Search results for: Mckinsey 7s

Uber marketing strategy integrates print and media advertising, sales promotions, events and experiences, public relations and others. Particularly, Uber marketing strategy is mainly based on the word-of-mouth. Moreover, media in general and social media in particular play instrumental roles in terms of increasing the levels of Uber brand awareness in the global scale. At the same time, it is important to note that during the past few years, Uber-related messages communicated by the media have been mainly focused on scandals involving Uber, thus damaging the company’s brand image. Uber sales and marketing costs amounted to USD 3,58 USD 4,63 and USD 3,15 billions in 2020, 2019 and 2018 respectively.[1] Uber’s “rider-focused ad spend has increased twentyfold in the last year and a half.”[2] However, Chief Operating Officer Barney Harford has announced his plans to decrease marketing expenses as part of his attempts “bring a dose of financial discipline.”[3] Uber 7ps of marketing focuses on product and price elements of the marketing mix to a greater extent compared to other elements. Specifically, the global transportation technology company is increasing the range of its services to target greater numbers of customer segments. At the same time, the majority of Uber services are cheaper than traditional taxi, illustrating company’s focus on cost element of the marketing mix. Uber’s unique selling proposition is associated with cost efficiency, increasing service range and high level of customer convenience. Particularly, customers greatly appreciate convenience aspect of Uber value proposition. Accordingly, the global transportation technology company targets wide customer segment in terms of geographical location, age, social status and other criteria. Uber Technologies Inc. Report contains the above analysis of Uber marketing strategy. The report illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces, Value Chain…
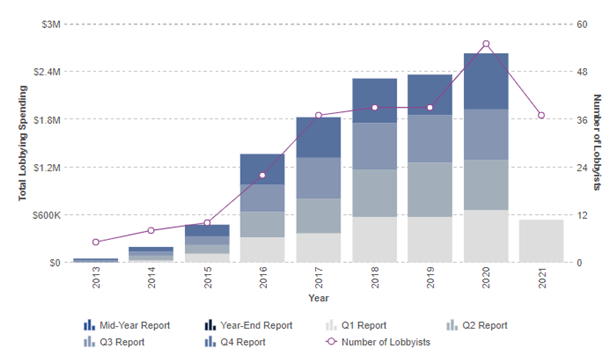
PESTEL is a strategic analytical tool and the acronym stands for political, economic, social, technological, environmental and legal factors. Uber PESTEL analysis refers to the analysis of potential impact of these external factors on the performance of the ride-hailing giant and its long-term growth prospects. Political Factors in Uber PESTEL Analysis Generally, political factors affecting businesses include government stability, bureaucracy, levels of corruption, impacts of home market lobbying groups and others. When Uber started its operations in 2009, there was no other ride-hailing taxi app. Accordingly, legislations related to the regulations of such services did not exist. Global disruption of taxi services: political implications With the advent of Uber, the following and other questions needed to be answered by local governments and authorities: Who is responsible in case of car accident: Uber or the driver? Does it need to be compulsory for Uber drivers to have taxi licences? Can Uber list thousands of its drivers as contractors, but not employees? Does Uber have to comply with minimum wage requirements? Dealing with above and other related questions in different countries and regions have caused charged political debates. Moreover, it can be argued that Uber has caused political debates in the global scale in a way that few companies have done. Different stance by local governments While some local governments have been favourable towards Uber taking into account its modern business model, others demanded strict adherence to the rules and regulations making no difference between Uber and regular taxi companies. As a result, Uber has been banned in a number of countries and such as Bulgaria, Hong Kong and Germany and certain cities such as London and Brno. Lobbying as attempts to affect political factors Uber engages in lobbying activities to try to impact legislations in the US and worldwide to…
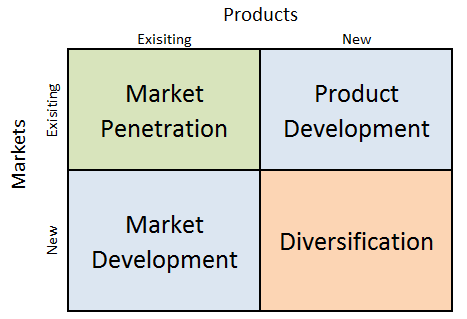
Uber Ansoff Matrix is a marketing planning model that helps the ride-hailing giant to determine its product and market strategy. Uber Ansoff Matrix illustrates four different strategy options available for the business. These are market penetration, product development, market development and diversification. Uber Ansoff Growth Matrix Within the scope of Ansoff Matrix, Uber uses all four growth strategies in an integrated manner: 1. Market penetration. Market penetration refers to selling existing products to existing markets. Uber engages in market penetration via application of various sales promotions techniques. These include distributing promo codes to allow users to have a discount for their next ride and “Uber VIP” loyalty program that rewards riders with special access to highest-rated drivers. Moreover, users can earn free rides by inviting their friends to sign up and ride with Uber. 2. Product development. This involves developing new products to sell to existing markets. The global transportation technology company consistently increases its service range. Currently, its extensive range of services include Uber X, Uber XI, Uber Pool, UberGO, Uber AUTO, Uber Access, Uber MOTO, Uber Premium and Uber Rush. Importantly, each new service introduced by the ride-hailing giant utilizes the same technological platform and competitive advantage of the business. 