Marketing
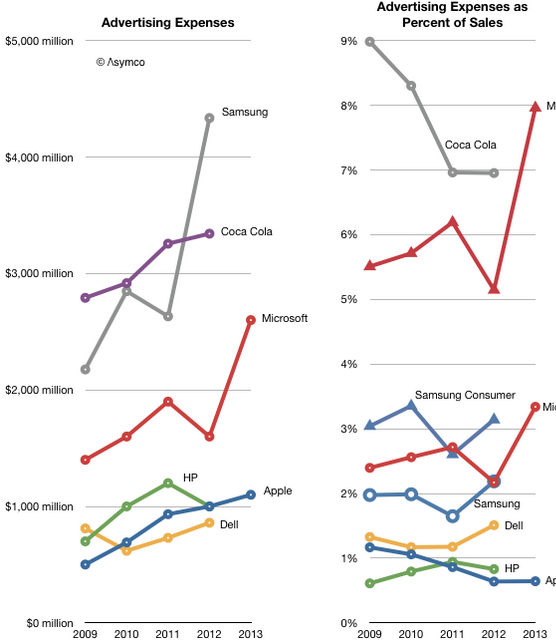
Dell is no longer under any legal obligations to reveal the details of its marketing and other expenses because the company became private as effective from September 2013. Nevertheless, data for the previous periods indicates that the company has been consistently increasing its advertising budget aftermath the global economic and financial crisis of 2007 – 2010. As it is illustrated in figure below, the same strategy has been followed by Dell’s major competitors such as Samsung and Apple, whereas marketing expenses were reduced in 2012 by Dell’s close competitor HP. Changes in Dell advertising expenses[1] Dell marketing message emphasizes low price of its products and the highest level of customization of design and experiences. The marketing message is transmitted to the target customer segment in an integrated manner via advertising, sales promotions, events and experiences, public relations, direct marketing and personal selling elements of the marketing mix. Advertising Dell relies on print and media advertising as one of its main marketing techniques. One of the latest media campaigns named “Future Ready” is a multi-million dollar attempt by Dell to promote its technology solutions for enterprise space makes an emotional appeal by illustrating the role of Dell technology in assisting a little girl receiving a new heart from a donor.[2] “Beginnings” is another noteworthy print and media marketing campaign launched by Dell and the campaign attempts to associate the brand with an entrepreneurial spirit, following the company becoming private in 2013. It is important to note that, “Beginnings” marketing video clip has emerged into a viral video in social media platforms, thus increasing the level of brand awareness to a significant extent. Sales Promotion Sales promotion as a marketing technique is used by Dell in a frequent manner. Dell official website has a dedicated page titled “Dell Coupons, Discounts…

Effective marketing strategy has played a critical role for Coca Cola’s success in the global marketplace. The company has declared its total compliance with the following 4 principles of Responsible Marketing Policy: Choice – providing a great range of product options, so that customers can choose according to balanced diets and active lifestyles. Balance – encouraging the consumption of beverages in sensible manners and moderated amounts. Honesty – adhering to the principles of honesty and transparency in all marketing and sales activities. No marketing to children – marketing of any products should not be aimed at children under the age of 12. In addition to its own marketing initiatives, Coca Cola provides promotional and marketing services to distributors, bottlers and resellers on a discretionary basis. In 2014 marketing expenses of this category amounted to $7 billion respectively[1]. The company has announced ‘One Brand’ marketing campaign that is aimed to unite four different brands – Coca Cola, Diet Coke, Coca Cola Zero and Coca Cola Life under the umbrella of Coca Cola. The level of marketing spending to advertise lower sugar, no sugar and no calorie beverages has been doubled in 2015[2]. Advertising Coca Cola advertising strategy is boldly experiential with innovative design of posters and print and media advertising. The company is announced that media advertising investments will increase by $1 billion by 2016[3]. According to “One Brand” marketing campaign Coca Cola advertising via various channels will feature all four different brands of Coca Cola as illustrated in Figure 2 above. Viral marketing is accepted as an important element of the advertising mix by the company and it is extensively applied to promote specific marketing initiatives such as ‘Sharing a Can, personalization of Cola cans and bottles by printing names, as well as, “Sing For Me” campaign, an initiative that…

