Management

McDonald’s leadership team is headed by the President and CEO, who is aided by nine senior managers, each overseeing a specific aspect of the business. [1] The previous President and CEO Mr. Steve Easterbrook took the helm in 2015 and he was widely considered as an effective leader until he was fired for having consent sexual relationships with subordinate employees. During his leadership tenure Mr. Easterbrook was credited with turning around the company and reviving its falling stock price. Most prominent changes introduced by Easterbrook include reducing costs, introducing touch-screen ordering and establishing all-day breakfast. The new President and CEO Chris Kempczinski has also proved to be effective business leader. Under the new leadership McDonald’s has emerged as a clear winner during the pandemic. Mr. Kempczinski has channelled his energy and focus on digital, drive thru and delivery to adjust the business model to the pandemic environment. McDonald’s leadership is currently faced with a serious challenge. In recent years the fast food chain has faced many lawsuits and claims involving sexual harassment and racial discrimination. The former President and CEO Mr. Easterbrook being found violating company code of conduct is the evidence of severity of the issue. One of the important tasks for the new leader Mr. Kempczinski is to create a corporate culture where sexual harassment and racial discrimination is not tolerated in practice. McDonald’s Corporation Report contains the above analysis of McDonald’s leadership. The report illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces, Value Chain analysis, Ansoff Matrix and McKinsey 7S Model on McDonald’s. Moreover, the report contains analyses of McDonald’s business strategy, organizational structure and organizational culture. The report also comprises discussions of McDonald’s marketing strategy, ecosystem and addresses issues of corporate social responsibility. [1] Annual Report…
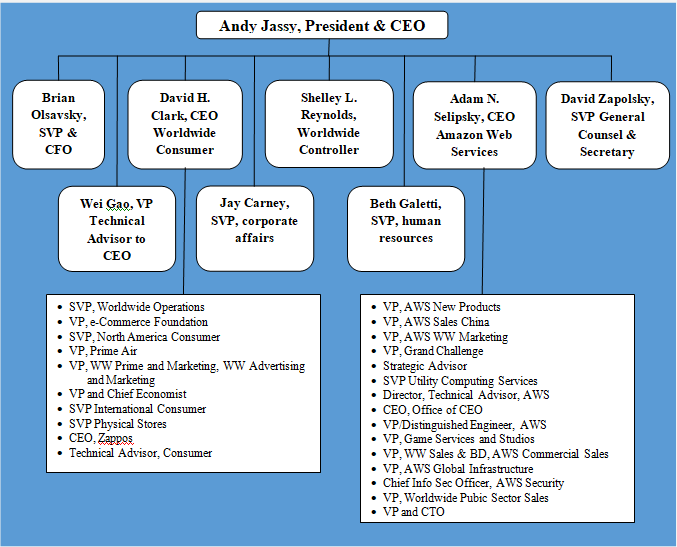
Amazon organizational structure can be classified as hierarchical. Senior management team include three CEOs and three senior vice presidents responsible for various vital aspects of the business reporting directly to CEO Andy Jassy. Amazon organizational structure has the following four key features: 1. Hierarchical corporate structure. Hierarchical structure at Amazon has developed due to the immense size of the business. The largest internet retailer in the world by revenue employs more than 1,3 million people worldwide.[1] 2. Hybrid project groups. Amazon corporate structure integrates hybrid project groups when developing new products and services. Specialists from various departments are attracted according to their skills and competencies required for the project. These employees can be attracted part-time reporting to both, the head of their departments and project leaders, or they can engage in the project full-time reporting to project manager only for the duration of the project. 