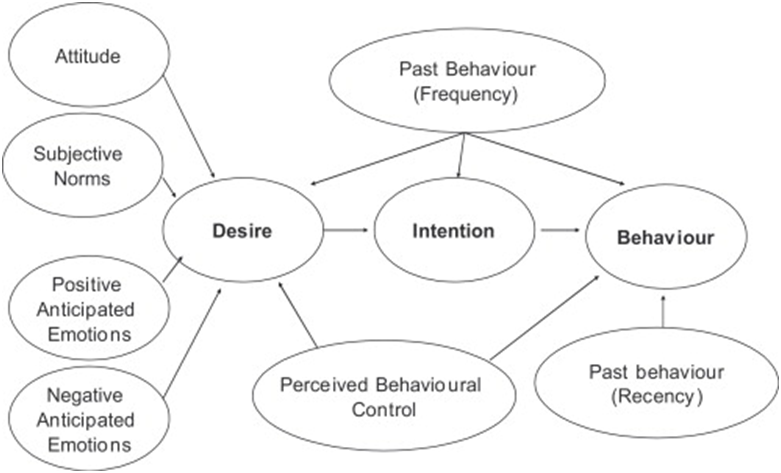
The Model of Goal Directed Behaviour
 The Model of Goal Directed Behaviour has been developed on the basis of the Theory of Planned Behaviour. This model “views the fundamental components of the theory of planned behaviour with respect to goals rather than behaviours” (Hagger and Chatzisarantis, 2009, p.36).
The Model of Goal Directed Behaviour has been developed on the basis of the Theory of Planned Behaviour. This model “views the fundamental components of the theory of planned behaviour with respect to goals rather than behaviours” (Hagger and Chatzisarantis, 2009, p.36).
Desire plays an integral role in The Model of Goal Directed Behaviour in a way that it is perceived to be stronger predictor compared to attitudes and subjective norms (Sutton, 1998). Explaining application of the model in practical levels Erasmus et al. (2001) explain that markets need to study primary desires of their target customer segment so that product and services can be developed to satisfy this desire or give the perception of satisfaction of the desire.
References
Erasmus, A. C., Boshoff, E. and Rousseau, G.G.(2001). “Consumer decision-making models within the discipline of consumer science: a critical approach”, Journal of Family Ecology and Consumer Sciences. 2001(29)
Hagger, M. & Chatzisarantis, N. (2007) “Social Psychology of Exercise and Sport” McGraw-Hill International
Sutton, S. (1998) “Predicting and explaining intentions and behaviour: how well we are doing? Journal of Applied Social Psychology, 28, pp. 1317-1318