Strategy

People-to-people platform of Airbnb benefits all its stakeholders, including hosts, guests, employees and the communities in which it operates. According to its CEO, Airbnb is “a more vertically integrated, end-to-end, full-stack ecosystem powered by people.”[1] Generally, Airbnb ecosystem can be divided into two groups: narrow and broad. Narrow Airbnb ecosystem comprises services that directly generate revenues for Airbnb, while broad ecosystem contributes to the development of peer-to-peer lodging, travel and experiences industry in general. Airbnb ecosystem in a narrow level integrates the following types of services: Accommodation Experiences Adventures Restaurants The travel industry disruptor supports stakeholders in its narrow ecosystem in various manners. For example, in a rare event of accidental damage, the property of every Airbnb host is covered up to a million dollars.[2] Airbnb has caused an ecosystem of new start-ups that produce products and services for peer-to-peer lodging industry. This can be specified as broad Airbnb ecosystem and includes a range of products and services. Table below illustrates the most popular types of such services referring to notable examples: Products and services within Airbnb ecosystems Notable examples Cleaning services of properties FlyCleaners: On-Demand Dry-Cleaning App Proply: Full-service cleaning, key delivery, welcome gifts and restocking Porter: laundry, cleaning, restocking Property management for hosts Guesty: responding to guest inquiries, screening potential guests, coordinating key exchange etc. Urban Bellshop: check-in, listing management, cleaning Nest: controlling temperature, Analytics Beyond Pricing: automated pricing suggestions Smart Host: pricing advice Everbooked: pricing suggestions based on a wide range of factors Services within broad Airbnb ecosystem Additional products and services within Airbnb broader ecosystem include automating check-in process, providing keyless entry around the clock, concierge services and welcoming guests and software products such as data presentation and analytics. Moreover, physical products such as toiletries, remote locks, and noise signallers and financing services for Airbnb hosts…
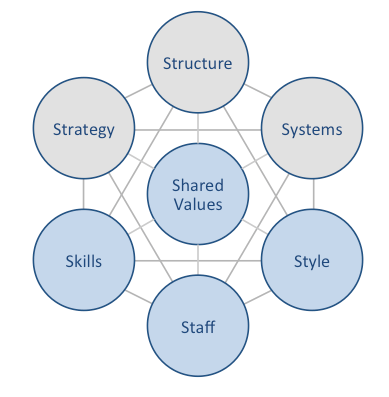
Airbnb McKinsey 7S model illustrates the ways in which seven elements of businesses can be aligned with positive implications on the overall effectiveness of the business. According to this framework strategy, structure and systems are grouped as hard elements, whereas shared values, skills, style and staff are considered soft elements. According to McKinsey 7S model, there are strong links between individual elements. Specifically, a change in one element causes changes in others. As it is illustrated in figure below, shared values are positioned at the core of Airbnb McKinsey 7S model; they guide employee behaviour with implications on their performance. Airbnb McKinsey 7S model Hard Elements in Airbnb McKinsey 7S model Strategy. Airbnb business strategy is associated with platform business model and accordingly, instead of owning the services it offers, the company engages as a broker between suppliers and consumers, receiving a commission of 9% to 15%. Moreover, increasing level of technological integration into various aspects of the business can be specified as one of the critical features of Airbnb business strategy. The global hospitality service brokerage company also places its community and trust among organizational stakeholders at the forefront of its business strategy. Structure. Airbnb organizational structure can be classified as matrix. The workforce is divided into teams of up to 10 people. Importantly, teams support each-other to a great extent. Team leaders and members feel free to ask other teams if they need resources or capabilities. Airbnb organizational structure can be also branded as holocratic, because decision making power is given to teams throughout organization to a great extent and majority of teams are self-managed. The corporate structure of Airbnb is highly dynamic due to rapidly increasing scale of the business worldwide. Systems. Airbnb business operations depend on a wide range of internal systems such as employee recruitment and…
