Search results for: Marketing Communication Mix

Red Bull GmbH is a multinational beverage company based in Austria that sells a famous Red Bull energy drink. The company sells its products in 162 countries, and 4,204 billion cans of Red Bull were sold during the year of 2010 alone (Company Figures, 2011, online). The company product range consists of Red Bull drink, Red Bull sugar free, Red Bull Cola and Red Bull energy shots. Its mission statement is: “We are dedicated to upholding Red Bull standards, while maintaining the leadership position in the energy drinks category when delivering superior customer service in a highly efficient and profitable manner” (Mission/Values, 2011, online) This article represents a report that presents analysis of marketing communication strategies of Red Bull in two countries – UK and China. The article comprises the review Red Bull’s current marketing communication strategy in UK and China and formulates recommendations for improvement and change for the company. Red Bull GmbH Report contains the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces, Value Chain analysis and McKinsey 7S Model on Red Bull GmbH. Moreover, the report contains analyses of Red Bull’s business strategy, leadership and organizational structure and its marketing strategy. The report also discusses the issues of corporate social responsibility. Review of the Current Practice Red Bull’s Marketing Communication Strategy Usage of Marketing Communication Strategies by Red Bull Marketing has been identified as one of the most crucial aspects of the business by Red Bull along with many other businesses. Red Bull relies in marketing communication in order to conduct its marketing strategy. Marketing communication can be defined as “all communication activities an organisation undertakes to promote its agenda to its audiences” (Gillis, 2006, p.392). Marketing communication mix, on the other hand, has been defined as “a number…

The classical business concept of Aldi that had proved to be successful in Germany and many other countries had to be altered in UK and Switzerland due to a set of reasons. As we know the main business model Aldi practiced consisted of offering low priced limited range of products that was achieved by compromising the quality of customer service and shop premises. However, this strategy did not prove to be successful in UK and Switzerland and Aldi management had to change its strategy in these countries by increasing the prices of their products and invest extra financial resources that were created in this way in increasing the number of product range, improving the quality of the customer services, and increasing the spending on marketing communication mix. Taylor and Lee (2007) stress the importance of cultural differences in international buyer behaviour. Culture itself, can be defined as shared values and mindsets and methods of doing things within a specific group (Holden, 2002). Therefore, local cultural differences in UK and Switzerland were the main reasons behind the change of strategy practiced by Aldi. To be more specific, in Germany and many other countries value of the product is usually associated with cheap price of the product. In other words, if the product is cheap it is perceived as value by customers in Germany and a range of other countries. And this fact has ensured the success of traditional strategy of low pricing practiced by Aldi in Germany and many other countries. However, culture in UK and Switzerland is different in a way that if the price of the product is very cheap, consumers tend to form low opinions about the quality of these products. Value in UK and Switzerland is mainly associated with the quality of the product, not necessarily with…