3. Flexibility of the business. It is important to note that despite its large size, unlike many other companies with hierarchical organizational structure, Amazon remains highly flexible to adapt to frequent changes in the external marketplace. Moreover, the online retail giant leads changes in external business environment; it has caused disruptive innovation in e-commerce and currently it is about to cause a disruptive innovation in global logistics industry. Successful organization of hybrid project groups plays an instrumental role in maintaining flexibility of the business. Amazon organizational structure integrates many small teams that deal with various aspects of the business. Amazon founder and former CEO Jeff Bezos is credited with the introduction of ‘two pizza rule”. According to this rule, meetings should be held in teams small enough that could be all fed with only two pizzas. “Two pizza rule” continues to this day under the new CEO Andy Jassy. 4. Stability in the top management.…
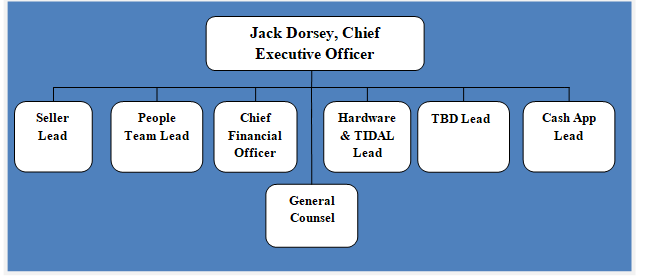
Square Inc. organizational structure can be classified as relatively flat, taking into account ever-growing size of the business. Co-founder and CEO Jack Dorsey attempts to maintain a start-up environment and culture and reduce bureaucracy in order to keep the business flexible to be able to respond to changes in the external environment. Therefore, it can be argued that Square organizational structure is designed to increase the speed of decision-making. Leads of units operate as a CEOs and they report only to Jack Dorsey. Leads oversee project leaders and project teams at Square are small groups comprising maximum 12 people of diverse backgrounds. As illustrated in figure below, Square’s cryptocurrency business unit TDB is a division separate from both, seller and cash units. One of the reasons for this separation may relate to regulatory reasons. Specifically, maintaining crypto separate from other units decreases the chances of regulatory interferences. Square organizational structure The company is increasing the range of products and services extensively. This strategy can increase complexity of the business with direct implications on Square organisational structure, despite CEOs attempts to maintain it simple. Accordingly, the senior management of the financial services platform has a challenging task of maintaining flexibility of the business amidst its exponential growth. Moreover, there are opinions among industry analysts that CEO Jack Dorsey’s ultimate plan is to make Square a holding company for autonomous fintech businesses[1]. A Tweet by Dorsey on July 2021 claiming that the payments company will create a new business line to help developers build financial services products focused on Bitcoin can be seen as a signal to support such as viewpoint. Square Inc. Report contains the above analysis of Square organizational structure. The report illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five…
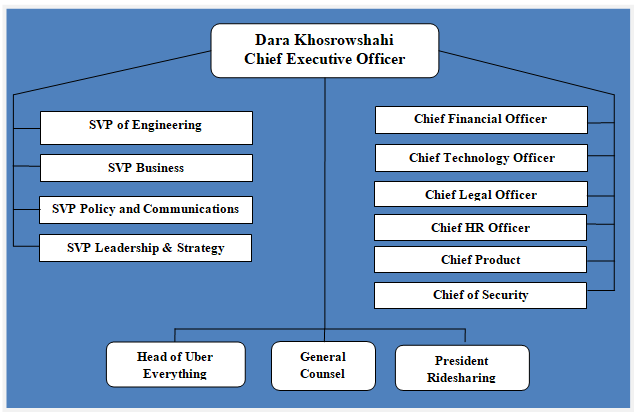
Uber organizational structure has been traditionally highly hierarchical with co-founder and former CEO Travis Kalanick yielding tremendous power and micromanaging the ride-hailing giant. Lack of Kalanick’s leadership skills resulted in a series of scandals involving bullying, discrimination at workplace, sexual harassment etc. Kalanick had to resign as a result of these scandals. After Dara Khosrowshahi became new CEO in 2017, Uber organizational structure has been subjected to certain changes.