Search results for: Ansoff Matrix

Microsoft segmentation, targeting and positioning can be explained as a set of activities that constitute the core of marketing efforts for the multinational technology company. Segmentation involves dividing population into groups on the basis of certain characteristics. Businesses focus on certain customer segments and position their products and services to satisfy needs and wants of these particular segments. Microsoft uses the following types of positioning: a) Multi-segment positioning. The company targets more than one customer segments at the same time with different product and service packages. For example, Dynamics 365, a software for building and supporting customer relationships starts with USD 115/month Customer Engagement Plan for cost-conscious customer segment. Unified Operations Plan starting from USD 190/month, on the other hand is developed for a different customer segment that do not mind to pay extra for additional set of functions and features within Dynamics 365. b) Standby positioning. Standby positioning technique involves the development of products and services that can await changes in the market to find demand in the future. When Microsoft announced its ‘cloud-first, mobile-first’ business strategy in 2014, cloud data storage was a new segment. CEO Satya Nadella saw a potential in cloud business, focused on the development of cloud services using standby positioning technique. The demand for cloud consistently increased and in Q2, 2018 alone, Microsoft commercial cloud revenues reached USD 6.9 billion, a growth of 53% compared to the previous period.[1] The following table illustrates Microsoft segmentation, targeting and positioning: Type of segmentation Segmentation criteria Microsoft target customer segment Geographic Region Global marketplace Density Urban and rural Demographic Age 16 and older Gender Males & Females Life-cycle stage Bachelor Stage young, single people not living at home Newly Married Couples young, no children Full Nest I youngest child under six Full Nest…

Microsoft Corporation is a US-based global technology company with headquarters in Richmond, Washington. Founded in 1975, Microsoft’s mission is ‘to empower every person and every organization on the planet to achieve more’. Microsoft employs more than 130 000 people internationally. During the fiscal year 2018 the tech giant generated USD 110.4 billion in revenue and USD 35.1 billion in operating income. Microsoft produces a wide range of products and services related to productivity and business processes and to support digital work and life of customers. Some of its products and services have become highly popular in the global scale. For example, more than 135 million people use Office 365 commercial every month and Outlook Mobile is installed into more than 100 million iOS and Android devices worldwide. Similarly, Microsoft Teams is used by more than 300 organizations worldwide, including 87 of the Fortune 100 and nowadays there are nearly 700 million devices around the world with active Windows 10. In 2014, Satya Nadella replaced Steve Ballmer as CEO of Microsoft. Since taking over the top job, Nadella has focused on ‘humanising’ the company by improving its organizational culture and he also enhanced the coordination of efforts across the departments and groups of the company. Microsoft business strategy can be classified as product differentiation. The company develops advanced technological products and services and sells them for premium costs. Moreover, Microsoft business strategy is currently focused on “cloud-first, mobile-first”, growth through mergers and acquisitions and exploring business opportunities related to augmented and virtual reality. Recently, the multinational technology company has also included ‘tech intensity’ as one of the important pillars of its business strategy Microsoft Corporation Report contains the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces, Value Chain analysis, Ansoff Matrix and…

