest growing hotel company in the world. Along with Hilton Hotels, a vast yet focused portfolio of Hilton Worldwide 13 brands in the premium hotels and resorts sector such as Waldorf Astoria, Conrad, Canopy, Curio, Double Tree, Embassy Suites and Hampton. Incorporated in 1919 by Conrad Hilton, currently, Hilton Worldwide owner base comprises 10,000 owners, of which 76% are repeat owners. The company has achieved Adj. ABITDA increase of 13 per cent in 2015 compared to the previous year. Importantly, the company converted 14,000 rooms from competitors’ brands and independent hotels during the same period. In 2015, the company earned the total revenues of about USD 11.2 billion, an increase of about 7 per cent compared to the previous year. In January 2016 Hilton Worldwide launched its latest brand Tru by Hilton which is intended to target mid-scale customer segment. Hilton Worldwide mission statement is formulated in the following manner: “To be the most hospitable company in the world – by creating heartfelt experiences for Guests, meaningful opportunities for Team Members, high value for Owners and a positive impact in our Communities.” Hilton business strategy can be described as service differentiation with a focus on quality, maintaining the highest level of standards and integrating IT systems into various aspects of service provision. The most noteworthy weaknesses associated with Hilton Worldwide include debts of more than USD 10 billion, overdependence on the US market and the lack of flexibility of the business due to its large size. Hilton Worldwide Holdings Inc. Report contains the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as…

Red Bull GmbH is a manufacturer of one of the most popular energy drinks Red Bull based in Austria. The company has been founded by Dietrich Mateschitz in the mid 1980’s and the first Red Bull Energy Drink was sold in Austria on April 1, 1987. Today, Red Bull beverages are sold in more than 169 countries and about 60 billion cans of Red Bull have been consumed so far. In 2015 alone, more than 5.9 billion cans were sold, which is an increase of 6.1 per cent compared to the previous year. In 2015, Red Bull GmbH revenues amounted to EUR 5.903 billion, a 15.5 per cent increase compared to the previous year. The company employs 10,997 people in 169 countries. Red Bull pursues product differentiation business strategy and the company differentiates its energy drinks according to its perceived positive effects in terms of enhancing physical and mental performance. Red Bull brand possesses solid competitive advantages in terms of the first mover advantage, high scope of brand recognition, an impressive level of profitability and effective marketing strategy. The marketing message of the brand ‘Red Bull gives you wings’ is effectively communicated to the target customer segment via multiple communication channels in an integrated manner. Along with its own media platforms, Red Bull owns a set of sports teams such as RB Leipzig, FC Red Bull Salzburg, Red Bull Brasil, New York Red Bulls, Red Bull Racing and Scuderia Toro Rosso. Despite the phenomenal success of the company, Red Bull has a set of weaknesses that include its overly expensive prices, limited range of products, portfolio of products that are rightly considered as unhealthy and concentrated production facilities. Red Bull GmbH Report contains the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five…