[1] Figure below illustrates Uber organizational structure: Uber Organizational Structure It can be argued that the current pattern of Uber’s organizational structure illustrated in Figure 1 above can be subjected to more changes by new CEO Dara Khosrowshahi in the medium-term perspective. Demoralized workforce and poor organizational culture belong to the list of major issues for the global transportation technology company. Dara Khosrowshahi is credited for creating collaborative work culture at Expedia where employees are encouraged to propose their ideas to management. Mr. Khosrowshahi is attempting to fix Uber organizational culture as part of his grand plans to turnaround the business. Accordingly, improvement in organizational culture may necessitate changes in organizational structure. Specifically, de-layering of organizational structure may be introduced, removing certain levels of management in order to make the business more flexible to respond to the changes in external marketplace. Moreover, advantages of flat organizational structure include faster speed of communication between the top management and floor-level employees. Senior leadership reorganization initiated by CEO Dara Khosrowshahi due to failed IPO in 2019 the roles of chief operating officer (COO) and chief marketing officer (CMO) were eliminated. Specifically, COO role was replaced by two executives who manage biggest businesses – ride-haling and food delivery. These two executives directly report to Khosrowshahi. Uber marketing operations, on the other hand, were combined with communications and policy departments. The rationale behind this specific change was…
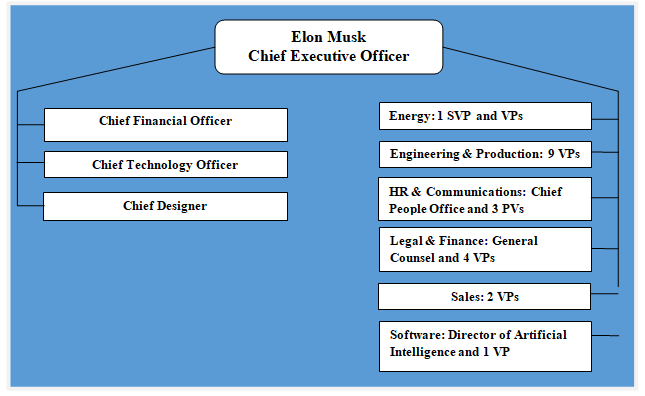
Tesla is a unique company in many ways and this uniqueness also extends to its organizational culture. Tesla organizational structure integrates the following: 1. Unique organizational structure. “Tesla, unlike most companies its size, doesn’t have any known management structure. There’s no organizational chart or public list of senior leaders.”[1] Nevertheless, Tesla organizational structure can be characterized as divisional. 2. Tesla CEO Elon Musk has issues with delegation. Workaholic and micromanagement nature of Elon Musk, as well as his sleep deprivation work habits have become well-known. Famous author and businesswoman Arianna Huffington even wrote an open letter to Musk urging him to get more sleep and learn to delegate. Musk’s issues with delegation has implications on Tesla corporate structure in a way that he has more people directly reporting to him than any other CEO in auto industry. 3. Divisional and flexible structure. Although it is difficult to list Tesla organizational structure under a specific rigid category due to its unique nature, the structure can be characterised as divisional and flexible. As it is illustrated in figure below, Tesla organizational structure comprises a number of divisions such as energy, engineering and production, HR and communications, legal and finance, sales and software. Each division is led by several vice presidents, except software division, which is led by one vice president and Director of Artificial Intelligence. Tesla Organizational Structure Tesla benefits from divisional organizational structure through less bureaucracy compared to many other companies of similar sizes. Divisional organizational structure also helps the electric automaker to increase the speed of communication among different layers of management with positive implications on decision making and flexibility of the business. Tesla Inc. Report contains the above analysis of Tesla organizational structure. The report illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as…