Tesla Inc. (formerly Tesla Motors Inc.) is an alternative fuel vehicles manufacturer founded in 2003 by Martin Eberhard and Marc Tarpenning in Palo Alto, California, USA. The company produces fully electric vehicles, energy generation and storage systems and also installs and maintains such systems and sells solar electricity. Tesla’s mission statement is ‘to accelerate the world’s transition to sustainable energy’. The electric automaker operates stores and galleries in the US and 35 other countries worldwide and employs more than 70,500 people globally. In 2020, Tesla achieved operating margin of 6,3% which is the highest in the industry. The electric automaker had an operating cash flow less capex (free cash flow) of USD 2.8 billion during the same period. In the last quarter of 2020 alone, Tesla had USD 4.9 billion increase in cash and cash equivalents. Free cash flow during the same period reached USD 1.9 billion. Tesla business strategy integrates focus on electric cars and ownership of distribution of products. Moreover, the company stresses the low cost of ownership of Tesla electric vehicles as one of the solid bases of its competitive advantage. The alternative fuel vehicles manufacturer has a divisional organizational structure and its divisions include energy, engineering and production, HR and communications, legal and finance, sales and software. Tesla organizational culture, on the other hand, is associated with ambitious innovation, adherence of First Principles method of decision making and lack of bureaucracy throughout the company. Tesla possesses a set of competitive strengths. These include the first mover advantage, increasing numbers of vehicles sales, expertise in innovation and a high level of brand recognition at an international level. At the same time, there are certain issues that cast a doubt over long-term growth prospects of the electric automaker. These points of concern for Tesla include overly expensive price…

Xiaomi does not publish annual CSR report. It has been noted that despite its branding effort to resemble the minimalist style of Apple, Xiaomi does not show similar commitment in environmental responsibility.[1] However, the mobile internet company may start publishing CSR reports after initial public offering (IPO) of its stocks that is expected to take place in the foreseeable future. Official Xiaomi website declares company’s pledge “to reduce the use of hazardous substances in products.”[2] However the website does not disclose any data at all regarding emissions or any other environmental impact of Xiaomi products and services. According to German Federal Office for Radiation Protection (Bundesamt für Strahlenschutz) Xiaomi smartphone Mi A1 has “Specific Absorption Rate” of 1,75 watts per kilogram, which is the highest level of radiation of smartphones worldwide.[3] In general, there is a lack of information related to Xiaomi CSR programs and initiatives, as it is illustrated in table below. CSR aspect of the business Xiaomi performance Supporting Local Communities No information available Educating and Empowering Workers No information available Labour and Human Rights No information available Employee Health and Safety No information available Gender Equality and Minorities It has been noted that Xiaomi uses “yanzhi,” or physical appearance metric when hiring, leading to discriminaton during employee recruitment and selection process.[4] Energy Consumption No information available Water Consumption No information available Waste Reduction and Recycling MI INDIA maintains PRODUCT TAKE-BACK & RECYCLING PROGRAM. Xiaomi Authorised e-waste recycler can collect e-waste from customer’s location, or customers can also drop e-waste at any of company’s service centers[5] Carbon Emissions No information available Sustainable Sourcing No information available other CSR Initiatives and Charitable Donations No information available Xiaomi CSR Programs and Initiatives Xiaomi Inc. Report contains a full analysis of Xiaomi corporate social responsibility including Xiaomi CSR issues. The report…
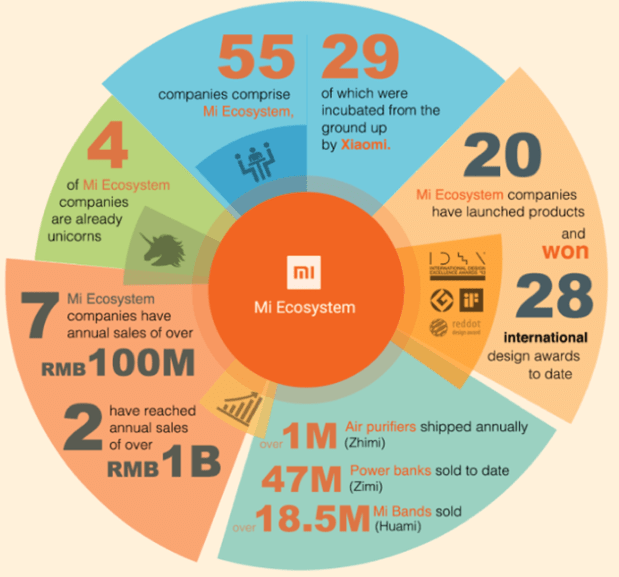