Gap Inc. is a San Francisco based American retailer which sells clothing and accessories. The company was founded in 1969 by Donald and Dorris Fisher. The aim of the company is to help people to express their personal style throughout their life. The company comprises five brands: Gap, Banana Republic, Old Navy, Piperlime and Athleta. The company has 3465 stores worldwide with spores in Canada, France, Ireland, Japan, UK and US owned by the company and stores in other companies are operated by franchisers. Advertising Print and broadcast ads. Gap uses print and broadcast ads intensively both in UK and USA placing advertisements in newspapers and broadcasting its ads in some TV channels in both continents. Along with traditional print and broadcast advertising, sometimes original marketing campaigns are launched, which proved to be memorable and highly efficient in numerous occasions. For instance, Gap launched a print and television advertising campaign, “Favourites” in 2005 with the participation of acclaimed musicians, including Brandon Boyd, Alanis Morisette, Liz Phair, Joss Stone, Keith Urban and others, where each musician performed an original remake of their favourite song wearing their favourite Gap jeans. Packaging outer. The outer packaging for the products of the company is being used as efficient advertising medium by Gap with the eye-catching company logo displayed in large font in it. Billboards. Being one of the most efficient advertising tools, billboards are used by Gap Inc. both in UK and USA. However it is more intensively used in US cities than in UK. Point-of-purchase displays. This advertising tool refers to products being displayed within the point of purchase area in a way that it is convenient to add them to their shopping basket for the people who are already paying for other items. These are usually items that are small in…
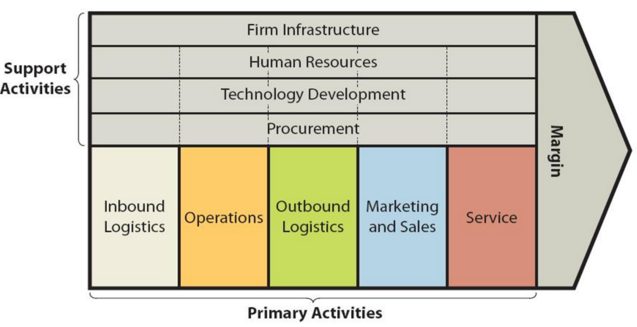
BYD value chain analysis is an analytical framework that assists in identifying business activities that can create value and competitive advantage to the business. Figure below illustrates the essence of BYD value chain analysis. BYD Primary Activities BYD Inbound logistics BYD inbound logistics is one of the key sources for value creation for the EV behemoth. BYD has more than 11,000 cooperative suppliers, 41% of which are located in Southern China, 34% in Eastern China, 9% in Northern China.[1] The electric automaker aims to produce as many spare parts in-house as possible, thus decreasing dependence on external vendors, at the same time increasing profit margins. For example, for BYD Dolphin only tyres and windows are delivered by suppliers and all other components are produced by the company itself.[2] BYD prioritizes long-term partnerships with reliable suppliers, securing stable access to critical materials and components like lithium, cobalt, and semiconductors. This reduces procurement risks and price fluctuations. The company leverages cutting-edge technologies like digital supply chain management systems, artificial intelligence for demand forecasting, and automated warehouse robots. BYD Operations In the operations stage, BYD engages in the manufacturing and assembly of its products. This includes the production of EVs, batteries, solar panels, and energy storage systems. Efficient production processes and quality control measures are crucial in this stage. BYD operations can be divided into the following four segments. Automobile. BYD delivered a total of 1,802,000 vehicles in 2022, with a year-on- year growth of 149.9%, including around 1,788,000 new energy vehicles, with a year-on-year growth of 217,6%.[3] Rail Transit. The company produces medium-capacity “SkyRail” and low-capacity “SkyShuttle” filling the technological and industrial gap in rail transit and providing effective solutions to traffic jams in cities all over the world. Renewable energy. As a provider of integrated renewable energy solutions, BYD produces relevant products like batteries, solar energy…

Effective BYD leadership is one of the main factors behind the phenomenal growth of the electric automaker. In April 2022, Wang Chuanfu, founder, Chairman and President of BYD, was listed on The 50 Most Influential Business Leaders in China 2022 by Fortune. Described as “a mix of Thomas Edison and Jack Welch, the former General Electric chief” by Charlie Munger in 2008[1], Wang Chuanfu is a charismatic and passionate leader known for his long-term vision and relentless work ethic. Transformational leadership principles prevail at BYD. Wang Chuanfu’s audacious vision for a sustainable future through EV and renewable energy motivates employees and stakeholders alike. He articulates a clear picture of BYD’s potential impact on the world, transcending mere financial goals. This inspires employees to see their work as contributing to a larger purpose. It is important to note that maintaining a transformational leadership style as the company scales can be challenging. Effective communication and delegation become crucial to keep everyone aligned with the vision and empowered to act. BYD Company Limited Report contains the above analysis of BYD leadership. The report illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces, Value Chain analysis, Ansoff Matrix and McKinsey 7S Model on BYD. Moreover, the report contains analyses of BYD business strategy, organizational structure and organizational culture. The report also comprises discussions of BYD marketing strategy, ecosystem and addresses issues of corporate social responsibility. [1] White, E. & Campbell, P. (2024) “Wang Chuanfu, the driving force behind BYD’s rise” Financial Times, Available at: https://www.ft.com/content/22527628-733e-4188-9678-ab3210fdb1ba