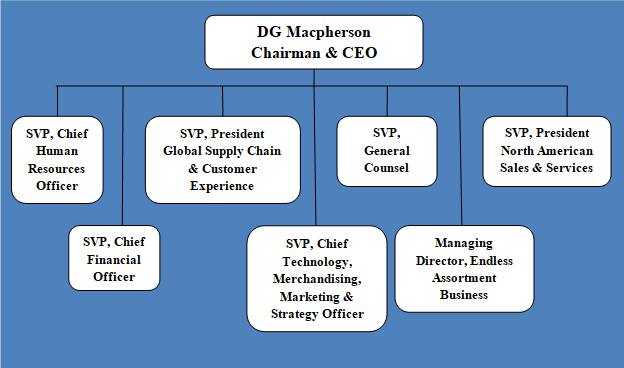
W.W. Grainger organizational structure can be classified as hierarchical. The decision making power is concentrated on the hands of Chairman and CEO DG Macpherson. The global industrial supply company maintains hierarchical type of organizational structure due to the massive size of the company that comprises about 2500 employees working in 457 branches, 31 distribution centres and offices worldwide.[1] Grainger organizational structure was subjected to major changes in 2013 “to provide greater focus and a more consistent integrated approach to pursue growth opportunities”[2]. Specifically, the B2B distributor established Americas business to include Canada, the U.S., Mexico, Panama, Puerto Rico, Dominican Republic, Costa Rica, Colombia and Peru. The figure below illustrates the top layer of Grainger organizational structure. Grainger Organizational Structure Hierarchical nature of Grainger corporate structure provides the worldwide distributor of industrial products a set of advantages. Specifically, the current pattern of Grainger corporate structure has a clear line of leadership, authority and responsibility. Moreover, hierarchical organizational structure is associated with employees having a narrow field of focus and accordingly, there is a potential for employees to become highly qualified experts in their fields. At the same time, hierarchical organizational structure is also linked to certain shortcomings that can have detrimental effects on Industrial products distributor’s long-term growth prospects. In hierarchical companies there is a risk of rivalry between different departments with negative implications for the overall profitability of the business. Moreover, centralization of power and authority at the highest level in hierarchical organizational structures may leave little room for initiatives for floor-level and medium level employees to adopt a creative and innovative approach to deal with various business processes. W.W. Grainger Report contains the above analysis of W.W. Grainger organizational structure. The report illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces, Value Chain analysis, Ansoff Matrix and…
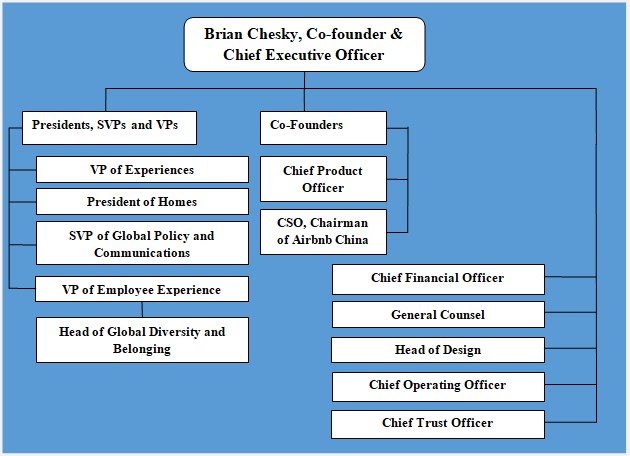
Since its founding in 2008, Airbnb organizational structure has been subjected to changes a number of times to adapt to the growth of the business in at a rapid pace. Furthermore, diversification of the business beyond home rentals to include experiences, adventures and restaurant services necessitated massive changes in its organizational structure. One of the main features of an effective organizational structure is to ensure a rapid flow of information across the company. In order to achieve this, Airbnb CEO Brian Chesky turned to executives from Apple, Facebook, Google and Amazon for advice on how to better organize the company.[1] The latest corporate restructuring at the peer-to-peer lodging company gave more decision making powers to its new business development teams. Holacracy is another important feature of Airbnb organizational structure. Holacracy can be explained as a type of organizational structure where “power is distributed throughout the organization, giving individuals and teams more freedom to self-manage, while staying aligned to the organization’s purpose.”