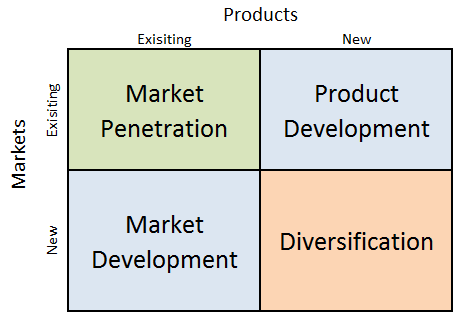
Airbnb Ansoff Matrix is a marketing planning model that helps the global hospitality service brokerage company to determine its product and market strategy. Ansoff Matrix illustrates four different strategy options available for companies. These consist of market penetration, product development, market development and diversification. Airbnb Ansoff Matrix Within the scope of Ansoff Matrix, Airbnb uses all four growth strategies in an integrated manner: 1. Market penetration. Market penetration involves the sales of existing products to existing markets. The accommodation and experience marketplace uses market penetration strategy extensively. Airbnb marketing strategy and exceptional customer services play instrumental role in engaging in market penetration by Airbnb. 2. Product development. This strategy is associated with developing new products to sell to existing markets. Product development is one of the main growth strategies for the global rental and experiences platform. Specifically, starting only as a short-term accommodation provider in 2008, Airbnb consequently increased its service portfolio to include experiences, adventures and restaurants services. 3. Market development. Market development strategy refers to finding new markets for existing products. The global rental and experiences platform aggressively engages in market development. Airbnb started its operations in San Francisco, California and today it has more than 6 million listings in more than 191 countries and regions worldwide.[1] Moreover, there are about 100000 cities with Airbnb listings.[2] 4. Diversification. Diversification can be explained as developing new products to sell to new markets. The global lodging company has engaged in diversification business strategy a number of times. Entering the industry as cost-effective accommodation provider for cost-conscious travellers, Airbnb has diversified the business to also serve premium market segment with respective offerings such as villas, mansions and even castles. Airbnb Inc. Report contains a full analysis of Airbnb Ansoff Matrix. The report illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks…

Airbnb, the lodging colossus, has been prudent from the financial point of view. It is important to note that the company hasn’t raised any money from investors since March 2017, when it raised USD448 million. CEO Brian Chesky has pledged to hold an IPO for the 10-year-old company before 2020 when some employee stock grants expire.[1] At a close look, Airbnb business strategy consists of the following three elements: 1. Following a platform business model. A platform business model can be defined as a “business model that focuses on helping to facilitate interactions across a large number of participants”[2] In case of Airbnb, participants are host who offer their properties or organize experiences for guests and travellers who use their services. Airbnb does not own any real estates it lists, not does it host events and experiences it offers. It serves as a broker between suppliers and consumers, receiving a commission of 9% to 15%. 2. High level of technology integration into various business processes. It is a cornerstone of Airbnb business strategy. The company uniquely leverages technology to economically empower millions of people around the world to unlock and monetize their spaces, passions and talents to become hospitality entrepreneurs.[3] The travel industry disruptor currently uses machine learning to improve search, prevent fraud, help hosts optimize pricing, match users with the most relevant listings and other practices vital for the business. Moreover, Airbnb is exploring machine learning algorithms and AI to build a deeper understanding of images, improve reviews using natural language processing (NLP) and support more advanced search using NLP. 3. Focus on community and trust. Cultivating community and maintaining trust among stakeholders is one of the solid bases of Airbnb competitive advantage. The global lodging company maintains a community centre as a place to connect…

