Search results for: Mckinsey 7s

Walmart marketing budget equaled to USD2.4 billion for both fiscal 2015 and fiscal 2014 and USD2.3 billion for the fiscal year of 2013[1]. These funds are invested in Walmart marketing communication mix that include print and media advertisements, viral marketing, sales promotions, events and experiences, public relations and direct marketing components of the marketing communication mix. Advertising Traditionally, print and media advertising has represented the core of Walmart marketing strategy for many years. However, in 2015, Walmart Vice President Wanda Young announced planned shift of the main focus from the print advertising to the mobile marketing campaigns.[2] Such a change in Walmart marketing strategy is expected to target young people in general and Millenials in particular. Viral marketing is another direction that is being extensively utilized by Walmart with varying levels of success. For example, Walmart marketing video ‘Work is a Beautiful Thing: Meet Patrick’ released in 2014 has attracted more than 1.2 million views in just six days with thousands of positive comments and with evident positive implications on the brand image.[3] Nevertheless, Walmart still uses print and media advertising to a considerable extent and the company places advertisements on newspapers, magazines and TV channels popular with the target customer segment. Sales Promotion Sales promotion is used by Walmart in an extensive manner. The retailer launches seasonal sales promotions in a regular manner along with sales promotions in before and during public holidays and other memorable days. Particularly, Black Friday is a massive sales promotion day for Walmart each year eagerly anticipated by millions of customers. Walmart maintains Daily Savings Center section in its official website where online and offline sales promotion offers are announced. Sales promotion also has been adapted as an effective tool to increase the sales of Sam’s Club segment of the business. Specifically, the emphasis of…
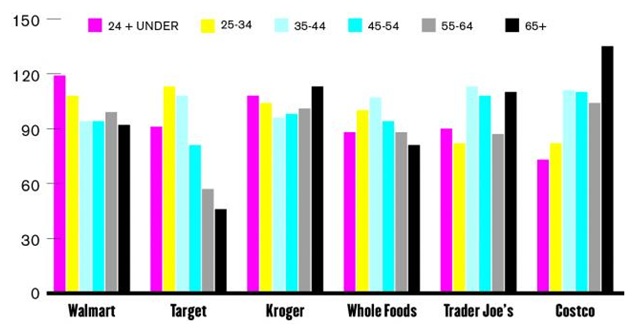
Walmart segmentation, targeting and positioning is the core focus of Walmart strategic marketing. Segmentation refers to dividing population into groups according to certain characteristics, whereas targeting is associated with choosing specific groups identified as a result of segmentation to sell products. Positioning refers to the selection of the marketing mix the most suitable for the target customer segment. Walmart uses mono-segment type of positioning and accordingly, Walmart marketing management appeals to single customer segment who place greater value on the price attribute of products compared to other attributes. The following table illustrates Walmart segmentation, targeting and positioning: Type of segmentation Segmentation criteria Walmart target segment Geographic Region Domestic and international Density Urban and rural areas Demographic Age Individuals of all age categories Gender Males and Females Life-cycle stage Bachelor Stage young, single people not living at home Newly Married Couples young, no children Full Nest I youngest child under six Full Nest II youngest child six or over Full Nest III older married couples with dependent children Empty Nest I older married couples, no children living with them Empty Nest II older married couples, retired, no children living at home Solitary Survivor I in labor force Solitary Survivor II retired Income Individuals and households with low incomes and middle class Occupation Students, manual workers, floor level employees and middle level managers in public and private sectors Behavioral Degree of loyalty ‘Hard core loyals’, i.e. individuals who always purchase the product / brand in question. ‘Switchers’, i.e.individuals who do not specifically seek out a particular brand, but rather purchase the brand available to them at time of need, or that which was on sale Benefits sought Cost advantage Personality Reserved and cost-conscious individuals User status non-users, potential users, first-time users, regular users, or ex-users of a product Psychographic Social class Lower class, working and middle class Lifestyle Resigned,…

Walmart 7Ps of marketing comprises elements of the marketing mix that consists of product, place, price, promotion, process, people and physical evidence. Product. Walmart sells a wide range of products belonging to the following categories: groceries entertainment health and wellness – including pharmacy hardlines – including stationery, auto spares, and accessories hardware apparel home furnishings household appliances Despite the low prices, Walmart attempts to position its products as quality and this message is integrated into company’s marketing strategy. For example, in China Walmart utilizes “Worry Free Fresh” program to provide a money-back guarantee if its produce and meats don’t meetcustomer expectations. Wallmart.com offers about 8 million items in the US[1] and it is duly considered to be one of the largest online stores in the world. Place. With more than 11,000 stores, websites and mobile apps, customers can access Walmart via multiple channels.