[2] Airbnb organizational structure can be also branded as inter-supportive matrix structure. Airbnb corporate structure integrates many small teams of up to 10 people. The global rental and experiences company promotes the principle of village ecosystem in relationships between its teams. Specifically, if team members need a capability or resource, they can ask other team that has it ask them to share or cooperate. In other words, rather than operating as a separate identities, individual groups within the global lodging company cooperate and support each-other to a great extent and this feature can be specified as one of the main advantages of Airbnb corporate structure. Airbnb Organizational Structure Airbnb Inc. Report contains a full analysis of Airbnb organizational structure. The report illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five…
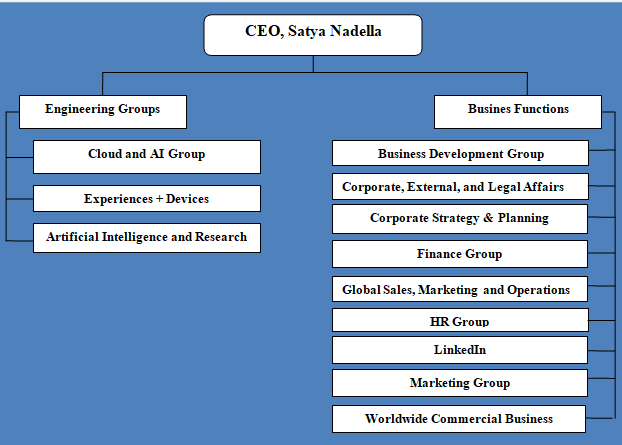
Microsoft organizational structure can be classified as divisional. In June 2015, the senior management announced a change in Microsoft organizational structure to align to its strategic direction as a productivity and platform company. This restructuring initiative resulted in elimination of approximately 7,400 positions in fiscal year 2016.[1] The current divisional pattern of Microsoft organizational structure is the result of this restructuring initiative. As it is illustrated in figure below, Microsoft organizational structure is divided into divisions according to engineering groups and business functions. Specifically, on the basis of engineering groups, the company is divided into three divisions, whereas according to business functions it is divided into 9 divisions: Microsoft Organizational Structure The latest restructuring of Microsoft organizational structure and shift to divisional organizational structure offers the following advantages to the business: Firstly, under the new organizational structure, heads of engineering groups directly report to CEO Satya Nadella with positive implications on new product development initiatives and innovation potential. This is particularly important to be able to introduce new products and services to the marketplace in the short duration of time. Moreover, a clear distinction between engineering groups and business functions, as illustrated in figure above, is an indication of the technology giant ‘s focus on business directions under engineering groups such as cloud and artificial intelligence. Secondly, organizational restructuring eliminates bureaucracy in business processes and procedures to a great extent, increasing the flexibility of the business to adapt to changes in the external marketplace. Thirdly, the initiative resulted in the elimination of approximately 7,400 positions, thus saving considerable amount of financial resources that can be channelled for new product development and increasing the competiveness of the business in many other ways. Another important aspect of corporate culture at Microsoft refers to a high level of dynamism. Specifically, the CEO of…
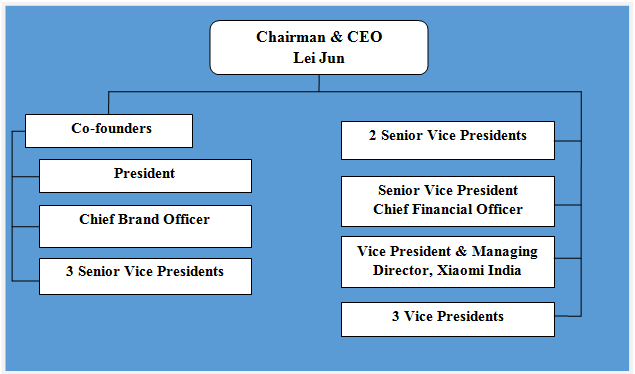
