Posts Tagged ‘IT’

This report has been written for Managing Director of a business organisation and the report illustrates company e-business strategy sample. The report has been written because although the current website of the company has some e-commerce facilities its contribution to the level of revenues is significantly below from its full potential. The report discusses specific elements and issues of e-business strategy such as intranets and extranets, security and legal issues facing an online business organisation, and role of search engine in e-business strategy. Moreover, the report contains explanations of potential impact of a well-designed website on an e-business entity. The 21st century is being rightly classified as the age of information and Internet and innovations in information technology (IT) play increasingly great role in processional and even personal lives of many people. Moreover, internet offers unprecedented opportunities for business organizations. 1. Introduction 1 2. The role of intranets and extranets in business communication 1 3. Security and legal issues facing an online business organisation 2 4. Role of search engines in e-business strategy 3 5. Impact of well-designed website on an e-business 4 6. Conclusions 6 References 8 Amazon Bing Facebook Google Next Tesco Twitter Yahoo How do I receive the report? Once payment is made you will receive a link to you e-mail you have registered with on Pay Pal or the e-email you have entered when specifying bank details to download the report. The report is downloaded in PDF format. The link will stay active for 7 days. How can I use the report to complete my academic assignment/research? Reports and essays offered by research-methodology.net are professionally written samples in their respective areas. Reports and essays are intended to be used as guides and sources of secondary data for reference purposes. I did not receive the link/I can…