Samsung segmentation, targeting and positioning involves a set of activities performed in a sequence. These activities constitute the essence of Samsung marketing strategy. Segmentation involves dividing population into different groups on the basis of their common characteristics. Targeting is associated with selecting specific group(s) as consumers of products and services. Lastly, positioning refers to the selection of the marketing mix the most suitable for the target customer segment. Samsung uses the following types of positioning: Multi-segment positioning. Samsung targets more than one segments at the same time through offering several packages of products and services. For example, there are several variations of Samsung SMART Signage professional displays with different sizes, screen resolutions and functionalities and ultimately with different price tags. Thus, Samsung appeals to the needs and wants of consumers with varying financial capabilities. Imitative positioning. Samsung is known to imitative its main competitor Apple in product in design, functionalities, as well, as marketing strategy. Anticipatory positioning. Certain Samsung products such as mobile image sensors currently have low turnover. However, these product have been developed with the anticipation that the turnover will increase in the future. The following table illustrates Samsung segmentation, targeting and positioning: Type of segmentation Segmen-tation criteria Samsung target customer segment Samsung IT & Mobile Communications Samsung Consumer Electronics Samsung Device Solutions Geog-raphic Region 80 countries worldwide 80 countries worldwide 80 countries worldwide Density Urban/rural Urban/rural Urban/rural Demo-graphic Age 18-65 25-65 25-60 Gender Males & Females Males & Females Males & Females Life-cycle stage Bachelor Stage Newly Married Couples Full Nest I Full Nest II Full Nest III Empty Nest I Empty Nest II Solitary Survivor I Solitary Survivor II Bachelor Stage Newly Married Couples Full Nest I Full Nest II Full Nest III Empty Nest I Empty Nest II Bachelor Stage Newly Married…

Facebook Inc. segmentation, targeting and positioning comprises a set of activities directed at identifying specific groups among the population as potential customers (site users) and developing products and services according to the needs and wants of this specific group. Segmentation involves dividing population into groups according to certain characteristics, whereas targeting implies choosing specific groups identified as a result of segmentation to sell products to. Since its launch in 2004 as a social networking site exclusively for Harvard students, Facebook’s target customer segment has been consistently expanding. Nowadays, the social media giant targets a wide range of customers aged from 13 years old and older. Positioning refers to the selection of the marketing mix the most suitable for the target customer segment. Facebook uses multi-segment type of positioning and accordingly, it targets multiple customer segments at the same time with different social media platforms. For example, Facebook social media site targets individuals interested in a full range of social media services such as pages, news feed events etc., whereas Instagram targets customer segment who are interested exclusively on photo sharing. Facebook Inc. also uses adaptive positioning strategy across its brands, repositioning products and services according to changes in preferences of the target customer segment. The following table 2 illustrates Facebook segmentation, targeting and positioning: Type of segmentation Segmentation criteria Facebook Inc. target customer segment Facebook Messenger Instagram What’s Up Oculus Geographic Region International International International International International Density Urban & rural Urban & rural Urban & rural Urban & rural Urban Demographic Age 13 and upwards 13 and upwards 13 – 40 16 – 45 13 – 40 Gender Males & Females Males & Females Males & Females Males & Females Males & Females Life-cycle stage Bachelor Stage Newly Married Couples Full Nest I Full Nest II Full Nest…