3. Market development. Market development strategy is associated with finding new markets for existing products. Launched only in San Francisco in 2009, the company currently operates in approximately 10000 cities worldwide. The global transportation technology company takes into account important aspects local culture when pursuing expansion strategy. The largest mobility platform in the world is expected to further engage in new market development business strategy. 4. Diversification. Diversification involves developing new products to sell to new markets. This is considered to be the riskiest strategy. Initially launched only as a taxi company, the ride-hailing giant has entered takeaway…
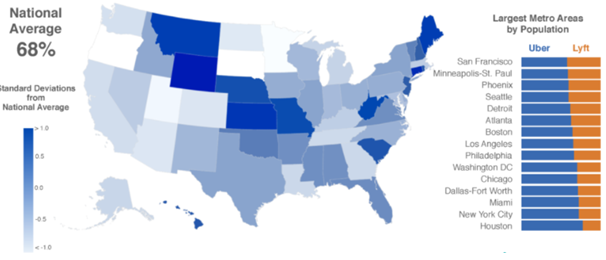
SWOT is an acronym for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats related to organizations. The following table illustrates Uber SWOT analysis: Strengths 1. First mover advantage and global market leadership 2. Low operational costs 3. Effective implementation of ‘Think Global, Act Local’ strategy 4. Uber ecosystem 5. High levels of user convenience Weaknesses 1. Damaged brand image due to a series of various scandals 2. Increasing losses of the business 3. Uber business model is easy to imitate 4. Only technically savvy individuals can use Uber services 5. Low earnings by Uber drivers Opportunities 1. Increasing popularity of sharing economy 2. Self-driving cars 3. Improving brand image through CSR programs and initiatives 4. Increasing internet penetration in the global scale 5. Increasing service range Threats 1. More legal actions in certain countries to ban Uber from operating 2. Further intensification of competition 3. The risk of new scandals and ethical issues 4. Growing protests and retaliations from traditional taxi services 5. Drivers leaving Uber due to low earnings Uber SWOT analysis Strengths in Uber SWOT Analysis 1. Uber is the largest global taxi technology company in the world and it has a first mover advantage in the ride-hailing segment in the global scale. The company has effectively utilised its fist mover advantage to build momentum and achieve global expansion in a short period of time. Moreover, thanks to first-mover advantage, the word Uber has become synonym for ride-haling internationally and the new term uberisation has emerged describing commodisation of various services. Uber is an undisputed market leader in ride-haling the global scale. The largest mobility platform in the world has more than 93 million monthly active riders in approximately 10000 cities worldwide. As illustrated in figure below, Uber is much more popular than its closest rival Lyft in the largest…

Uber organizational culture has been associated with sexual harassment and discrimination during the leadership period of co-founder and former CEO Travis Kalanick. In June 2017 the global transportation technology company “fired more than 20 employees after a company investigation into sexual harassment claims and workplace culture.”[1] Uber company culture crisis has resulted into the resignation of CEO Travis Kalanick. Uber’s new CEO Dara Khosrowshahi, has successfully led internet travel company Expedia for 12 years. Mr. Khosrowshahi had an important task of sophisticating Uber organizational culture so that the ride-hailing giant can improve its image and eventually become profitable. Change management of Uber organizational culture initiated by Dara Mr. Khosrowshahi can be explained applying Lewin’s Model of Culture. The model divides change management in organizational culture into 3 stages: Stage 1: Unfreezing. During this stage, the necessity of cultural changes for the long-term growth prospects of the company needs to be explained to employees at all stages. Khosrowshahi had dealt with this stage effectively. The new CEO stressed the importance of appropriate organizational culture in a majority of meetings with internal and external stakeholders. Moreover, “Uber’s new CEO had employees write and vote on cultural guidelines for the workplace”[2]. In total about 12000 employees voted and the results of voting determined underlying principles for Uber’s new organizational culture. Stage 2: Implementing changes. According to results of the voting discussed above, new principles of Uber organizational culture have been developed as the following[3]: We build globally, we live locally. We are customer obsessed. We celebrate differences. We do the right thing. We act like owners. We persevere. We value ideas over hierarchy. We make big bold bets. Stage 3: Refreezing. Uber is attempting to promote its new culture to all organizational stakeholders in general and employees in particular. The global transportation technology…