Xiaomi ecosystem is vast and comprises 55 companies including 29 companies that have been incubated from the beginning by Xiaomi. The company sells a wide range of products from smartphones to kettles and gloves. [1] Moreover, ever-expanding corporate ecosystem has been placed at the core of Xiaomi business strategy. Usually, producing a wide range of products and services threats to compromise the focus on core products and services. However, Xiaomi claims to have addressed this threat in a proactive manner. Specifically, according to its official website, while the company focuses on its core products – smartphones, smart TVs and smart routers, Xiaomi invests in companies that produce other types of products without being involved in operational management.[2] Xiaomi Ecosystem[3] Smartphones are placed at the core of Xiaomi ecosystem. Moreover, smartphones are used to facilitate the sales and use of many other products and services. Xiaomi smart devices include Mi Water Purifier, Mi Air Purifier, Mi Induction Heating Rice cooker and other products. All smart devices are connected to Xiaomi IoT platform and can be managed though Xiaomi smartphone. In 2013, the electronics and software company announced its plans to invest in 100 hardware startups.[4] The company also sells a range of “non-smart” products, like towels, and suitcases. Increasing numbers of startups are currently joining Xiaomi ecosystem to gain support to grow rapidly. Xiaomi has experienced technical staff, engineers and product managers, who can play an instrumental role in fuelling the growth of small-sized companies. At the same time, joining Xiaomi ecosystem also has some drawbacks. Specifically, start-ups need to operate with low profit margin according to Xiaomi business strategy. Moreover, over-dependence on Xiaomi for branding and distribution can be mentioned as another drawback of belonging to Xiaomi ecosystem.[5] Xiaomi Inc. Report contains a full analysis of Xiaomi ecosystem. The report illustrates…
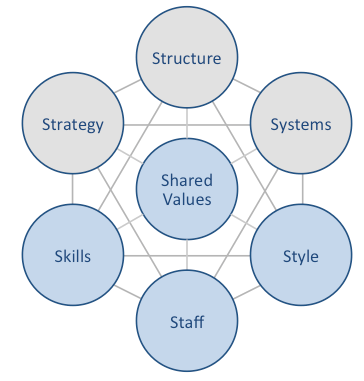
Xiaomi McKinsey 7S model illustrates the ways in which seven elements of businesses can be aligned so that overall effectiveness can be increased. According to the framework strategy, structure and systems are hard elements, whereas shared values, skills, style and staff are considered as soft elements. McKinsey 7S model stresses the presence of strong links between elements in a way that a change in one element causes changes in others. As it is illustrated in figure below, shared values are positioned at the core of Xiaomi McKinsey 7S model, since shared values guide employee behaviour with implications in their performance. Xiaomi McKinsey 7S Model Hard Elements Strategy. Xiaomi business strategy is based on cost leadership. Company’s business strategy also integrates gathering and utilising a large fan base and aggressively increasing the ecosystem of products and services. Moreover, Xiaomi positions itself as an internet and software company rather than a hardware company. Accordingly, the sales of hardware are perceived as a means to deliver software and services in the long-term perspective. Structure. Xiaomi has a matrix organizational structure. The electronics and software company has various business units that are managed independently. Xiaomi organizational structure can also be also classified as flat. Despite its large size employing more than 18000 people in 70 countries, the company has only a few layers of management. Systems. Xiaomi’s business depends on a wide range of systems such as employee recruitment and selection system, team development and orientation system and transaction processing systems. Moreover, there are critically important systems for the company such as customer relationship management system, business intelligence system, and knowledge management system. The mobile internet company aims to increase the efficiency of these and other systems via the integration of internet-based information technologies. Xiaomi Inc. Report contains a full analysis…
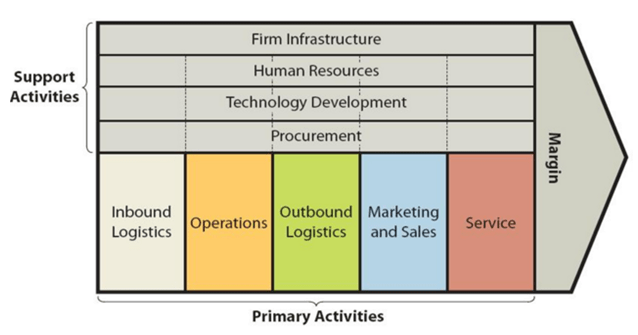