Marketing research can be specified as the main tool to impact consumer behaviour in order to increase the levels of consumer loyalty and achieve long-term growth of the businesses. Marketing research can be divided into the following stages: The first stage is associated with problem definition. Range of marketing research problems related to consumer behaviour may include but not limited to assessment of impacts of prices changes or re-branding initiatives on consumer attitudes, establishing the levels of brand value amongst target customer segment etc. The second stage relates to secondary data collection and analysis. Relevant data available in government publications, statistical information, as well as, findings of previously published marketing research papers can be utilised in an extensive manner during this stage. The third stage in marketing research process refers to collection of primary data. The majority of marketing researches are facilitated through primary data collection and analysis. The most popular methods of primary data collection for marketing research include surveys, focus groups, interviews, storytelling, experiments and observations. Moreover, marketing research can also be conducted with application of conjoint analysis, purchase panels, database marketing and netnography. The fourth stage involves primary data analysis. Data analysis can be qualitative, quantitative or integrated according to the nature of problems being researched. Adoption and maintenance of an objective approach plays important role at this particular stage of marketing research process. The fifth stage is devoted to formulation of recommendations. Specifically, alternative set of recommendations or inter-related recommendations can be offered to senior level management on the basis of primary data analysis. The sixth stage in marketing research process involves selection and implementation of a strategy. In most cases internal or external members of team responsible for conducting marketing research do not engage in implementation of recommendations in practical levels. Therefore, it is important…
By John Dudovskiy
Category: Consumer Behaviour

Competition is becoming intensive for virtually all types of products and services and due to this tendency responsibilities of marketing department of companies have increased. Marketing mix can be specified as an effective framework that can be used to increase the overall value of products and services to customers. This article contains analysis of each element of marketing mix by using a variety of secondary data sources. The notion of marketing mix refers to a balance of marketing methods needed to sell products and services. Marketing mix consists of four core elements – product, price, place and promotion that are jointly known as ‘four Ps’. Extended marketing mix contains additional ‘three Ps’ consisting of people, process and physical evidence. Product element of marketing mix Anything that has a potential to satisfy specific customer needs can be specified as product. In modern marketplace learning about customer needs and wants through marketing research precedes development of products and services. Product variables include but not limited to its design, durability, technical features and capabilities, ease of maintenance and others. Businesses use branding in order to differentiate their products and services from other products and services offered in the market. For example, while there is a wide range of soft drinks offered in the market, Coca-Cola drink in particular has a large market share, partially due to successful branding strategy of the company. Importantly, benefits of successful branding go beyond any particular single product to assist the sales of other products offered by the company as well. Positive image of Apple brand assists sales of MacBook desktop computers, as well as, other products offered by the company such as IPhone and IPad. Benefits of products and services have tremendous on the levels of revenues and these benefits can be divided into three categories:…

This article represents a critical analysis of marketing communications materials used by Coca-Cola Company, a global beverage manufacturer and retailer based in Georgia, United States. The Coca Cola Company is a global manufacturer, marketers and seller of non-alcoholic beverages and syrups based in Atlanta, US. Range of brands owned by the company includes Coca-Cola, Diet Coke, Coca Cola Zero, Sprite, Fanta, Powerade, Minute Maid, Aquarius, Dasani, Schweppers and others. This article focuses on marketing communication materials associated with one of its core products, the Coca-Cola drink. Established in 1886, the company currently sells in more than 200 countries and beverage trademarks owned and licensed by the company account for 1.9 billion of approximately 57 billion beverage servings around the globe on a daily basis (Annual Report, 2013). The article starts with description and analysis of various types of media employed in order to promote the Coca-Cola, followed by the identification of objectives of Coca-Cola campaign. Then, extensive analysis of images and words used in Coca-Cola campaign is undertaking in order to ensure a greater scope for the current research. Moreover, attempts are made to analyse the appeal of Coca-Cola marketing messages, as well as, assessments are provided at what extent Coca-Cola marketing campaigns were achieving their objectives. Types of Media used to Promote Coca-Cola Media can be defined as a “facilitating institution who suggest appropriate message within the operative constraints of space” (Tyagi and Kumar, 2004, p.341) and is considered to be one of the most effective advertisement methods among marketing practitioners. Spurgeon (2008) divides media into two categories: published media and visual/aural media. Published media includes newspapers, magazines, trade and professional press, as well as internet. Visual and aural media, on the other hand, include television, radio, cinema, posters, billboards, and direct mailing. Various types of media are used…

The 21st century has been dubbed as an information age (Bell and Blanchfower, 2011) and internet in general, and social media in particular are playing an instrumental role in facilitating the spread of information throughout the globe at a rapid speed. Moreover, increasing levels of interactivity of social media platforms is further contributing to the level of their popularity, and nowadays social media has been effectively adopted by many businesses along a wide range of industries as a highly effective marketing and communication platform. At the same time, the level of use of social media varies between various industries, as well as, individual organisations within a particular industry, and while some organisations are beginning to realise substantial opportunities offered by social media, others are already utilising these opportunities to a full extent. This essay contains a critical evaluation of the role of social media on the popularity of a tourism destination. The essay starts with discussions about increasing influence of social media on consumer behaviour. This is followed by critical analyses of potential benefits of social media to hospitality organisations. Moreover, issues related to negative impacts of social media on the performance of hospitality organisations are also addressed in this essay. Essay is concluded by providing a set of recommendations to strategic and marketing managers of hospitality organisations in terms of benefiting from opportunities offered by social media to a maximum extent. Introduction 1 Increasing influence of social media on consumer behaviour in service sector 2 Potential benefits of social media to hospitality organisations 5 Negative impacts of social media on the performance of hospitality organisations 8 Recommendations for managers of hospitality organisations in relation to social media 10 Conclusions 14 References 16 Cathay Pacific DoubleTree Club Hotel Facebook Hampton Hotels Twitter How do I receive the report? Once payment…