Uber leadership style was authoritative with co-founder and first CEO Travis Kalanick attempting to micromanage the company. The global transportation technology company had to face a leadership crisis due to incompetency of Travis Kalanick. Mr. Kalanick’s leadership style was criticized as ‘one-man-show’[1]. Moreover, it has been noted that “the sexual harassment claims, the bullying, the intellectual property lawsuit – are attributable to former leader Travis Kalanick’s brash take-no-prisoners, admit-no-errors leadership style.”[2] Scandals at the global taxi technology company escalated to an extent where Kalanick was pressured by investors to step down as Uber CEO in June 2017. The search for new CEO by the Board of Directors took two months and experienced leaders such as former CEO of HP Meg Whitman and former CEO of General Electric Jeff Immelts were shortlisted as potential heads of new Uber leadership. Expedia CEO Dara Khosrowshahi was chosen as a person to lead Uber effective from August 30, 2017. Dara Khosrowshahi was CEO of Expedia for 12 years and has proved himself as an effective business leader. Expedia’s stock has climbed more than 500% since the 2005 spinoff under the leadership of Khosrowshahi.[3] New Uber leadership is faced with a set of complex challenges that include improving organizational culture, building gender-balanced senior management team and improving relationships with drivers.[4] Changes made by Mr. Khosrowshahi so far include securing USD 7,7 billion investment from Softbank[5], emphasizing diversity and inclusion, acknowledging and apologizing for past misdeeds by the company.[6] At the same time, certain aspects of Khosrowshahi’s leadership of Uber have been subjected to criticism. First of all, Uber initial public offering (IPO) which took place on May 2019 has been rather unsuccessful. Shortly after the IPO, shares of the ride-hailing giant dropped by 11%, which was the biggest IPO first-day dollar loss in US history.[7] Moreover, certain analysts note…
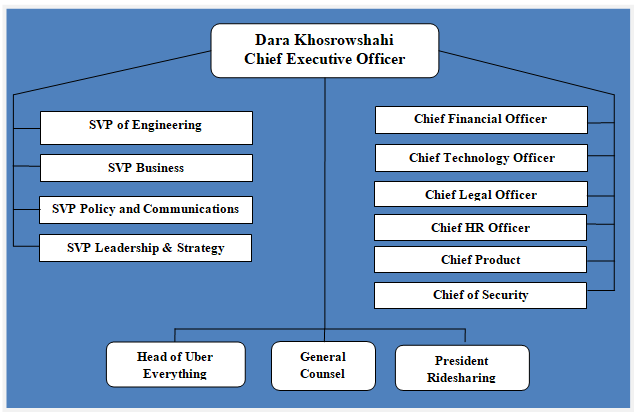
Uber organizational structure has been traditionally highly hierarchical with co-founder and former CEO Travis Kalanick yielding tremendous power and micromanaging the ride-hailing giant. Lack of Kalanick’s leadership skills resulted in a series of scandals involving bullying, discrimination at workplace, sexual harassment etc. Kalanick had to resign as a result of these scandals. After Dara Khosrowshahi became new CEO in 2017, Uber organizational structure has been subjected to certain changes.[1] Figure below illustrates Uber organizational structure: Uber Organizational Structure It can be argued that the current pattern of Uber’s organizational structure illustrated in Figure 1 above can be subjected to more changes by new CEO Dara Khosrowshahi in the medium-term perspective. Demoralized workforce and poor organizational culture belong to the list of major issues for the global transportation technology company. Dara Khosrowshahi is credited for creating collaborative work culture at Expedia where employees are encouraged to propose their ideas to management. Mr. Khosrowshahi is attempting to fix Uber organizational culture as part of his grand plans to turnaround the business. Accordingly, improvement in organizational culture may necessitate changes in organizational structure. Specifically, de-layering of organizational structure may be introduced, removing certain levels of management in order to make the business more flexible to respond to the changes in external marketplace. Moreover, advantages of flat organizational structure include faster speed of communication between the top management and floor-level employees. Senior leadership reorganization initiated by CEO Dara Khosrowshahi due to failed IPO in 2019 the roles of chief operating officer (COO) and chief marketing officer (CMO) were eliminated. Specifically, COO role was replaced by two executives who manage biggest businesses – ride-haling and food delivery. These two executives directly report to Khosrowshahi. Uber marketing operations, on the other hand, were combined with communications and policy departments. The rationale behind this specific change was…
Uber business strategy consists of the following 4 pillars: 1. Increased service range to cater for the needs of great amount of customers. Extensive offering is rightly considered as Uber competitive advantage. Depending on their budget, the occasion and purpose of ride, customers can choose among Uber X, Uber XI, Uber Pool, UberGO, Uber AUTO, Uber Access, Uber MOTO, Uber Premium or Uber Rush. It is important to note that the ride-hailing giant has been consistently increasing its range of service on the basis of the same platform and therefore, utilizing the same set of competitive advantages. Accordingly, each additional service comes for little additional cost for the company, effectively contributing to the bottom line. 2. High level of user convenience. Uber offers unprecedented user convenience at multiple levels. No need to call dispatch, wait in a line, or wave from a curb. Customers can tap ‘Request” on their phone from comfort of indoors and wait for notification that their driver is “arriving now.” Even in dense urban locations Uber drivers usually arrive in 1-2 minutes. When they reach their destination, customers just say thanks and get out of the car. No need to reach for cash or credit card. The payment is automatically charged to card on customer’s Uber account and receipt is sent via email. Moreover, dispute resolution with Uber is easy. Each ride receipt includes a map and a GPS track, customers can complain if their driver took a longer route and Uber is prompt with refunds. 