Search results for: Mckinsey 7s

Starbucks segmentation, targeting and positioning comprise marketing decisions directed at identifying appropriate group of people among the general public as future customers for the business and targeting this segment via positioning products and services that resonates well with their needs and wants. In simple terms, segmentation, targeting and positioning refers to deciding whom to sell to, and positioning products and services accordingly. Starbucks Coffee uses the following types of positioning: – Mono segment positioning. The coffee chain giant targets premium customer segment only i.e. individuals who are willing to pay extra for the quality of products and services. – Adaptive positioning. Due to the tendency of increasing consumer health awareness, Starbucks Coffee developed coffee beverages with less calories such as Chai Tea Latte (103 calories) Caffe Misto (63 calories) and Iced Americano (11 calories). – Standby positioning. Certain Starbucks beverages such as Frappuchino had to await changes in the market for certain period of time to find demand. – Sustainability positioning. The world’s largest coffeehouse chain attempts to shift customer attention to sustainability aspect of its business. For example, by the end of FY21 there were 2779 Greener Store framework Starbucks branches[1]. This store format aims to achieve reductions in carbon emissions, water usage and landfill waste. The following table illustrates Starbucks segmentation, targeting and positioning: Type of segmentation Segmentation criteria Starbucks target customer segment Geographic Region US, Canada, Latin America, Europe, Middle East, Africa, China and Asia Pacific region Density Urban Demographic Age 18 – 60 Gender Males & Females Life-cycle stage Bachelor Stage young, single people not living at home Newly Married Couples young, no children Full Nest I youngest child under six Full Nest II youngest child six or over Full Nest III older married couples with dependent children Occupation Students, employees, professionals Behavioral Degree of loyalty ‘Hard core loyals’…