Microsoft ecosystem integrates the following types of products and services: Category Products and services Productivity and Business Processes Microsoft 365, SharePoint, Skype for Business, Outlook Mobile, One Drive, Dynamics 365, Microsoft Teams, Linked In Intelligent Cloud Server products and cloud services, including SQL Server, Windows Server, Visual Studio, System Center, and related CALs, as well as Azure Enterprise Services, including Premier Support Services and Microsoft Consulting Services More Personal Computing Windows Devices, including Microsoft Surface (“Surface”), phones, and PC accessories. Gaming, including Xbox hardware; Xbox Live, Search advertising. Products and services within Microsoft Ecosystem It can be argued that Microsoft ecosystem is aimed at enterprise customers to a greater extent compared to individual users. Specifically, Microsoft enterprise products and cloud services are effectively tied together and this generates strong incentives for businesses to use Microsoft products and services. For example, OneDrive for Business leads into Sharepoint, Teams integrates with Outlook and is about to swallow Skype for Business, Dynamics CRM and SQL Server can integrate and pull data from Azure AD. Moreover, there are many Office 365 programs and services that integrate with each other under a single sign-on. Similarly, Windows ecosystem which includes the platform, games, apps, the Store, and Minecraft, as well as the Windows 10 family of devices, including Surface, Xbox, and HoloLens. the multinational technology company is expected to further invest into its ecosystem to make it stronger in the medium-term and long-term perspectives. Microsoft Corporation Report contains a full analysis of Microsoft ecosystem. The report illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces, Value Chain analysis, Ansoff Matrix and McKinsey 7S Model on Microsoft. Moreover, the report contains analyses of Microsoft leadership, business strategy, organizational structure and organizational culture. The report also comprises…
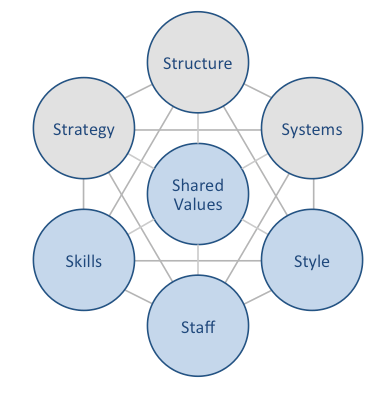
Microsoft McKinsey 7S model shows how seven elements of businesses can be aligned to increase effectiveness. According to this framework, strategy, structure and systems represent hard elements, whereas shared values, skills, style and staff are soft elements. McKinsey 7S model stresses the presence of strong links between elements in a way that a change in one element causes changes in others. As it is illustrated in figure below, shared values are positioned at the core of Microsoft McKinsey 7S model, since shared values guide employee behaviour with implications in their performance. Microsoft McKinsey 7S model Hard Elements in Microsoft McKinsey 7S Model Strategy. Microsoft business strategy can be classified as product differentiation. The company develops advanced technology products and services and sells them for premium costs. Moreover, Microsoft business strategy is currently focused on “cloud-first, mobile-first”, growth through mergers and acquisitions and exploring business opportunities related to augmented and virtual reality. As the latest addition to its business strategy, the multinational technology company is focusing on the concept of ‘tech intensity’, which aims to position Azure as the worlds’ computer with evident positive implications on the long-term growth prospects of the business. Structure. Microsoft organizational structure is divisional and such a structure resulted from a restructuring initiative introduced by CEO Satya Nadella in 2015. Microsoft engineering group is divided into three divisions: Cloud and AI Group, Experiences + Devices and Artificial Intelligence and Research. Business functions, on the other hand, are divided into nine divisions. Microsoft corporate structure is highly dynamic and ever-evolving to meet the demands of changing external market place. Systems. There is a wide range of systems that are critically important to run Microsoft successfully. These include employee recruitment and selection system, team development and orientation system, transaction processing systems, customer relationship management system, business…