[2]During the fiscal year of 2016, Walmart is planned to expand by approximately 15 to 16 million total net retail square feet, representing between 240 and 270 units[3]. Walmart stores are operated in the following four formats: Walmart discount stores Walmart express stores Walmart super centers Walmart neighborhood markets Walmart has launched its dedicated e-commerce websites in 11 countries and the proportion of online sales compared to the traditional offline sales has been consistently increasing for the past 10 years. Price. Walmart has based its competitive advantage on cost leadership. Accordingly, the retailer aims to offer the lowest price possible according to its motto ‘everyday low prices’. Walmart Price Match Policy formulated on its website states the following: “We’re committed to providing low prices every day, on everything. So if you find a lower price from an online retailer on an identical, in-stock product, or the item purchased from Walmart.com is now listed at a lower price, tell us and…
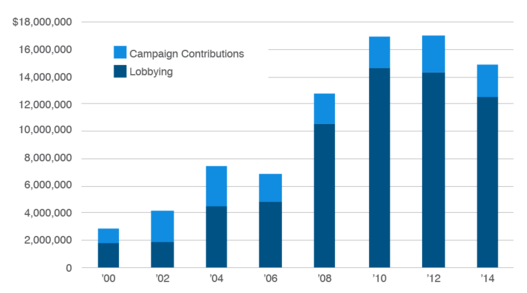
PESTEL is a strategic analytical tool and the acronym stands for political, economic, social, technological, environmental and legal factors. Walmart PESTEL analysis involves the analysis of potential impact of these factors on the bottom line and long-term growth prospects. Political Factors Because of its massive size and significance for the US economy, Walmart has been observed to interfere with politics a number of times. The primary reasons for Walmart’s political interferences via lobbying and other means have been an attempt to gain positive political impact on the business. In 2013 Walmart has been caught convincing employees to make political contributions to republicans to support pro-business conservatives like Cruz and Boehner[1]. Walmart has been ranked among the top 100 political donors overall for the period since 1989[2]. As it is illustrated in Figure 5 below, Walmart political spending has vastly increased during the past one and half decade and these funds have been used to influence corporate tax and labour legislations to a certain extent.[3] Changes in Walmart’s political spending[4] Apart from campaign contributions and lobbying activities, Walmart has attempted to interfere directly in certain political debates a number of times. In one notable case, Walmart voiced its opposition to religious freedom law in its home state of Arkansas in 2015. Arguing that religious freedom laws would open the door to discrimination against gay and lesbian customers, Walmart emerged victorious and Republican Gov. Asa Hutchinson refused to sign the legislation.[5] Additionally, Walmart is impacted by a wide range of political factors such as political stability in places where the company operates, market lobbying protectionism policies in international markets, the freedom of press, extent of corruption and others. Economic Factors Walmart revenues and profits are impacted by a range of external economic factors either, directly or indirectly. For example, currency exchange rate…
SWOT is an acronym for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats related to organizations. The following table illustrates Walmart SWOT analysis: Strengths 1. Efficient utilization of online sales channels 2. Huge financial resources 3. Leadership position in the US 4. Sophisticated supply chain operations 5. High brand value Weaknesses 1. Low profit margin 2. Brand image damaged by a series of scandals 3. Lack of flexibility due to its large size 4. Business model easy to replicate Opportunities 1. Further international market expansion 2. Formation of strategic alliances 3. Vitalizing CSR programs and initiatives 4. Exploring diversification opportunities Threats 1. Failure to sustain cost advantage 2. Eruption of quality-related or ethics-related scandals 3. Negative impact to revenues from currency fluctuations 4. Risk of a new global economic crisis Walmart SWOT Analysis Strengths 1. Walmart has an impressive online presence. There are 11 countries with a dedicated Walmart e-commerce websites and the total e-commerce sales increased by 22 per cent in 2015, and about 75 percent of walmart.com sales come from non-store inventory[1]. Moreover, in Brazil, Walmart’s online assortment, including from marketplace partners grew 10 times and in China, Yihaodian saw traffic increase more than 60 percent in 2015[2]. Such a solid presence in online platform and an efficient utilization of online sale channel is a significant strengths that immensely contributes to Walmart’s core competitive advantage of cost leadership. 2. Walmart’s consolidated revenues during the fiscal year of 2015 equaled to USD 486 billion and free cash flow of more than USD 16 billion was generated during the same period[3]. This amount is more than the revenues of the following four companies combined—Costco, Kroger, Tesco in the United Kingdom, and Carrefour SA in France. Walmart’ AA credit rating, which is rare in retail further contributes to the financial strengths of the company. In other…