Starbucks marketing strategy is based on the following principles: 1. Focus on product and place elements of the marketing mix. Marketing mix comprises 7 elements – product, place, price, promotion, process, people and physical evidence. Businesses choose to concentrate on one or two elements as their sources of competitive advantage according to their business strategy. Accordingly, Starbucks marketing mix focuses on product element through offering foods and beverages of high quality and providing respective level of service. Place element of the marketing mix represents an additional source of Starbucks competitive advantage in a way that stores are usually located at high-traffic, high-visibility locations. 2. Customer segmentation and targeting premium customer segment. The world’s largest coffee retailer targets males and females from middle and upper class who can afford expensive prices of Starbuck products for regular consumption. The company uses mono-segment, adaptive and standby product positioning techniques in order to appeal to the needs and wants of the target customer segment. 3. Integrated application of multiple marketing communication channels. Starbucks marketing communications mix utilises a number of marketing communications channels such as print and media advertising, sales promotions, events and experiences, public relations and direct marketing in an integrated manner to communicate the marketing message to the target customer segment. 4. Consistent increase of the marketing budget to implement the above measures and initiatives. Starbucks has been consistently increasing its marketing budget for a number of years. Starbucks marketing expenses totalled USD305.1 million, USD258.8 million and USD245.7 million in fiscal 2021, 2020 and 2019, respectively. The Seattle-based coffee chain spends this budget to communicate its marketing message to the target customer segment in creative ways. 5. Extensive use of celebrity endorsements. Efficient use of celebrity endorsement is one of the cornerstones of Starbucks marketing strategy. The world’s largest coffeehouse chain…
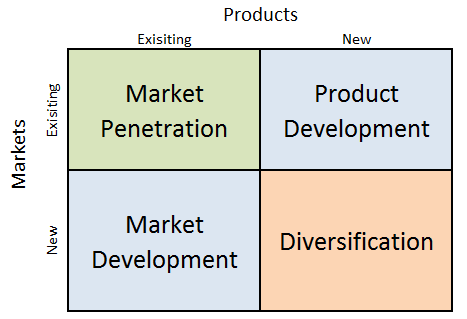
Starbucks Ansoff Matrix is a marketing planning model that helps the multinational chain of coffeehouses to develop its product and market strategy. Ansoff Matrix focuses on four different strategy options businesses can use. These are market penetration, product development, market development and diversification. Ansoff Growth Matrix Starbucks uses all four growth strategies within the scope of Ansoff Matrix. 1. Market penetration. Market penetration refers to selling existing products to existing markets. Starbucks usually has the largest share in the majority of markets it operates. The world’s largest coffeehouse chain relies on its integrated marketing strategy to pursue market penetration strategy. Specifically, the Seattle-based coffee chain effectively positions itself as a third place away from work and home. 2. Product development. This strategy implies developing new products to sell to existing markets. The global coffeehouse chain pursues product development strategy aggressively. The company sells many variations of coffee, tea and other beverages and a variety of fresh food items, including snack under the brand names of Starbucks, Teavana, Seattle’s Best Coffee, Evolution Fresh, Ethos, Starbucks Reserve and Princi. 3. Market development. Market development strategy is associated with finding new markets for existing products. It is one of the main growth tools actively used by Starbucks Corporation. Started with only one coffee shop in Seattle’s 1912 Pike Place in 1971, the company has expended into 84 markets with 17133 company-operated stores and 16700 licensed stores as of October 3, 2021.[1] 4. Diversification. Diversification involves developing new products to sell to new markets and this is considered to be the riskiest strategy. The world’s largest coffeehouse chain engages in diversification sparingly. Rare occasions of diversification by Starbucks include selling CDs with own musical compilations. Starbucks Corporation Report contains the above analysis of Starbucks Ansoff Matrix. The report illustrates the application of the…
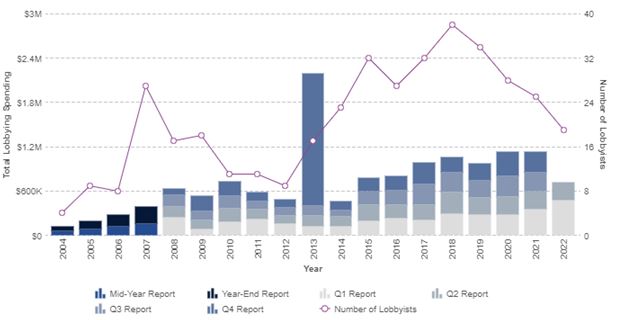
PESTEL is a strategic analytical tool and the acronym stands for political, economic, social, technological, environmental and legal factors. Starbucks PESTEL analysis involves an analysis of potential impact of these factors on the bottom line and long-term growth prospects. Political Factors in Starbucks PESTEL Analysis Starbucks sales are affected by a wide range of political factors, directly and indirectly. The patterns of sourcing raw materials have evolved into a significant political factor that affects the business in a direct manner. Specifically, nowadays it has become compulsory for Starbucks and other global businesses to engage in sourcing of raw materials complying to environmental and social norms that are becoming stricter. Neglecting such norms intentionally or unintentionally are likely to cause political pressure on the business. Starbucks performance can also be affected by the level of relationships between the USA and countries that produce coffee beans, as well as, countries where Starbucks operates. Additional political factors affecting the business include political stability in the country, the impact of home market lobby groups and a wide range of non-government organizations. Labour Union Issues Labour unionisation can be mentioned as a stark political factor within PESTEL analysis of Starbucks. The coffee chain has ongoing issues with unionisation of its workforce for many years, but this problem escalated last year with increasing numbers of employees willing to join unions. This was one of the main reasons for the return of Howard Schultz as CEO for the third time. The world’s largest coffeehouse chain strongly opposes unionisation of its workforce and occasionally engages in contradictory practices to express its opposition. For example, in May 2022 the company announced a pay raise for all non-unionized workers and in August 2022 Starbucks sent formal complain to National Labour Relations Board (NLRB) questioning the fairness of the…

SWOT is an acronym for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats related to organizations. The following table illustrates Starbucks SWOT analysis: Strengths 1. Extensive, but focused brand portfolio 2. High profit margin and solid financial position 3. Market leadership in the global scale 4. Customer services and brand positioning 5. Increasing presence in emerging economies Weaknesses 1. Overly dependence on the US market 2. Overly expensive prices 3. Brand image weakened due to a number of incidents 4. Extensive dependence of revenues on Arabica coffee beans price 5. Imitable products and competitive advantage Opportunities 1. Diversification of business 2. Increased focus on organizational ethical behaviour 3. Entering into strategic cooperation 4. Reforming the pricing structure 5. Increasing focus on mobile ordering Threats 1. Leadership failure by new CEO Laxman Narasimhan 2. Dramatic increase of coffee beans costs 3. Decline in consumption of coffee due to health concerns 4. Emergence of direct and indirect competition 5. Disruption in supply-chain Starbucks SWOT Analysis Strengths in Starbucks SWOT Analysis 1. Starbucks Corporation maintains an extensive, yet highly focused brand portfolio. At the same time, all brands belonging to Starbucks portfolio including Teavana, Tazo, Seattle’s Best Coffee, Evolution Fresh, La Boulange and Ethos are popular drinks and beverages of premium class. The company also sells merchandise products such as coffee- and tea-brewing equipment, Verismo® System by Starbucks, mugs and accessories, packaged goods, books and gifts. Starbucks is able to apply its competitive advantage and extensive experience in the promotion and sales towards each product within its portfolio thanks to the shared features of these products associated with high quality for a premium price. 2. In fiscal year 2021 Starbucks generated consolidated revenues of USD 29,1 billion an increase of 24% compared to the previous year. The global coffeehouse chain enjoyed a…