There is a set of macro and micro environmental factors that affect marketing decisions of Tesco marketing management in direct and indirect manners. Macro-environmental factors impacting Tesco marketing decisions are identified through the process of environmental scanning and they include political, economic, social, cultural, technological and legal factors. Micro-environmental factors, on the other hand, relate to the impact of internal and external organisational stakeholders, and the extent of competition in supermarket industry in general. Products and services offered by Tesco and other businesses cannot be attractive to all people in equal terms, because differences in needs and wants among people. Therefore businesses do engage in market segmentation and targeting practices. It can be specified that “market segmentation is based on the generally true concept that the market for a product is not homogenous to its needs and wants”[1]. In simple terms, market segmentation is dividing population members into groups according to their needs, wants and other criteria and developing products and services that aim to satisfy needs and wants of particular groups. Segmentation can be divided into geographic, demographic, psychographic, and behavioural bases. Segmentation, targeting and positioning can be implemented in relation to Tesco brand in general, as well as, its individual products. The Table 2 below specifies target customer segment for Tesco’s own brand TV – Tesco 19-230 18.5 inch Widescreen HD Ready LCD TV DVD Combi with Freeview: Segmentation bases Target customer segment for Tesco Technika 19-230 18.5 inch Widescreen HD Ready LCD TV Geographic Region UK, and 13 other countries Density Rural and urban Demographic Age All age categories Gender Males and females Income Low and middle income category Occupation Students, employees, professionals Education High school, technical, Bachelors, Social status Working class, skilled working class, lower middle class, middle class Family size Single individuals, nuclear…
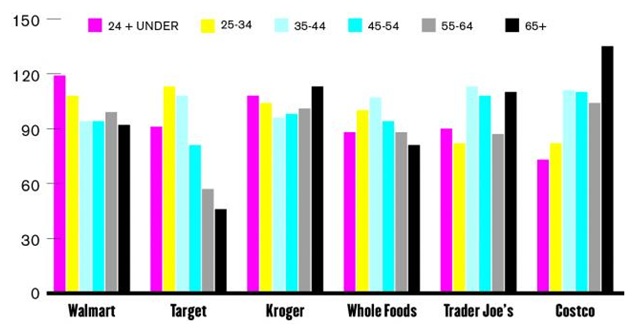
Walmart segmentation, targeting and positioning is the core focus of Walmart strategic marketing. Segmentation refers to dividing population into groups according to certain characteristics, whereas targeting is associated with choosing specific groups identified as a result of segmentation to sell products. Positioning refers to the selection of the marketing mix the most suitable for the target customer segment. Walmart uses mono-segment type of positioning and accordingly, Walmart marketing management appeals to single customer segment who place greater value on the price attribute of products compared to other attributes. The following table illustrates Walmart segmentation, targeting and positioning: Type of segmentation Segmentation criteria Walmart target segment Geographic Region Domestic and international Density Urban and rural areas Demographic Age Individuals of all age categories Gender Males and Females Life-cycle stage Bachelor Stage young, single people not living at home Newly Married Couples young, no children Full Nest I youngest child under six Full Nest II youngest child six or over Full Nest III older married couples with dependent children Empty Nest I older married couples, no children living with them Empty Nest II older married couples, retired, no children living at home Solitary Survivor I in labor force Solitary Survivor II retired Income Individuals and households with low incomes and middle class Occupation Students, manual workers, floor level employees and middle level managers in public and private sectors Behavioral Degree of loyalty ‘Hard core loyals’, i.e. individuals who always purchase the product / brand in question. ‘Switchers’, i.e.individuals who do not specifically seek out a particular brand, but rather purchase the brand available to them at time of need, or that which was on sale Benefits sought Cost advantage Personality Reserved and cost-conscious individuals User status non-users, potential users, first-time users, regular users, or ex-users of a product Psychographic Social class Lower class, working and middle class Lifestyle Resigned,…

The topic of consumer behaviour is one of the massively studied topics by the researchers and marketers in the past and still being studied. Researchers show different reasons as to why consumer behaviour has been the topic of many academics and researchers. One of the common views is that understanding consumer behaviour has become a factor that has a direct impact on the overall performance of the businesses (Kotler and Keller, 2012). Another view suggests that understanding consumer behaviour has become crucial especially due to fierce competition in retail industry in the UK and worldwide (Lancaster et al, 2002). This chapter will introduce some other areas of research background of consumer behaviour addressing the works of researchers and marketers. Moreover, consumer decision making process, in particular, five stages of consumer decision making process will be discussed in detail. Introduction It is worth noting that consumer buying behaviour is studied as a part of the marketing and its main objective it to learn the way how the individuals, groups or organizations choose, buy use and dispose the goods and the factors such as their previous experience, taste, price and branding on which the consumers base their purchasing decisions (Kotler and Keller, 2012). One of such studies of consumer buying behaviour has been conducted by Acebron et al (2000). The aim of the study was to analyze the impact of previous experience on buying behaviour of fresh foods, particularly mussels. In their studies the authors used structural equation model in order to identify the relationship between the habits and previous experience on the consumer buying decision. Their findings show that personal habits and previous experience on of the consumers have a direct impact on the consumers’ purchase decision in the example of purchasing fresh mussels. They also found that the image of the…