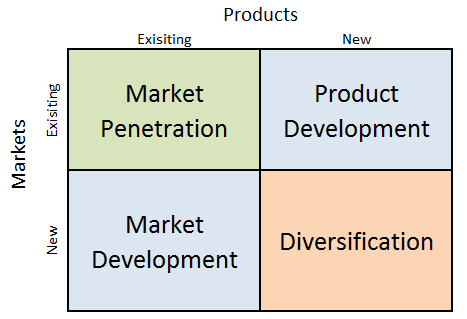
Microsoft Ansoff Matrix is a marketing planning model that helps the multinational technology company to select its product and market strategy. Ansoff Matrix distinguishes between four different strategy options available for businesses. These business growth strategies are market penetration, product development, market development and diversification. Microsoft Ansoff Matrix Microsoft uses all four strategy options within the scope of Ansoff Growth Matrix in an integrated way. 1. Market penetration. Market penetration refers to selling existing products to existing markets. Microsoft uses market penetration strategy to sell its Windows software and devices and other products in 116 Microsoft stores worldwide as well as through online channels and authorised distributors. The multinational technology company uses Microsoft Rewards loyalty program to pursue its market penetration strategy. 2. Product development. This growth strategy involves developing new products to sell to existing markets. Microsoft engages in product development strategy systematically. The tech giant’s research and development expenses increased USD 1.7 billion or 13% in 2018 compared to the previous year.[1] Microsoft develops most of its products and services internally through three engineering groups. Applications and Services Engineering Group, focuses on broad applications and services core technologies in productivity, communication, education, search, and other information categories. Cloud and Enterprise Engineering Group, focuses on our cloud infrastructure, server, database, CRM, enterprise resource planning, management, development tools, and other business process applications and services for enterprises. Windows and Devices Engineering Group, focuses on our Windows platform across devices of all types, hardware development of our devices, and associated online marketplaces. 3. Market development. Market development strategy is associated with finding new markets for existing products. Microsoft enters a new market whenever it sees there potential for its products and services. For example, HoloLens was made initially available only in 10 countries such as United States, United Kingdom, Canada, Australia…

Microsoft business strategy integrates the following 3 elements: 1. “Cloud-first, mobile-first”. Intelligent cloud represents one of the solid sources of Microsoft competitive advantage and Microsoft business strategy places a great emphasis on cloud segment of the business. ‘Mobile first’ part of this strategy stands for the mobility of experiences[1] and the technology giant pays a due attention to this direction as well. Nadella’s bet on cloud has paid off handsomely. By October 2018, Microsoft surprised Amazon in 12-month cloud revenues. Specifically, while Microsoft earned USD 26,7 billion revenues, Amazon’s revenues totalled to only USD 23,4 billion for the same period.[2] 2. Growing through mergers and acquisitions. Mergers and acquisitions play an important role in Microsoft business strategy and the multinational technology company engages in mergers and acquisitions to increase its capabilities, product range and value offering. The list of the most notable recent acquisitions include Nokia Corporation’s Devices and Services business for USD 9.4 billion in 2014 and Mojang Synergies AB the Swedish video game developer of the Minecraft gaming franchise, for USD 2.5 billion.[3] Moreover, in June 2016, Microsoft acquired LinkedIn for USD 196 per share in an all-cash transaction valued at USD 26.2 billion.[4] This particular acquisition plays an instrumental role to connect the world’s professional cloud and the world’s professional network – creating new experiences and new value for business users. With more than 1.2 billion Office users and 433 million LinkedIn members, the combined data graphs is expected to improve how Sales, HR, and other professionals get work done.[5] In 2018 alone, Microsoft completed 16 acquisitions of companies ranging from video games producers to artificial intelligence to employee engagement. 3. Focusing on augmented and virtual reality (VR). CEO Satya Nadella has placed augmented and virtual reality at the core of Microsoft business strategy. It has been noted…