Xiaomi organizational structure can be classified as matrix. Specifically, Xiaomi organizational structure is decentralized, where different business units are managed independently. Despite the large size of the business involving presence in 70 countries with more than 18000 employees, the company has less layers of management compared to other businesses of similar sizes. Figure below illustrates Xiaomi organizational structure: Xiaomi organizational structure Matrix organizational structure allows the mobile internet company to develop its new products and services in a short duration of time. This is due to absence of bureaucracy that is associated with hierarchical organizational structures. However, disadvantages of matrix organizational structure for the business may include lack of strict control by the top management over separate business units and lack of integration between the operations of individual business units. Nevertheless, it is important for Xiaomi to maintain its flat organizational structure in order to remain flexible, so that the mobile internet company can adapt to frequent changes in the global marketplace. Xiaomi Inc. Report contains a full analysis of Xiaomi organizational structure. The report illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces, Value Chain analysis, Ansoff Matrix and McKinsey 7S Model on Xiaomi. Moreover, the report contains analyses of Xiaomi leadership, business strategy and organizational culture. The report also comprises discussions of Xiaomi marketing strategy, ecosystem and addresses issues of corporate social responsibility.
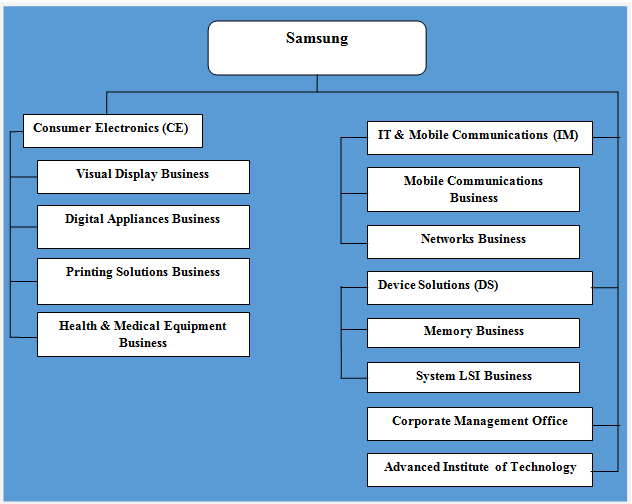
Samsung organizational structure is divisional and the company is divided into three key divisions: IT & Mobile Communications (IM), Consumer Electronics (CE), and Device Solutions (DS). The rationale behind the choice of divisional organizational structure relates to Samsung’s large product portfolio and differences between products and services the company offers to the market. Accordingly, Samsung’s each division is managed separately taking into account the characteristics of their products that have implications on new product development, marketing, selling and other aspects of the business. Moreover, Samsung Electronics has more than 200 subsidiaries around the world. Figure below illustrates Samsung organizational structure: Samsung organizational structure As it is illustrated in figure above, apart from three divisions, Samsung organizational structure also integrates corporate management office and Samsung Advanced Institute of Technology (SAIT). Corporate management office deals with overall management of the group and also has administrative responsibilities. SAIT is Samsung Group’s R&D hub, established as the incubator for the development of new products and services. The senior management completed its review of optimal organizational structure on April 2017 and decided not to convert to a holding company structure.[1] Following a series of recent scandals involving Samsung management that culminated in Jay Y. Lee, the former de facto head of the Samsung conglomerate being jailed for 5 years[2], it can be argued that Samsung organizational structure will change in the foreseeable future. Specifically, Samsung organizational structure may change to make governance and decision making practices more transparent to eliminate or at least to reduce the cases of future scandals. Samsung Group Report contains a full analysis of Samsung organizational structure. The report illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces, Value Chain analysis and McKinsey 7S Model on Samsung. Moreover, the report contains analyses…