Competitive advantage has been defined as “something that the firm does better than its competitors that give it an edge in serving customers’ needs and/or maintaining mutually satisfying relationships with important stakeholders” (Ferrell, 2012, p.16). Core competency has been explained by Prahalad and Hamel (1990) as collective learning within organisations in terms of coordinating various kills and increasing the level of integration of multiple streams of technology. The concept of core competency is proposed by Prahalad and Hamel (1990) as collective learning within organisations in terms of coordinating various kills and increasing the level of integration of multiple streams of technology. Prahalad and Hamel (1990) argue that core competencies can be identified by asking following three questions: Firstly, which aspects of a product or service can provide it access to other markets? Secondly, which aspects of a product or service are perceived by potential and current customers as increasingly valuable? Thirdly, what are the specific elements associated with brand in general and/or product or service in particular that are difficult to be imitated by competitors? According to William and Curtis (2008) basing core competencies on product features and capabilities may prove to be counter-productive in terms of adapting to changes in external market environment. In other words, William and Curtis (2008) argue that core competency may become a core rigidity imposing threats to long-term growth prospects of the business. Practical implications of the concept of core competency are credited for the appreciation of importance of competitive advantage. It has been noted that “competitive advantage results when more customers become strong attached to the products of the organisation” (Sekhar, 2010, p.51). Boone and Kurtz (2013) discuss the role of imitability of competitive advantages for long-term growth prospects of businesses. Boone and Kurtz (2013) propose that low-order competitive advantages such as cost advantage…

