Posts Tagged ‘Retail’

Tesco business strategy can be described as cost leadership and its motto ‘Every Little Helps’ guides its business strategy to a considerable extent. Economies of scale is one of the main competitive advantage extensively exploited by Tesco due to the vast scale of its operations. Tesco business strategy has traditionally involved experimentation with various aspects of the business and this strategy changed the overall retail industry in the UK to a certain extent. For example, Tesco was the first retailer to introduce 24-hour shopping experience and today it has thousands of Click & Collect points across the country.[1] Tesco business strategy for the short-term is aimed at regaining stakeholder trust in general and customer trust in particular following commercial income reporting scandal in 2015. The senior level management has announced that this objective will be achieved via the following set of initiatives: Focusing on availability, service and selectively on price Undertaking a significant programme of restructuring and financial discipline Launching a programme of renewal to restore trust in every aspect of the brand Moreover, as an outcome of income reporting scandal combined with a set of other factors, Tesco is currently in a difficult financial position with a total leverage debt of GBP 22 billion and the net debt of GBP 8.5 billion.[2] The following initiatives have been introduced by the senior level management in order to reduce the volume of debt: Not paying final dividends to shareholders for the financial year 2014/15 Reducing the amount of capital expenditure to GBP 1 billion Replacing defined benefit pension scheme for all employees Reviewing Tesco’s property portfolio, including leases that amount to GBP 1.5 billion annual rent bill The sale or closure of all three Blinkbox businesses (movies, music and books) and Tesco Broadband Tesco PLC Report contains more detailed discussion of…

There is a set of macro and micro environmental factors that affect marketing decisions of Tesco marketing management in direct and indirect manners. Macro-environmental factors impacting Tesco marketing decisions are identified through the process of environmental scanning and they include political, economic, social, cultural, technological and legal factors. Micro-environmental factors, on the other hand, relate to the impact of internal and external organisational stakeholders, and the extent of competition in supermarket industry in general. Products and services offered by Tesco and other businesses cannot be attractive to all people in equal terms, because differences in needs and wants among people. Therefore businesses do engage in market segmentation and targeting practices. It can be specified that “market segmentation is based on the generally true concept that the market for a product is not homogenous to its needs and wants”[1]. In simple terms, market segmentation is dividing population members into groups according to their needs, wants and other criteria and developing products and services that aim to satisfy needs and wants of particular groups. Segmentation can be divided into geographic, demographic, psychographic, and behavioural bases. Segmentation, targeting and positioning can be implemented in relation to Tesco brand in general, as well as, its individual products. The Table 2 below specifies target customer segment for Tesco’s own brand TV – Tesco 19-230 18.5 inch Widescreen HD Ready LCD TV DVD Combi with Freeview: Segmentation bases Target customer segment for Tesco Technika 19-230 18.5 inch Widescreen HD Ready LCD TV Geographic Region UK, and 13 other countries Density Rural and urban Demographic Age All age categories Gender Males and females Income Low and middle income category Occupation Students, employees, professionals Education High school, technical, Bachelors, Social status Working class, skilled working class, lower middle class, middle class Family size Single individuals, nuclear…
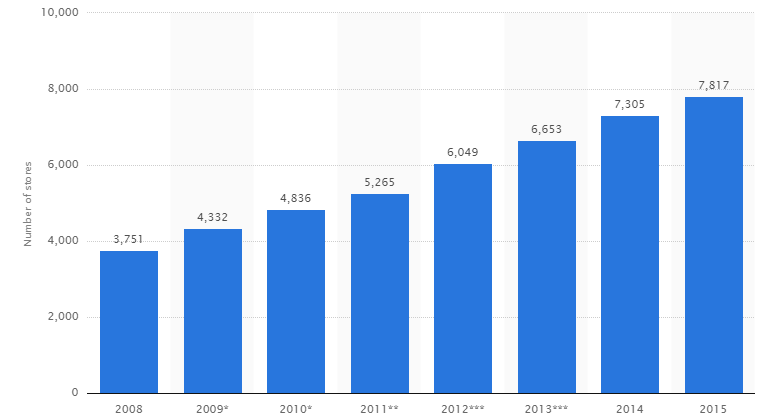
The term marketing mix “is used to describe the tools that the marketer uses to influence demand”[1]. Traditionally, marketing mix contained four elements – product, price, place, and promotion, and additional elements that have added to the concept of marketing mix consist of people, process and physical evidence. Tesco marketing mix is manipulated by the marketing and the senior management to a great extent in order to offer competitive benefits to target customer segment with positive effects on the bottom line. Product. Tesco offers a comprehensive range of products. Specifically, along with food and grocery products the following product categories can be purchased from the supermarket chain: Clothing & jewelry Technology & gaming Health & beauty Home electrical Entertainment & books Home appliances Baby & toddler Garden Toys DIY & Car accessories The range of product