Service Quality Model
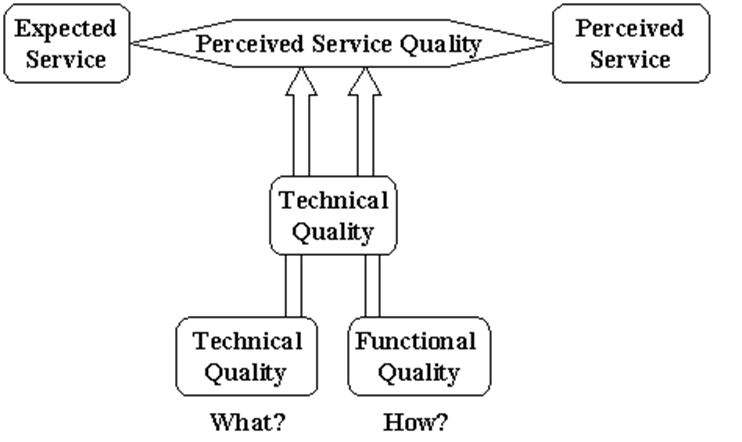
Service Quality Model pioneered by Gronroos (1982) states that customer’s perception of quality, and ultimately customer satisfaction depends on customer’s perception of two dimensions of the service: technical quality and functional quality.
Technical quality dimension of the service concentrates on what the customer receives, focusing on the technical outcome of the process. Functional quality, on the other hand, concentrates on how the consumer receives the technical outcome.
A service concept is explained by Johnston and Calrk (2008, p.42), as a shared understanding of the service nature provided and received, which should encapsulate information about:
– The organizing idea, which is the essence
– The experience.
– The outcome.
Lancaster et al (2002, p. 75) inform that consumer buyer behaviour is influenced by a range of environmental and individual factors. Environmental influencers include cultural, social class, groups/family, situational factors and marketing efforts, and individual influencers include psychological aspects, lifestyle, demographics and economic situation.
References
- Johnson, R & Clark, G, 2008, “Service Operations Management”, third edition, Prentice Hall
- Lancaster, G, Massingham, L & Ashford, R, 2002, “Essentials of Marketing”, fourth edition, McGraw-Hill