The Chartered Institute of Marketing defines marketing as “the management process responsible for identifying, anticipating, and satisfying customer requirements profitably”. Definition of marketing offered by American Marketing Association, on the other hand, is worded as “the activity, set of institutions, and processes for creating, communicating, delivering, and exchanging offerings that have value for customers, clients, partners, and society at large” (AMA, 2014, online) Alternatively, marketing can be defined as “a business orientation that focuses on satisfying customers’ needs at acceptable levels of revenues and costs” (Loudon et al., 2010, p.2). Elements of marketing process of Tesco contain the following: 1. Analysis of the market and environment. Strategic tool to conduct this analysis include PESTEL, SWOT, Porter’s Five Forces, Value-Chain analysis and others. 2. Identification of the marketing target. Tesco targets specific segment of population in the UK and other countries where the supermarkets of the company operate. 3. Setting marketing objectives. Marketing objectives of Tesco include profit maximisation in short-term and long-term perspectives and increasing the value of the brand image. Marketing objectives of Tesco are closely associated with their business strategy which consist of the following seven elements (Vision and Strategy, 2013, online): a) to be growing the UK core, b) increasing international presence through offline and online channels, c) growing retail services in present markets, d) focus on corporate social responsibility, e) enhancing brand value, f) engaging in more diversification and g) creating value through teamwork. 4. Dealing with elements of the marketing mix. The importance of dealing with each elements of marketing mix taking into account needs, wants and other unique characteristics of target customer segment is fully understood by Tesco management. 5. Reflection, control and revision. This element of marketing process is used by Tesco marketing management in a periodic manner in order to assess the levels of effectiveness of…
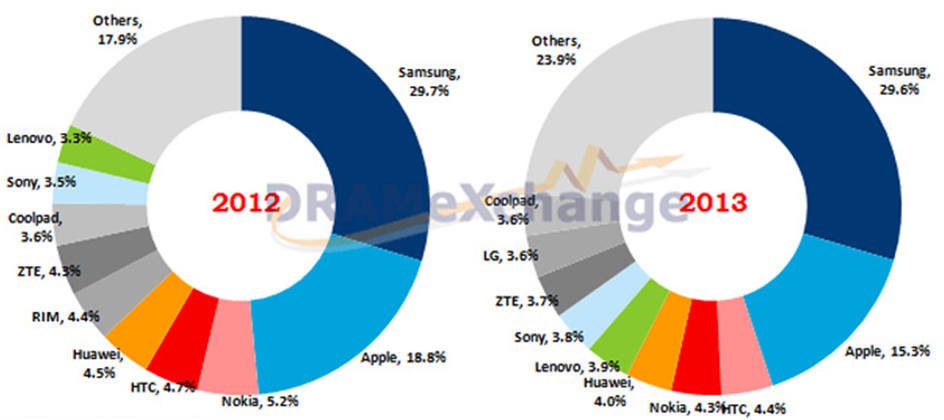
Effectiveness of branding strategy is one of the most important critical success factors in business regardless of industry or geographical location of the company. Donelly (2009) stresses the importance of intangible elements of brands that include social meanings, symbolism, and a type of culture associated with the brand. Boone and Kurtz (2013) confirm this viewpoint and relate the benefits derived from intangible elements of brand to high levels of customer loyalty. Moreover, business scholars convincingly argue that “a brand represents the full ‘personality’ of the company and is the interface between a company and its audience” (Davis, 2009, p.12). HTC has been founded in 1997, and has shorter history and heritage compared to its major competitors. Nevertheless, HTC marketing management has been able to link the brand image with an effective harmony between the price and quality. This marketing message is integrated into the official slogan of the brand ‘quietly brilliant’ that can be interpreted in a way that although HTC does not engage in expensive marketing campaigns, its smartphones can compete with the products of other brands in equal terms. HTC operational cost advantage achieved through economising on marketing and a set of other business processes are passed to consumers to sustain its main competitive advantage of cost effectiveness. Changes in global smartphone market share Source: DrameXchange (2014, online) As it is illustrated in Figure above HTC market share in the global marketplace has decreased by 0.4 per cent, from 4.7 per cent in the first quarter of 2012 to 4.3 per cent of the same quarter of 2013. Generally, the global market of smartphones has grown by 37 per cent during 2012, and the extent of market penetration in smartphone industry within top 19 markets has been assessed at 35.5 per cent and this number is expected to…
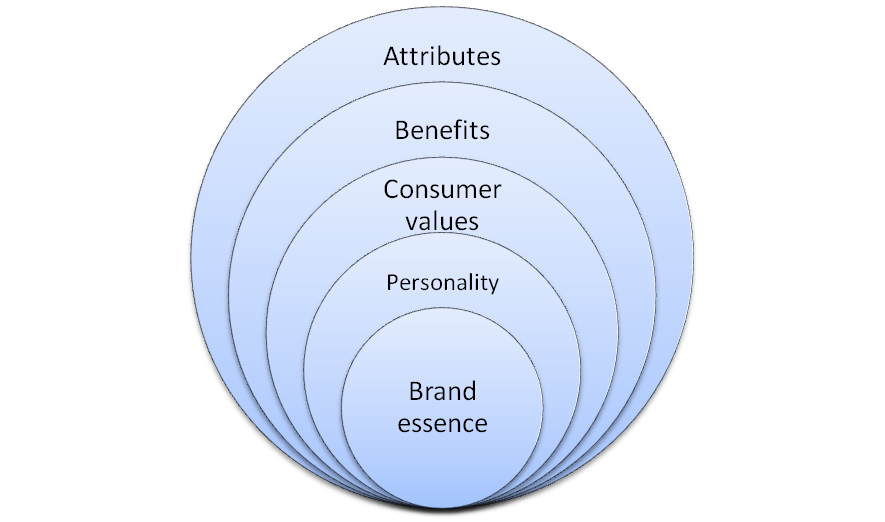
HTC Corporation is a global smartphone designer and manufacturer based in Taiwan and the company has generated the revenues of NT$289 billion in 2012 with consolidated operating margin at 6.51% (Annual Report, 2012). Brand essence represents the core of the company and it is impacted by the following elements that constitute brand essance wheel: Attributes of HTC brand in general relate to thin, candy bar form of smartphones with large displays and these attributes have been applied to HTC Desire 600 model as well. Benefits offered by HTC Desire 600 include using certain functionalities of a computer on a mobile phone, whereas on emotional level, these benefits also include sense of being cool, trendy and productive. Consumer values associated with HTC Desire 600 relates it the price aspects of the product. Specifically, while product benefits discussed above are offered by other companies as well such as Apple, Samsung, and Google, cheaper price of HTC Desire 600 compared to many other similar products is perceived to be as a valuable point by consumers. Brand personality relates to a set of human characteristics that can be applied to brands. Components of brand personality include sincerity, excitement, competence, ruggedness and sophistication (Franzen and Moriarty, 2009). According to this categorisation, HTC brand personality can be classified as excitement, because it integrates the elements of cool, youth and fun. HTC Desire 600 benefits and value as explained above reflects changes in consumer needs and wants in a direct manner. In other words, intensive levels of competition in smartphone industry have increased the levels of customer expectations, needs and wants in relation to smartphones. HTC Desire 600 addresses this change by integrating most of the latest developments in smartphone technology in the product and offering the product for a competitive price. References Annual Report (2012)…