Howard Schultz has been at the helm of Starbucks leadership for more than two decades in total. He is rightly credited for making the business the world’s largest coffee retailer with 17133 company-operated stores and 16700 licensed stores in 84 markets employing 254,000 people.[1] On June 2000 Howard Schultz stepped down and assumed a new position as chief global strategist to focus on international expansion in general and expansion in China in particular. New internally promoted CEO Orin Smith oversaw store count to increase to 10000 locations with more than USD 5 billion annual sales. However, at the same time Starbucks market share at US decreased due to increased competition from McDonald’s, Dunkin’ Donuts and other competitors. Schultz returned at the helm of Starbucks leadership as CEO on January 2008 in the middle of global financial crisis to replace Jim Donald, who had succeeded Orin Smith in 2005. After a series of massive changes such as closing many underperforming stores, re-training employee and enforcing fair trade in coffee supply-chain, Schultz stepped down as CEO for the second time and became executive chairman. Kevin Johnson was appointed as a new Starbucks CEO effective from April 2017. Kevin Johnson admitted having ‘venti-sized shoes to fill” referring to successful leadership by Howard Schultz. At the same time, the new CEO stated “I’m not going to fall into the trap of trying to be Howard. I’m going to be authentic to who I am as a person and who I am as a leader”[2]. Howard Schultz returned for his third stint as CEO on April 4, 2022. This time the role was interim CEO until more suitable person is found. The main reason for his latest return was to actively block attempts by baristas to form unions. In September 2022, former CEO of Reckitt Benckiser…

Starbucks business strategy is based on the following four pillars: 1. Offering ‘third-place’ experience. Starbucks stores are effectively positioned as a ‘third place’ away from home and work, where people can spend time in a relaxed and comfortable environment with their friends or alone. Customers are even welcome to get their work done in a Starbucks store. All company-owned stores in the US and most company-owned stores abroad offer free wi-fi. “Starbucks stores are meticulously designed to make customers stay longer, buy more, and return for another visit.”[1] After returning as CEO for the third time in April 2022, Howard Schultz announced his plans for the company. Plans include building drive-through in 90% of new locations and machinery that will allow baristas to handle increasingly complex customer orders more quickly. Some analysts note that while drive through may increase profit martin, at the same time they may compromise the essence of third place experience for customers. Furthermore, according to Starbucks Chief Marketing Officer Mr. Brady Brewer the Seattle-based coffee chain is also creating digital third place. Mr. Brewer shares his vision the global coffeehouse chain creating a new global digital community on the basis of Web3 in general and NFTs (non-fungible tokens) in particular.[2] 2. Selling coffee of the highest quality. Starbucks business strategy can be classified as product differentiation. Accordingly, the coffee chain giant focuses on the quality of its products and customers pay premium prices for high quality. Excellent customer services as one of the solid sources of Starbucks competitive advantage further increases the attractiveness of the coffee retailer. The multinational chain of coffeehouses duly recognizes the paramount role of its employees in customer-facing positions to sustain high level of customer service. Accordingly, the company refers to its employees as partners and offers them a wide…