Xiaomi value chain analysis is an analytical framework that assists in identifying business activities that can create value and competitive advantage to the mobile internet company. Figure below illustrates the essence of Xiaomi value chain analysis. Xiaomi Value Chain Analysis Xiaomi Primary Activities Xiaomi Inbound logistics Xiaomi inbound logistics involves the delivery and storage activities of raw materials by the mobile internet company. Strategic relationships with Taiwan-based manufacturers of various components is one of the main sources of value for Xiaomi inbound logistics. Specifically, Xiaomi partners with Inventec and Hon Hai for assembly, Wintek and TPK for screen technology and Unicorn for PCB (printed circuit boards). Moreover, Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Corporation (TSMC) is the main processor supplier for the company. Xiaomi also procures various electronic components from nearby countries. For example, MOS and batteries are mainly imported from Thailand. Xiaomi Operations Operations activities within Xiaomi value chain analysis refer to the processes of transforming raw materials into ready products. The mobile internet company has established its presence in 70 countries and regions and it is among the top 5 in 16 markets. Xiaomi manufactures locally more than 75% of smartphones it sells in India.[1] Location of manufacturing units in China and India is one of the main sources of value in Xiaomi operations. This is because the costs of human resources in these developoing countries are cheap. Along with proximity of manufacturing units to the sources of raw materials, cost-effective human resources play an instrumental role in sustaining cost advantage competitive edge of the business. Moreover, Xiaomi sophisticates its manufacturing processes in a systematic manner using advanced technologies and benefiting from technological innovations. Xiaomi Outbound Logistics Initially, Xiaomi outbound logistics practices were limited to the shipment of products directly to end-users via couriers. At that stage the company…
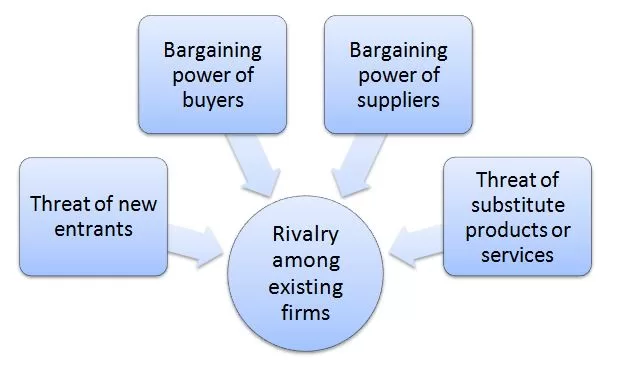
Porter’s Five Forces is an analytical framework developed by Michael Porter (1979)[1]. Xiaomi Porter’s Five Forces consists of five individual forces that shape an overall extent of competition in the industry. These forces are illustrated in Figure 1 below: Figure 1 Xiaomi Porter’s Five Forces Threat of New Entrants in Xiaomi Porter’s Five Forces Analysis Threat of new entrants into the internet technology is low. There are entry barriers for potentially new market players. Economies of scale is one of the major factors and entry barrier for new companies. Xiaomi is able to offer its products for competitive prices because it purchases raw materials in bulk and benefits from the economies of scale to a large extent. Moreover, entry into the electronics and software industry requires formidable capital investments. Xiaomi was initially funded with USD41 million in 2010 and the company went through series of funding and debt financing of several billion USD to reach its current state.[2] It may not be easy for new market entrants to secure funding at such a scale to enter the industry. Additional range of factors that decrease the threat of new entrants to the industry include access to distribution channels and likely retaliation from existing market players such as Apple, Samsung, Xiaomi and Huawei. Bargaining Power of Buyers in Xiaomi Porter’s Five Forces Analysis Bargaining power of buyers in technology and the mobile internet industry is significant. This is caused by primarily high level of competition in the global marketplace. Nevertheless, companies try to reduce buyer bargaining power through developing their ecosystem. For example, “all products belonging to Apple ecosystem are highly compatible with each-other and the purchase of one product belonging to the brand’s portfolio often leads to the purchase of other products. Gradually, it will come to the point that consumers…