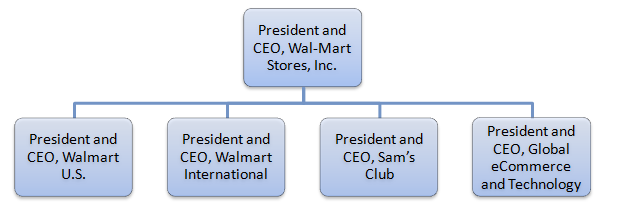
Traditionally, Walmart leadership attempts to integrate the values of its founder Sam Walton into the organizational culture in order to improve employee morale with positive implications on the bottom line. In 1988 the roles of Chairman and CEO were separated and today these roles are performed by Gregory B. Penner and Doug McMillion respectively. Doug McMillion has assumed Walmart leadership position in February 2014 and a range of initiatives introduce by the new CEO include enhancing the priority for customer services via employee training and development and increasing wages of floor-level employees and focusing on improving nutritional aspects of foods. Walmart leadership academy, instituted in 2009 aims to accelerate the preparedness of leaders and is modelled after the Royal Military Academy Sandhurst[1] Walmartorganizational structure is highly hierarchical due to the massive size of the company. In other words, the company employs about 2.2 million people globally[2] and therefore, there is no alternative organizational structure for Walmart to ensure effective management of such a large number of employees.The Board of Directors consists 16 members and it includes two members of Walton family, as well as, young, but proven business executives such as Kevin Systrom, CEO and Co-Founder, Instagram and Marissa A. MayerPresident and CEO of Yahoo!, Inc. Walmart organizational structure at the very top executive has a pattern as illustrated in Figure 1 below: One step down the hierarchy form the above, Walmart executive team comprises 29 senior managers for the following roles: Executive Vice President and Treasurer Executive Vice President, Softlines and General Merchandise, Walmart U.S. Executive Vice President, Corporate Affairs Chief Operating Officer, Global eCommerce Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer Chief Merchandising Officer, Walmart U.S. Executive Vice President, Global People Division Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer, Walmart U.S. Executive Vice President, Chief Administrative Officer Executive…

Walmart business strategy is based on ‘everyday low prices’ philosophy of the company. In other words, Walmart pursues cost leadership business strategy enabled by the economies of scale derived by the company in a significant extent. An efficient utilization of online sales channel contributes to the level of cost-efficiency of retail operations and about 75 percent of walmart.com sales come from non-store inventory[1]. Constant improvements of assortment, price and access are basis of Walmart business strategy. In simple terms, Walmart strives to offer the widest choice of products for the cheapest price, along with giving customers the opportunity of choosing the most convenient channel to facilitate the purchase. Wall Mart competitive advantage relies on cost leadership. Moreover, the strategic level management consistently aim to associate Wall Mart competitive advantage with price, access, assortment and experience. Since his appointment as CEO in February 2014, Doug McMillion introduced important changes in Walmart business strategy in the following three directions:[2] Increasing focus on customer services. In February 2015, the company announced a USD1 billion investment in U.S. hourly associates to provide higher wages, more training and increased opportunities to build a career with Walmart.[3] Improving groceries. Due to increasing level of health-consciousness of consumers, Walmart is attempting to increase its range of organic options and fresh produce. This change is more evident in the US market and it is being actively integrated into marketing communication message of the brand. Enhancing the flexibility of the shopping experience. It has been noted that “Wal-Mart is working to integrate its physical stores with the digital business”[4]. For example, thanks to the latest changes, customers are able to collect their online orders from stores and they can also get text reminders from the pharmacy. Generally, Walmart competitive advantage can be sustained in the global marketplace in long-term…