Starbucks organizational culture is based on values and principles of its former long-term CEO Howard Schultz. It has been noted that “Starbucks’ culture is powerful because it is tightly linked to the company’s distinctive capabilities[1].” Starbucks organizational culture integrates the following four key elements: 1. Valuing employees and their contribution. At Starbucks employees are referred to as partners and they are taken care of by the company via competitive compensation packages. For example, the coffee chain offers stock options and health insurance even to part-time employees in the US. Moreover, “at the height of the global financial crisis, when other companies were cutting HR costs wherever they could, Starbucks invested in staff training, including coffee tastings and courses that ultimately qualified for credit at higher education institutions”[2] 2. Presence of close bonds among employees. The company firmly believes in relationship-driven approach to the business and encourages the formation of close bonds between employees in its stores. One can easily witness the presence of close bonds among employees by simply observing their interaction in any store belonging to the Seattle-based international coffee chain. This contributes to the formation of relaxing and comfortable environment in Starbucks store, effectively strengthening its role as ‘third place’ away from work and home, where customers can spend good time alone or with their friends. 3. Culture of inclusion and diversity. Embracing inclusion and diversity is placed at the core of Starbucks corporate culture. The world’s largest coffee retailer runs 12 diverse Partner Networks, representing the broad spectrum of employee backgrounds. These include Armed Forces Network, Black Partner Network, Disability Advocacy Network and others. The multinational chain of coffeehouses received 100% score on the Disability Equality Index. The principles of inclusion and diversity prevail not only among the workforce, but also have reflections on customer…
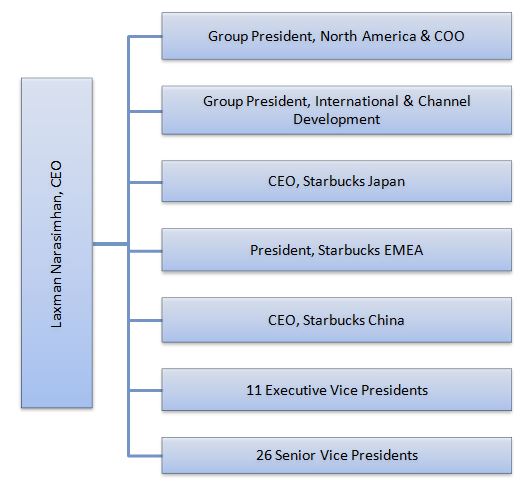
Starbucks corporate structure sustains international scope of its business operations that encompasses more than 34000 stores in 84 markets. Starbucks organizational structure is hybrid and integrates geographic, brand-based and functional hierarchy structures. Organizational structure of Starbucks can be divided into the following divisions: 1. Geographic divisions. Starbucks operations are divided into the following geographic divisions or segments: a) North America division. This division consists of USA and Canada b) International division consisting of China, Japan, Asia Pacific, Europe, Middle East, Africa, Latin America and Caribbean 2. Brand-based divisions. Each brand within Starbucks Corporation portfolio represents a separate division led by the head of division. The world’s largest coffeehouse chain has brand-based divisions as illustrated in table below: Brand Founded Products Starbucks 1971 Coffee, non-alcoholic beverages, food Teavana® 1997 Variety of teas La Boulange® 1999 French pastries and breads Evolution Fresh™ 1992 Nourishment juices and foods Seattle’s Best Coffee 1991 Coffee, non-alcoholic beverages, food Tazo Tea 1994 Teas, herbs, roots and spices Brand-based divisions within Starbucks organizational structure Starbucks corporate structure is functional hierarchy and accordingly, groups are formed according to business functions on Executive Vice President (EVP) and Senior Vice President (SVP) levels. Specifically, as illustrated in figure below organizational structure of Starbucks includes 11 Executive Vice Presidents each leading a separate function below: Chief Financial Officer Chief Marketing Officer Chief Strategy & Transformation Officer Global Coffee, Tea and Cocoa Global Supply Chain Chief Technology Officer Public Affairs Chief Partner Officer Global Channel Development Starbucks North America General Counsel Starbucks Organizational Structure Similarly, there are 24 functions headed by 26 executives at Senior Vice Presidents level: Store Development Ethics and Compliance officer Chief Procurement Officer, Global Sourcing Product Experience Global Chief Inclusion and Diversity Officer Starbucks Canada Americas Finance Latin America & Caribbean Partner…

Founded in 1985 by Howard Schultz, Starbucks Corporation (NASDAQ:SBUX) currently operates in more than 34,000 stores in 84 markets according to its mission statement “to inspire and nurture human spirit – one person, one cup and one neighbourhood at a time”. Starbucks Corporation brand portfolio consists of Teavana, Tazo, Seattle’s Best Coffee, Evolution Fresh, La Boulange and Ethos and it sells coffee, tea, other beverages, and a variety of food products. There are two formats of Starbucks stores: company-operated and licensed stores. By the end of fiscal year of 2021, Starbucks had 17,133 (51%) company-operated stores and 16,700 (49%) licensed stores. As of October 2021, Starbucks had approximately 383,000 employees worldwide, including 245,000 employees in the US. The world’s largest coffeehouse chain refers to its employees as partners. Starbucks results for fiscal 2021 demonstrate the overall strength and resilience of the brand. Consolidated revenues increased 24% to USD29.1 billion in fiscal 2021 compared to USD23.5 billion in fiscal 2020, primarily due to business recovery from the COVID-19 pandemic. Also contributing to the increase was USD576 million of incremental revenue attributable to the extra week in fiscal 2021. Starbucks business strategy is associated with providing customers a Starbucks Experience, i.e. a ‘third place’ experience away from work and home, where people can have quality time with friends or alone enjoying quality coffee, beverages and fresh food. Currently, the company is following international business expansion strategy with a particular focus on China and Asia Pacific market segment. Starbucks is an acknowledged leader in the industry in terms of exploiting information technology and technological developments. The company has adapted mobile apps for the promotion of its brand and sales of products earlier than the competition. Starbucks app offers multiple features such as store locator, nutrition-based information and rewards program. Moreover, ‘MyStarbucks Signature’ initiative…