Xiaomi marketing communication mix explains the extent of usage of individual elements of marketing communication channels by the mobile internet company. Generally, elements of the marketing communication mix consist of print and media advertising, sales promotions, events and experiences, public relations, direct marketing and personal selling. Xiaomi Print and Media Advertising “Xiaomi once touted its avoidance of advertising as one of the keys to its early success—saving money on commercials helped keep the overall price of the phones lower. Instead, it relied on its upper executives and its “fans” to spread the word and attract new customers through social media.”[1] However, due to increasing competition from its local rivals Oppo and Vivo, The mobile internet company had no choice but to engage in certain forms of traditional advertising such as posters and newspaper advertising. Nevertheless, viral marketing remains as the most important form of marketing for Xiaomi. The internet technology company also uses celebrity endorsement from the likes of top Hong Kong actor-singer, Tony Leung, a 54-year-old best-known to English-speaking audiences for movies like “In the Mood for Love” and “Lust, Caution.”[2] Xiaomi Sales Promotions Xiaomi uses the following sales promotions techniques: Flash sales. Flash sales refer to sales of products and services online at a heavily discounted price for a short period of time. Xiaomi uses flash sales extensively, especially in India. Customer Loyalty Scheme. Reward Mi is a customer loyalty program that rewards loyal customers with exclusive benefits such as priority passes a.k.a F-codes and discount coupons which can be redeemed on selected products across Mi Store.[3] Seasonal sales promotions. The electronics and software company announces sales promotions on notable occasions as Christmas day and anniversaries of notable days for the company. Point of sale materials. The company uses point of sale materials such as posters and…

Xiaomi segmentation, targeting and positioning is needed to indentify the target customer segment for the company and to develop products and services that are attractive to this segment. Segmentation involves dividing population into groups according to certain characteristics, whereas targeting implies choosing specific groups identified as a result of segmentation to sell products. Positioning refers to the selection of the marketing mix the most suitable for the target customer segment. Xiaomi uses mono-segment and imitative types of positioning. The internet technology company uses mono-segment positioning, appealing to the needs of a single customer segment. Specifically, Xiaomi targets a customer segment that want to use smartphones and other technology products, but have limited budget to make such a purchase. Xiaomi also uses imitative type of positioning by closely imitating the products of market leaders such as Apple and Samsung. The electronics and software company has even earned the nickname “Apple of the East” due to its close imitation of Apple products and Apple product presentation. The following table illustrates Xiaomi segmentation, targeting and positioning: Type of segmentation Segmentation criteria Xiaomi target customer segment Geographic Region 70 countries and regions globally Density Urban and rural Demographic Age 18 – 65 Gender Males & Females Life-cycle stage Bachelor Stage young, single people not living at home Newly Married Couples young, no children Full Nest I youngest child under six Full Nest II youngest child six or over Full Nest III older married couples with dependent children Empty Nest I older married couples, no children living with them Empty Nest II older married couples, retired, no children living at home Solitary Survivor I in labour force Solitary Survivor II retired Occupation Students, employees, professionals Behavioural Degree of loyalty ‘Hard core loyals’ ‘Soft core loyals’ ‘Switchers’ Benefits sought Cost attractiveness Personality Easygoing, determined and ambitious personality types User status non-users, potential…