categories sold in Tesco stores depend on the type of store with Express stores having the least variety of products and Extra stores offering the widest choice. Moreover, Tesco Bank offers a range of popular banking products such as mortgages, credit cards, personal loans and savings. Place. Place element of the marketing mix relates to locations where customers purchase products and services and the distribution of products to those locations. Tesco utilises two channels to sell its products and services: online and offline. As it is illustrated in figure below, despite the global financial and economic crisis of 2007 – 2009 and other challenges faced by the company, the number of Tesco stores have been consistently increasing for the last eight years to reach 7817 stores in 11 countries by the end of 2015. More than two-thirds of total Tesco sales are made in the UK.[2] Stores are operated in the following format: Metro Express Extra Superstore Changes in the number of Tesco stores worldwide[3] Online sales…

Tesco PLC is a UK-based global supermarket chain and it has 7817 shops and 517,802 employees around the world. Founded in 1919 by Jack Cohen, Tesco has emerged to become the biggest retailer in the UK and more than 80 million shopping trips are made to Tesco stores each week (Annual Report, 2015). Tesco’s mission statement is “to be the champion for customers – to help everyone who shops with us enjoy a better quality of life and an easier way of living”. Tesco business strategy can be described as cost leadership with a focus on availability, range and customer service. During the financial year of 2015, the group sales amounted to GBP 69.7 billion with the group trading profit of GBP 1.4 billion, however, the company made a net loss of GBP 6.4 billion during the same period (Annual Report, 2015). Along with market saturation, such a poor financial performance has been caused by a series of scandals that include an overstatement of commercial income by GBP 208 million (Rigby, 2015) and the cases of supplier mistreatment. It has been revealed that the supermarket chain demanded a payment of GBP 1 million from one of its suppliers, L’Oreal (Ahmed, 2015) and the company has been found to delay payment to suppliers in order to improve its operational profit margins in 2014 (Simpson, 2016). These scandals caused a severe damage to Tesco’s brand image and replacement of the leadership at the top level. The new leadership headed by a new Chairman of the Board John Allan and new CEO Dave Lewis pledged to restore the trust towards the brand via focusing on the core values that had made Tesco popular in the first place. Tesco PLC Report contains the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such…
SWOT is an abbreviation that is interpreted as strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats related to businesses. The table below illustrates the main points of Tesco SWOT analysis: Strengths 1. Leadership position in the UK 2. Effective online operations 3. Clubcard as an effective consumer information tool 4. Strong property portfolio Weaknesses 1. Weak financial performance 2. Serious damage to the brand image due to commercial income scandal in 2015 3. Reliance on the UK market 4. Diminished employee morale Opportunities 1. Pursuing international market expansion strategy 2. Increasing presence in financial services industry 3. Increasing non-food retail range 4. Enhancing the effectiveness of the marketing strategy Threats 1. Inability of the new leadership to turn over the business 2. Inability to sustain cost leadership competitive advantage 3. Currency fluctuations 4. Emergence of new ethics-related problems Tesco SWOT analysis Strengths 1. Tesco is the biggest retailer in the UK with a grocery market share of 27.9 per cent. Its closest competitor Sainsbury’s has the market share of only 16.6 per cent and the market share of Walmart-owned ASDA is equal to 16.4 per cent.[1] Possessing the largest market share is an important strength regardless of the industry and this position allows Tesco to generate substantial revenues, given it addresses 7Ps of marketing mix in an appropriate manner. 2. The company utilizes online sales channel with a high level of efficiency. Tesco was among the first retailers in the UK to successfully implement online sales channel and currently, revenues generated via online sales account for a solid share of the total revenues. Specifically, in 2015 Tesco online grocery market grew ahead of the market at 20 per cent although the company posted pre-tax loss of GBP 6.37 billion during the same year.[2] The growth of online sales ahead of the market despite…

Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) is a critically important aspect of the business for any company of a large size, including Walmart. Walmart CSR strategy rely on the following three principles[1]: Creating economic opportunity for our employees, suppliers and people who work in retail and retail supply chains beyond Walmart Enhancing the sustainability of operations and product supply chains for people and the planet Building strong communities where the retailer operates Walmart’s aims to achieve the following 3 aspirational goals formulated in 2005 by Lee Scott, who was Walmart CEO at the time: Supply the company with 100 per cent renewable energy Create zero waste Sell products that sustain people and the environment The company releases Global Responsibility Report annually and it includes the details of Walmart CSR programs and initiatives engaged by the company. The table below illustrates highlights from the latest report for 2015: Categories of CSR activities Walmart Performance Supporting local communities In UK, Asda donated more than 10,000 grants as part of the Chosen By You, Given By Us program in 2014More than USD 100 million awarded in state and neighbourhood grants by Walmart and Walmart foundation in the US Walmart employees in the US volunteered over 1.5 million hours in their local communities in 2015 USD 14 million was donated by Walmart to the causes in “dollar-for-doer” grants Educating and empowering workers Results if a survey involving more than 2 million employees worldwide indicate that 4 or 5 are proud to work at WamartIn February 2015, the company announced a USD1 billion investment in U.S. hourly associates to provide higher wages, more training and increased opportunities to build a career with Walmart.[2] More than USD 100 million grants will be funded by Walmart foundation to accelerate mobility of retail workers from entry- to middleskills jobs, Labor and human…
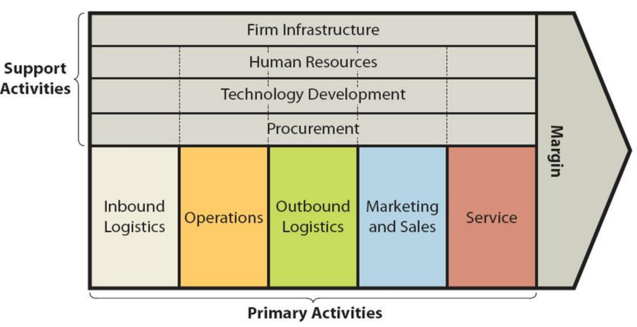
Value chain analysis is an analytical framework that assists in identifying business activities that can create value and competitive advantage to the business. The figure below illustrates the essence of value chain analysis. Walmart Value chain analysis Primary Activities Inbound logistics It has been estimated that more than 50 per cent of Walmart products in the US come from overseas suppliers[1] and about 75 percent of walmart.com sales come from non-store inventory [2]. Generally, Walmart inbound logistic practices are based on the following three principles: Using the minimum amount of links in the supply chain. Starting from 1980s, Walmart began to ruthlessly eliminate traders in its supply chain opting to work with manufacturers directly. Such a strategic decision proved to have a positive impact on the bottom line after a few years. Specifically, “in 1989, Wal-Mart was named Retailer of the Decade, with distribution costs estimated at a mere 1.7% of its cost of sales – far superior to competitors like Kmart (3.5%) and Sears (5%)”[3]. The efficiency of Walmart supply chain practices has further improved since in a consistent manner. Forming strategic partnerships with vendors. Walmart imposes strict conditions on various aspects of the business when negotiating with potential suppliers. The company also attempts to purchase for the lowest prices applying its huge bargaining power in order to be able to maintain cost leadership competitive advantage. However, once a potential vendor is contracted as a supplier, Walmart offers a strategic partnership for long-term perspective and engages in high volume purchases, although for lower prices. Using cross docking as an inventory tactic. Cross docking implies “the direct transfer of products from inbound or outbound truck trailers without extra storage, by unloading items from an incoming semi-trailer truck or railroad car and loading these materials directly into outbound trucks, trailers, or…
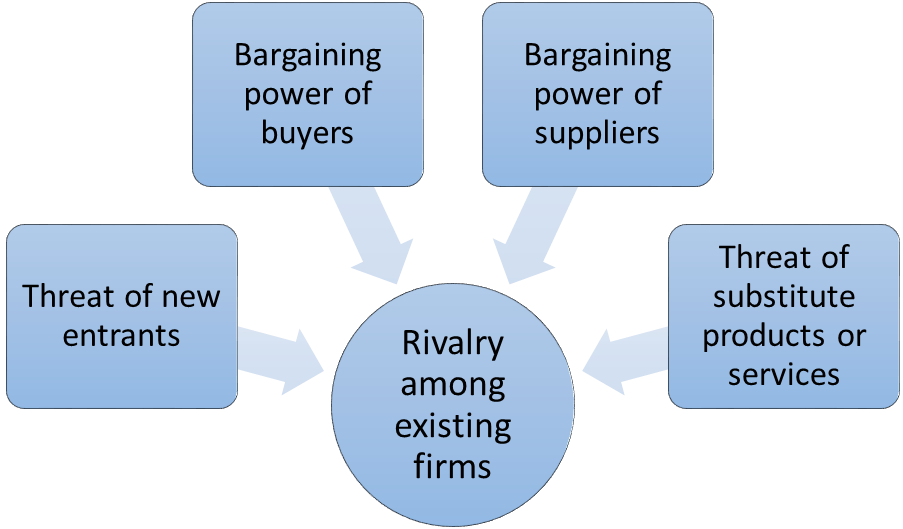
Porter’s Five Forces analytical framework developed by Michael Porter (1979)[1] represents five individual forces that shape the overall extent of competition in the industry. Walmart Porter’s Five Forces are represented in Figure 1 below: Figure 1. Walmart Porter’s Five Forces Rivalry among existing firms is intense. Walmart is engaged in cut throat competition with many other grocery retail chains and supermarkets such as Costco Wholesale Corporation, Dollar General Corporation, Dollar Tree, Inc., Kohl’s Corporation, Macy’s Inc, Sears Holdings Corporation, Target Corporation and others. At the same time, as it is illustrated in Figure 2 below, the pattern of changes of grocery industry concentration for more than two decades has been in favor of major market players such as Walmart, Kroger, Costco and Safeway. Market share of these large companies have been consistently increasing compared to grocery stores of smaller sizes partially due to the cost advantage gained via economies of scale. Figure 2. Changes in industry concentration in the US grocery market[2] Threat of substitute products or services. Walmart sells thousands of products belonging to the following categories: groceries entertainment health and wellness – including pharmacy hardlines – including stationery, auto spares, and accessories hardware apparel home furnishings household appliances It can be argued that the threat of substitute products is irrelevant for Walmart due to the abundant range of products sold by the retailer. In other words, Walmart sells a wide range of products, as well as, substitutes to this products, therefore, the impact of this particular threat to Walmart can be stated to be irrelevant. Bargaining power of Walmart suppliers is insubstantial. Due to the size and the scope of its business, Walmart secures the lowest prices from its suppliers to sustain its cost leadership competitive advantage. Walmart paid its suppliers USD 13.5 billion in total in 2015 alone.[3] Along with…

Walmart marketing budget equaled to USD2.4 billion for both fiscal 2015 and fiscal 2014 and USD2.3 billion for the fiscal year of 2013[1]. These funds are invested in Walmart marketing communication mix that include print and media advertisements, viral marketing, sales promotions, events and experiences, public relations and direct marketing components of the marketing communication mix. Advertising Traditionally, print and media advertising has represented the core of Walmart marketing strategy for many years. However, in 2015, Walmart Vice President Wanda Young announced planned shift of the main focus from the print advertising to the mobile marketing campaigns.[2] Such a change in Walmart marketing strategy is expected to target young people in general and Millenials in particular. Viral marketing is another direction that is being extensively utilized by Walmart with varying levels of success. For example, Walmart marketing video ‘Work is a Beautiful Thing: Meet Patrick’ released in 2014 has attracted more than 1.2 million views in just six days with thousands of positive comments and with evident positive implications on the brand image.[3] Nevertheless, Walmart still uses print and media advertising to a considerable extent and the company places advertisements on newspapers, magazines and TV channels popular with the target customer segment. Sales Promotion Sales promotion is used by Walmart in an extensive manner. The retailer launches seasonal sales promotions in a regular manner along with sales promotions in before and during public holidays and other memorable days. Particularly, Black Friday is a massive sales promotion day for Walmart each year eagerly anticipated by millions of customers. Walmart maintains Daily Savings Center section in its official website where online and offline sales promotion offers are announced. Sales promotion also has been adapted as an effective tool to increase the sales of Sam’s Club segment of the business. Specifically, the emphasis of…
Walmart segmentation, targeting and positioning is the core focus of Walmart strategic marketing. Segmentation refers to dividing population into groups according to certain characteristics, whereas targeting is associated with choosing specific groups identified as a result of segmentation to sell products. Positioning refers to the selection of the marketing mix the most suitable for the target customer segment. Walmart uses mono-segment type of positioning and accordingly, Walmart marketing management appeals to single customer segment who place greater value on the price attribute of products compared to other attributes. The following table illustrates Walmart segmentation, targeting and positioning: Type of segmentation Segmentation criteria Walmart target segment Geographic Region Domestic and international Density Urban and rural areas Demographic Age Individuals of all age categories Gender Males and Females Life-cycle stage Bachelor Stage young, single people not living at home Newly Married Couples young, no children Full Nest I youngest child under six Full Nest II youngest child six or over Full Nest III older married couples with dependent children Empty Nest I older married couples, no children living with them Empty Nest II older married couples, retired, no children living at home Solitary Survivor I in labor force Solitary Survivor II retired Income Individuals and households with low incomes and middle class Occupation Students, manual workers, floor level employees and middle level managers in public and private sectors Behavioral Degree of loyalty ‘Hard core loyals’, i.e. individuals who always purchase the product / brand in question. ‘Switchers’, i.e.individuals who do not specifically seek out a particular brand, but rather purchase the brand available to them at time of need, or that which was on sale Benefits sought Cost advantage Personality Reserved and cost-conscious individuals User status non-users, potential users, first-time users, regular users, or ex-users of a product Psychographic Social class Lower class, working and middle class Lifestyle Resigned,…