Walmart Stores Inc. is a US-based global discount supermarket chain that has more than 11,000 stores in 27 countries and serves nearly 260 million customers each week under 72 banners (Annual Report, 2015). Founded in 1962 by Sam Walton, today Walmart employs 2.2 million people globally and it is the world’s largest retailer. Walmart U.S. delivered net sales of USD 288 billion, a more than 3 percent increase in the fiscal year of 2015 and consolidated fiscal revenues equaled to USD 486 billion (Annual Report, 2015). During the fiscal year of 2015 Walmart revenues grew by more than USD9 billion to nearly USD 486 billion and earnings per share were USD 4.99, a nearly 3 percent increase from the previous year . On a constant currency basis, net sales surpassed USD 141 billion, while operating income increased to more than USD6 billion (Annual Report, 2015). ‘Everyday low prices’ is Walmart’s marketing communication message and this message serves as a guiding principle for Walmart business strategy. Specifically, Walmart strives to achieve cost leadership by the use of economies of scale to a great extent, exercising its huge bargaining power in dealing with suppliers and paying low wages to employees. Walmart Report contains the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces, Value Chain analysis and McKinsey 7S Model on Walmart. Moreover, the report contains analyses of Walmart’s business strategy, leadership and organizational structure and its marketing strategy. The report also discusses the issues of corporate social responsibility. 1. Introduction 2. Business Strategy 3. Leadership and Organizational Structure 4. SWOT Analysis 4.1 Strengths 4.2 Weaknesses 4.3 Opportunities 4.4 Threats 5. PESTEL Analysis 5.1 Political Factors 5.2 Economic Factors 5.3 Social Factors 5.4 Technological Factors 5.5 Environmental Factors 5.6 Legal Factors 6. Marketing Strategy…
Strategy is “means to ends, and these ends concern the purpose and objectives of the organization”[1]. Strategy is “used in business to describe how an organization is going to achieve its objectives”[2]. It has been noted that “strategy is about marshalling the gross resources of the organization to match the needs of the marketplace and achieve the business objective, this cannot be a short-term activity”[3]. In simple terms, business strategy “consists of what management decides about the future direction and scope of the business”[4]. There is a wide range of strategic analytical tools, models and frameworks that can assist with the various aspects of development and implementation of business strategy. These include the following: Gaps Model of Service Quality Greenfield investment McKinsey 7s Model New market entry strategies PESTEL analysis Porter’s Five Forces analysis Strategy as Revolution SWOT analysis “Think Globally, Act Locally”: a critical analysis Value chain analysis Some of the above (hyperlinked) are explained in this portal. The list above is going to be regularly expanded to include in-depth explanation of the most important strategic analytical tools, models and frameworks. [1] Thompson, J.L. & Martin, F. (2010) “Strategic Management: Awareness & Change” Cengage Learning [2] Sekhar, G.V.S. (2010) “Business Policy and Strategic Management” I.K. International Pvt Ltd [3] Fiflied, P. (2012) “Marketing Strategy” 3rd edition, Routledge [4] Rao, C.A., Rao, B.P. & Rao, K. (2009) “Strategic Management and Business Policy: Text and Cases” Excel Books
Theory can be defined as “a formal logical explanation of some events that includes predictions of how things relate to one another”[1]. Concepts are “collectives used to label certain bits of experience. In other words, they are elementary constructs by which reality is classified and categorised”[2]. Alternatively, concepts are “mental constructs or images developed to symbolise ideas, persons, things, or events”[3] Model can be defined as “a set of ideas and numbers that describe the past, present or future state of something”[4] A framework is “a system of rules, laws, agreements, etc. that establish the way that something operates”[5] A tool is “a thing used to perform a job”[6]. There are many theories, concepts, models, frameworks and tools in the area of business that you will have to use at some stage of your studies. The following are the most popular ones listed in alphabetical order: Change Kotter’s Eight Steps Model Lewin’s Force-Field Theory of Change Lewin’s Model of Change Consumer behavior Behaviorist approach to consumer behavior Cognitive approach to consumer behavior Consumer buyer behavior Consumer decision making process Customer perceived value Economic Man approach to consumer behavior Model of Goal Directed Behavior Psychodynamic Approach to consumer behavior Theory of Trying Corporate Social Responsibility Approaches to CSR Carrol’s CSR Pyramid Code of Ethics Culture Cross-cultural competencies Cross-cultural management Elements of organizational culture Harrison’s Model of Culture Hofstede’s Cultural Dimensions Trompenaars and Hampden-Turner Cultural Dimensions Economics Foreign Direct Investment Inter-industry and intra-industry trade Liberal and coordinated market economies Specialization for developing countries Theory of absolute advantage Theory of comparative advantage Human Resources Management Cognitive Theory of Training Transfer Continuous Professional Development Equity Theory of Motivation Employee training and development Forms of training transfer Frederick Hertzberg’s Two Factor Theory Hertzberg’s Motivation and Hygiene Factors Honey and…