Leadership styles exercised in two global companies – Microsoft, a global software corporation based in Washington and Apple, consumer electronics and software manufacturer headquartered in California can be compared in detailed manner. Microsoft can be mentioned as one of the stark case studies, where democratic leadership style of its founder and former CEO, Bill Gates contributed to the global success of the company making Bill Gates the richest person in the world for several years. There was a little or no change in leadership style when Steve Ballmer took over as CEO in 2000, with employees being involved in strategic decision making. On the contrary, there is a consensus amongst business researchers that late Apple CEO Steve Jobs exercised autocratic leadership style with lack of concern for employee engagement in strategic decision making (Isaakson, 2011). Moreover, Steve Jobs famously dismissed marketing research as a waste of time, stating that customers did not know what they wanted, and this fact further emphasises his autocratic leadership style. According to Steve Jobs, rather than spending large sums of money on marketing research and involving employees to discuss research findings, organisational leaders need to be engaged in developing innovative products and add innovative features in existing products that people would like to purchase (Isaakson, 2011). It is important to note that despite large differences between Microsoft and Apple leadership styles as discussed above, both organisations have been able to be highly successful in global scale. Accordingly, rigid generalisations about effective and ineffective leadership styles needed to be avoided. In other words, each individual leadership style can be effective or ineffective depending on a wide range of factors such as personality, skills and competencies of the leader, organisational culture, specifications of the industry, level of education of employees etc. Amazon.com Inc. Report contains the application…
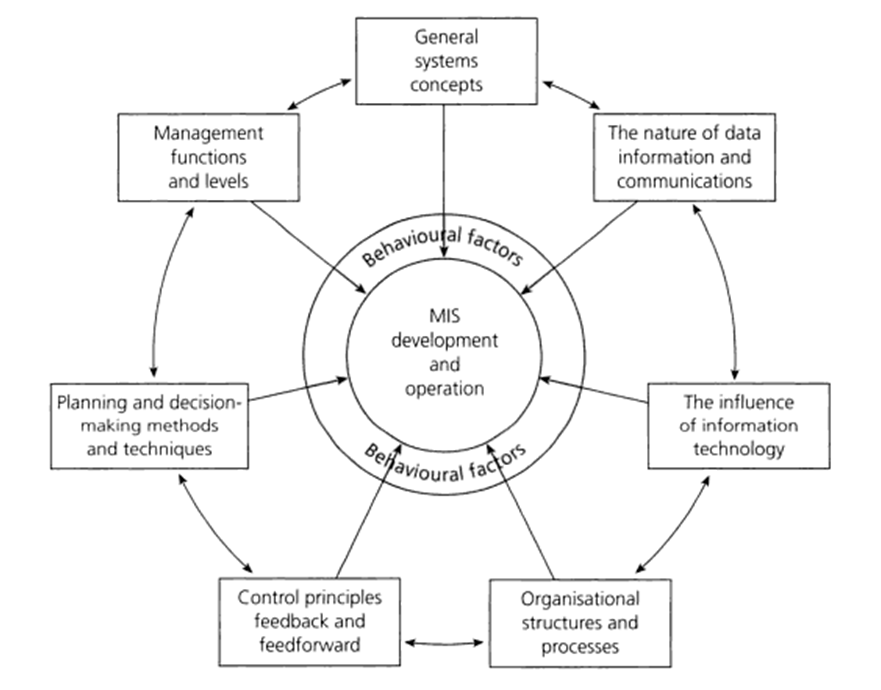
Management Information System can be defined as “a system to convert data from internal and external sources into information and to communicate that information, in an appropriate form, to managers at all levels in all functions to enable them to make timely and effective decisions for planning, directing and controlling the activities for which they are responsible” (Lucey, 2004, p.2). Alternatively, Management Information System can be defined as “a computer-based system that provides information and support for managerial decision making” (Daft et al, 2010). In simple terms, Management Information System represents a system used by managers to collect updated and comprehensive data in order to engage in informed and effective decision making. Management Information System is a much broader concept than just handling data in a way that Management Information System stands for data analysis in accordance with a range of important factors such as organisational culture, relevant policies and procedures and wider business environment. Adoption of Management Information System principles in an appropriate manner is going to provide Company the advantages of engaging in informed planning, mini Management Information Systeming the level of information overload, and increasing the level of coordination between various departments of the company. Moreover, Management Information System can have a positive contribution on employee performance evaluation and improvement at Company and it can also serve as a valuable tool for identifying current position of the company in the marketplace and formulating growth strategies. The five important functions of management information systems have been identified by Pride et al (2009) to consist of the following points: Collecting data. The collection of data that is necessary for decision making in short-term and long-term perspectives. Storing data. Keeping the data in an effective format in order to ensure that they can be the right of data can be…
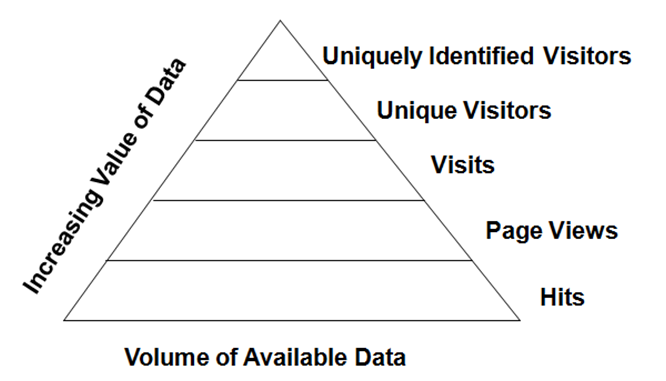
The Pyramid Model of Web Analytics Data associates the increasing value of data with filtering hits to the site towards uniquely identified visitors. According to the Pyramid Model of Web Analytics Data an e-commerce web-site gets certain amount of hits (visits) associated with a certain numbers of web site page views. This data is perceived to be the most basic information and the level of its value is highly compromised from an organisational viewpoint. Pyramid Model of Web Analytics Data Further in the line of increasing value of data come the actual visits to the site and the proportion of unique visitors within overall visits. This information can be used by e-commerce business management to assist in decision making. In Pyramid Model of Web Analytics information about uniquely identified visitors is considered to be the most valuable set of data. Data at this level may include geographical locations of uniquely identified visitors, landing and exit pages on the e-commerce website, the duration of time spent on each specific web page and other important aspects of consumer behaviour. From this perspective, the Pyramid Model of Web Analytics represents an effective model in terms of explaining the value of data provided by web analytics tools.

Being updated with the relevant legislations is the main responsibility of organisational managers in dealing with the legal aspects of firm’s information system. Moreover, major legal areas of information systems to be addressed by managers include Data Protection Act(1998), appropriate dealings with intellectual properties, abiding to relevant contractual obligations and safeguarding the firm from breaching relevant criminal and civil laws. Main legal requirements of dealing with information in UK are specified in Data Protection Act (1998) and these are formulated through eight main principles. Neglecting or abusing these principles can result in civil or criminal charges for firms involved. The present age of information is causing the importance of management information systems to increase at a rapid pace and this tendency is expected to continue in the foreseeable future. Moreover, today firms have an opportunity of increasing the level of their competitiveness through increasing the level of information systems in decision making at strategic and operational levels. However, there is a set of important security, ethical and legal implications of management information systems discussed in this paper that should not be neglected by organisational managers. Neglecting or abusing these security, ethical and legal aspects of information systems can result in highly negative implications for the company such as damage to the brand image, loss of customer loyalty, or even civil or criminal prosecution in some instances.