3. Cost-saving through innovation. Extensive user conveniences described above come for a little cost for the company, thanks to the app that integrates innovative features and capabilities. Therefore, it can be argued that operating at low costs thorough innovation is placed at the core of Uber business strategy. Moreover, first…
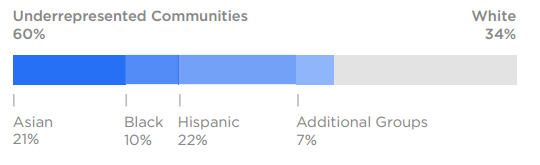
Tesla CSR programs and initiatives are currently led by Vice President of People Valerie Chapman. Tesla did not pay due attention to social responsibility aspect of the business and did not engage in corporate sustainability reporting for a long time. Although the electric automaker was founded in 2003 and became publicly traded company in 2010, the company released its first CSR report titled Impact Report only in 2018. The alternative fuel vehicles manufacturer has Diversity, Equity and Inclusion (DEI) team that uses data-driven approach to champion diversity, equity and inclusion in business practices and communities.[1] Tesla produces electric vehicles, energy storage systems and solar panels. These products are perceived to promote environmental sustainability and this perception is effectively integrated into company’s marketing communication message. Tesla CSR Programs and Initiatives Employee Health and Safety at Tesla Production employees are required to participate in a multi-day training program before ever setting foot on the factory floor. Tesla provides zero-cost health care and benefits to full-time employee positions. Employee engagement in health risk reduction measured by employee suggestions, good observations, Find it-Fix it program and continuous improvement ideas have increased from 3,000 engagements in 2017 to almost 23,000 in 2019. Tesla and Gender Equality and Minorities Tesla was recognised as Best Employer for Diversity in 2019 by Forbes The electric car maker attempts to ensure a fair representation of traditionally underrepresented communities among its workforce. As it is illustrated in Figure 1 below, traditionally underrepresented groups amount to the majority 60% at Tesla. Figure 1 Underrepresented communities representation at Tesla US Traditionally underrepresented communities are also present in Director and Vice President positions at Tesla, as illustrated in Figure 2 below. Figure 2 Underrepresented communities in leadership positions at Tesla US Gender representation is an issue at Tesla. Only 21% of US…

Tesla ecosystem at the moment comprises electric vehicles, charging infrastructure and solar systems. Energy solution products such as Powerwall, Powerpack and Solar Roof, enable homeowners, businesses and utilities to manage renewable energy generation, storage, and consumption. The following are important considerations related to Tesla ecosystem: 1. Tesla mobile app is the linking point of various elements of its ecosystem. Although Tesla ecosystem is rather small at present, nevertheless, it is highly sophisticated. Tesla mobile app provides customers control over many features of cars. The same app is also used to control solar panels and Powerwall so that customers have power flow detail and control in a single place.[1] The alternative fuel vehicles manufacturer can integrate additional range of products and services into the same app to further strengthen Tesla ecosystem. 2. Supercharging networks are competitive advantage and important element of Tesla’s ecosystem. Unlike its competitors, Tesla heavily invested in developing and spreading its supercharging networks from the early stages of its business operations. Currently, Tesla has more than 20,000 Superchargers globally, which is unparalleled in electric auto industry. Growing numbers of charging stations strengthens ecosystem of Tesla and creates solid foundation for long-term growth of the business. 3. Immense potential for development. There is a consensus among industry analysts about immense potential of Tesla ecosystem. Analysts forecast that “the electric vehicle will not be simply a plug-in replacement for the legacy gas-burner, but rather a part of a new paradigm that includes charging infrastructure, vehicle autonomy, new ownership models and renewable energy.”[2] Moreover, self-driving cars are widely seen as inevitable future of transportation for medium to long-term prospects. There are differences in strategies of leading market players to establish their firm presence in self-driving segment. On one hand, companies such as Alphabet Inc.’s (Google) and Apple are seeking to form…