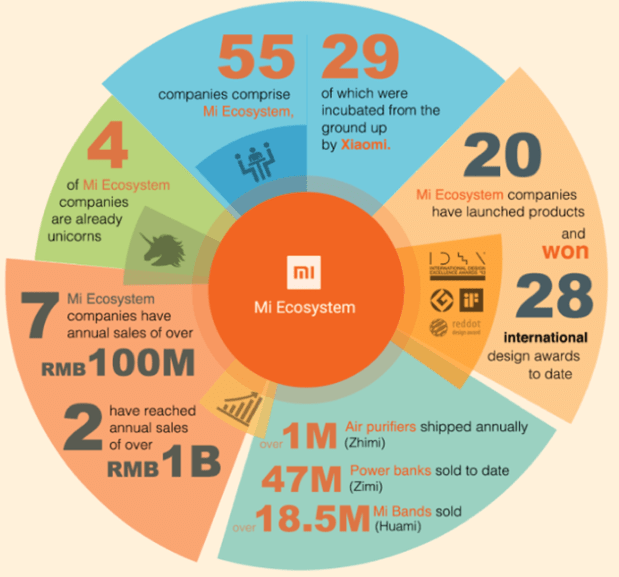
Xiaomi ecosystem is vast and comprises 55 companies including 29 companies that have been incubated from the beginning by Xiaomi. The company sells a wide range of products from smartphones to kettles and gloves. [1] Moreover, ever-expanding corporate ecosystem has been placed at the core of Xiaomi business strategy. Usually, producing a wide range of products and services threats to compromise the focus on core products and services. However, Xiaomi claims to have addressed this threat in a proactive manner. Specifically, according to its official website, while the company focuses on its core products – smartphones, smart TVs and smart routers, Xiaomi invests in companies that produce other types of products without being involved in operational management.[2] Xiaomi Ecosystem[3] Smartphones are placed at the core of Xiaomi ecosystem. Moreover, smartphones are used to facilitate the sales and use of many other products and services. Xiaomi smart devices include Mi Water Purifier, Mi Air Purifier, Mi Induction Heating Rice cooker and other products. All smart devices are connected to Xiaomi IoT platform and can be managed though Xiaomi smartphone. In 2013, the electronics and software company announced its plans to invest in 100 hardware startups.[4] The company also sells a range of “non-smart” products, like towels, and suitcases. Increasing numbers of startups are currently joining Xiaomi ecosystem to gain support to grow rapidly. Xiaomi has experienced technical staff, engineers and product managers, who can play an instrumental role in fuelling the growth of small-sized companies. At the same time, joining Xiaomi ecosystem also has some drawbacks. Specifically, start-ups need to operate with low profit margin according to Xiaomi business strategy. Moreover, over-dependence on Xiaomi for branding and distribution can be mentioned as another drawback of belonging to Xiaomi ecosystem.[5] Xiaomi Inc. Report contains a full analysis of Xiaomi ecosystem. The report illustrates…
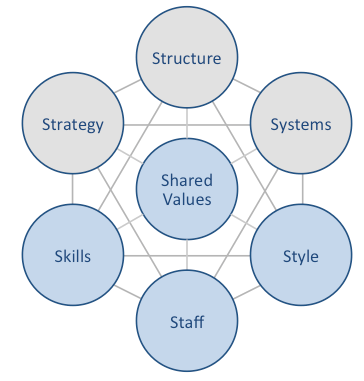
Xiaomi McKinsey 7S model illustrates the ways in which seven elements of businesses can be aligned so that overall effectiveness can be increased. According to the framework strategy, structure and systems are hard elements, whereas shared values, skills, style and staff are considered as soft elements. McKinsey 7S model stresses the presence of strong links between elements in a way that a change in one element causes changes in others. As it is illustrated in figure below, shared values are positioned at the core of Xiaomi McKinsey 7S model, since shared values guide employee behaviour with implications in their performance. Xiaomi McKinsey 7S Model Hard Elements Strategy. Xiaomi business strategy is based on cost leadership. Company’s business strategy also integrates gathering and utilising a large fan base and aggressively increasing the ecosystem of products and services. Moreover, Xiaomi positions itself as an internet and software company rather than a hardware company. Accordingly, the sales of hardware are perceived as a means to deliver software and services in the long-term perspective. Structure. Xiaomi has a matrix organizational structure. The electronics and software company has various business units that are managed independently. Xiaomi organizational structure can also be also classified as flat. Despite its large size employing more than 18000 people in 70 countries, the company has only a few layers of management. Systems. Xiaomi’s business depends on a wide range of systems such as employee recruitment and selection system, team development and orientation system and transaction processing systems. Moreover, there are critically important systems for the company such as customer relationship management system, business intelligence system, and knowledge management system. The mobile internet company aims to increase the efficiency of these and other systems via the integration of internet-based information technologies. Xiaomi Inc. Report contains a full analysis…