It is important to distinguish between ethical and legal implications of information system management in a way that unlike legal issues, ethical issues do not necessarily result in the organisations being punished by law; nevertheless, unethical behaviour can have highly negative implications for the society. Ethical implications of information system management cover a wide range of issues such as disclosure of information to third parties, accuracy of information, information ownership issues, appropriate access to information and others. Moreover, increasing popularity of social networking sites such as Facebook, Twitter and YouTube in the global scale are proving to be another source of information system management ethical issues. Specifically, “a number of information system companies have sprung up to provide products designed to monitor social media” (Stair and Reynolds, 2011, p.30) and this practice is attracting criticism from various parties for being contradictory form ethical viewpoint. Critics argue that information posted in social networking sites are private and firms do not possess ethical rights to use this information for marketing and other purposes. References Stair, R & Reynolds, G. (2011) “Principles of Information Systems” Cengage Learning

Widely considered as a controversial genius and a charismatic leader, Steve Jobs has served as chairman and CEO of Apple for 14 years and he is credited for the global success of the company. The decease of Steve Jobs on October 5, 2011 because of cancer implications resulted in grievances for millions of people around the globe, at the same time casting concerns for the future of Apple Inc. Although, a long-term Apple executive with impressive track record – Tim Cook has been named apple CEO several months before the decease of Steve Jobs, nevertheless, there are concerns about the sustainability of Apple’s innovative corporate culture, as this culture had been closely associated with the former CEO. Apple Organisational Culture on Steve Jobs Era Late Apple chairman and CEO, Steve Jobs is widely perceived as unconventional leader who was able to rally various stakeholders of the company for his vision and at the same time “demanded excellence from his staff and was known for his blunt delivery of criticism” (McInerney, 2011). According to Harrison’s Model of Culture (1972) Apple organisational culture when Steve Jobs was in charge can be classified as a power culture. Accordingly, Steve Jobs had concentrated most of the decision making powers at his hands, constantly challenging subordinates for better performance, and criticising employees blatantly and undiplomatically if their performances did not meet his expectations (Arneson, 2011). Moreover, described as “antithesis of servant leadership model” (Katzenbach, 2012), Steve Jobs was famous for pressurising teams and individuals to better performance and creating a corporate culture of high level of performance where A list employees would thrive, however B list employees, comprising the majority of workforce, would be subjected to unnecessary level of stress. According to Harrison’s Model of Culture (1972) the power culture has both advantages, as well…

Information can be specified as a compulsory element to be used in decision making in organisations. Decisions taken in organisations can be divided into two categories – strategic and operational, and each type of decision is associated with relevant information needs. Specifically, decision making at a strategic level addresses issues that have long-term implications for the performance of the whole organisation in general. For example policy formulation, new market development, new product development, or decisions related to corporate social responsibility issues can be mentioned as instances for strategic decision making. The type of information needed for strategic decision making may include market share, tendencies in global marketplace, consumer preferences, proposed changes in relevant legislation etc. Operational decision making, on the other hand, relate to the type of decisions relating to daily operations that have implications to a particular department, not necessarily the whole organisation. Information needs for operational decision making may relate to regional sales data, supply-chain management for a specific product, or any other similar information. Critical success factors (CSF) can be defined as “the limited number of areas in which satisfactory results will ensure successful competitive performance for the individual, department, or organisation” (Mard et al., 2004, p.114) and CSF can prove to be instrumental in determining organisational need for information. The nature of CSF for any given organisation depends on a range of factors such as the type of industry, the level of competition, the source of competitive advantage for the firm etc. For example, a CSF for a fast-food restaurant can be specified as reducing the duration of time a customer waits for his food without compromising the quality of the food. Accordingly, key decisions (KD) directly related to CSF for this specific business can be specified as deciding what goes into the menu of the…

‘The Grange’ needs to adopt a Decision Support System (DSS). This system is used as an analytical model, for the specialization of databases within the hotel.DSS is made so that it can help the managers with decision making, this system does not make the decision but it provides insights and judgments to manager. DSS also provide support to the manager especially when they are making semi-structured and unstructured business decisions. Decision Support System (DSS) will provide the management team of ‘The Grange’ to create an interactive modeling process for the hotel and its expansion plan. For example, if The Grange uses a DSS software package for decision making regarding expansion plans, the software is going to alternatives to the manager regarding the outcome and this is going to help the management team to make the right decision. What happens is that in this system the manager enters different variables to see different outcomes. But if we look at it from the demand response it is quite difficult to comprehend since the decision makers are not very determined to demand pre-specified information while making the right decision. Therefore the management team will not have the right information that they need in advance and this might lead them to make a wrong decision. Hence with the help of DSS the management team at ‘The Grange’ will be able to find the information they need to help make the right decision regarding the expansion plan. Information System Diagram (DSS) Therefore DSS was created so that they are considered to be ad hoc and would respond quickly when there is a need. And lastly the DSS is controlled by the individuals who make the decision within the company. DSS supports the decisions in a direct manner to a specific decision making styles and…
