Samsung Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
Porter’s Five Forces analytical framework developed by Michael Porter (1979)[1] represents five individual forces that shape the overall extent of competition in the industry. Samsung Porter’s Five Forces are represented in Figure 1 below:
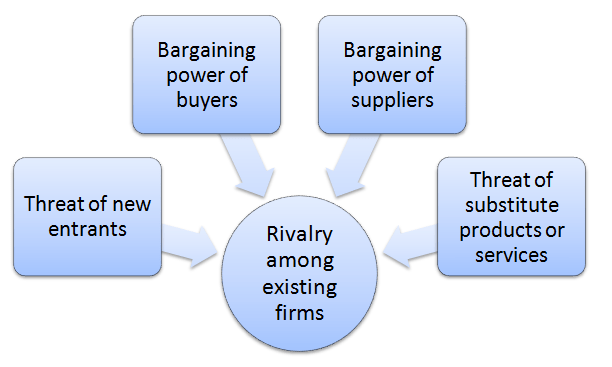
Figure 1 Samsung Porter’s Five Forces
Threat of substitute products or services for each product category offered by Samsung is substantial. Samsung smartphones can be substituted with ordinary mobile phones at any time with no additional costs for customers. Moreover, there is an increasing range of mobile and desktop applications that represent relevant substitute for Samsung’s mobile communications business.
Samsung visual display business is threatened by indirect substitution such as increasing popularity of leading active lifestyle and spending time outdoor. In other words, representatives of Samsung target customer segment may prefer to spend time outdoors, rather than in front of TV with negative implications on the volume of sales of Samsung TV’s. Furthermore, increasing popularity of cloud storage is emerging as viable alternative for printing and this tendency may decrease the sales of Samsung printing solutions products in the foreseeable future.
Rivalry among existing firms is intense. Approaching market saturation for many product categories in consumer electronics industry intensifies the rivalry among existing firms and there is a little differentiation among the range of products offered. Moreover, the great number and diversity of competitors operating in the market fuels the extent of competition in the industry.
In smartphone market segment, one of its critical product categories, Samsung competes with a wide range of suppliers such as Apple, LG, Lenovo, ZTE, Huawei, OPPO and others. Nevertheless, as it is illustrated in Figure 2 below, Samsung has been able to maintain leadership position in the global scale for the last six years.
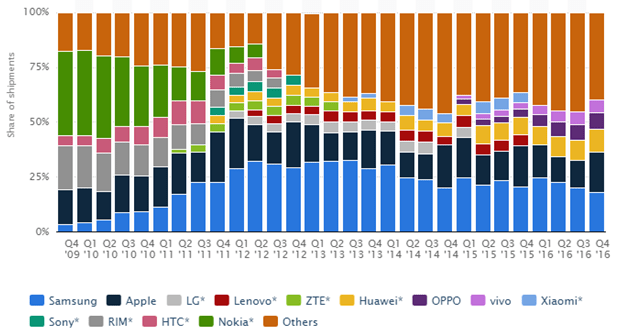
Figure 2 Global market share by leading smartphone manufacturers[2]
Bargaining power of suppliers working with Samsung depends on the specific type of supplier. Samsung has 579 suppliers globally and the company’s supply chain includes over 2,700 suppliers in various industries across the world.[3] Businesses supplying general parts and components do not yield substantial bargaining power due to the importance of Samsung’s order volume and its ability to negotiate prices. However, one particular supplier, Google exercises an immense bargaining power as the supplier of Android platform due to the lack of alternative platforms available to Samsung.
Samsung Electronics duly recognizes the importance of developing strategic cooperation with suppliers and about 71,4% of total economic value was shared with suppliers in 2015.[4] Moreover, Samsung maintains an extensive communication with its suppliers within the scope of various programs and initiatives such as Shared Growth Day, Supplier Dialogue Fair, Hot Line and informal meetings with suppliers.
Samsung Group Report contains a full analysis of Samsung Porter’s Five Forces Analysis. The report illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Value Chain analysis and McKinsey 7S Model on Samsung. Moreover, the report contains analyses of Samsung leadership, business strategy, organizational structure and organizational culture. The report also comprises discussions of Samsung marketing strategy and addresses issues of corporate social responsibility.
[1] Porter, M. (1979) “How Competitive Forces Shape Strategy” Harvard Business Review
[2] Statista (2017) Available at: https://www.statista.com/statistics/271496/global-market-share-held-by-smartphone-vendors-since-4th-quarter-2009/
[3] Samsung Sustainability Report (2016) Samsung Electronics
[4] Samsung Sustainability Report (2016) Samsung Electronics

