Posts Tagged ‘catering’

McDonald’s segmentation, targeting and positioning is one of the integral components of its marketing strategy. Segmentation involves dividing population into groups according to certain characteristics, whereas targeting implies choosing specific groups identified as a result of segmentation to sell products. Positioning refers to the selection of the marketing mix the most suitable for the target customer segment. McDonald’s uses the following types of segmentation: 1. Multi-segment positioning. The fast food chain exploits multiple segments in terms of geography and demographics at the same time. The fast food giant develops items that appeals to the needs and preferences of each segment. 2. Adaptive positioning. McDonald’s periodically repositions its products according to changes in customer tastes and preferences. For instance, reflecting increasing health concerns by customers the fast food chain introduced a number of healthy items in its menu such as Fruit & Maple Outmeal and Southwest Grilled Chicken Salad. The following table illustrates McDonald’s segmentation, targeting and positioning: Type of segmentation Segmentation criteria McDonald’s target segment Geographic Region Operating in 119 countries Density Urban/rural Demographic Age 6 – 70 Gender Males & Females Life-cycle stage Bachelor Stage: young, single people not living at home Newly Married Couples: young, no children Full Nest II: youngest child six or over Income Low and middle Occupation Students, employees, professionals Behavioral Degree of loyalty ‘Hard core loyals’ and ‘Switchers’ Benefits sought Cost benefits, time efficiency Personality Easygoing& careless User status Potential and regular fast foodeaters Psychographic Social class Lower, working and middle classes Lifestyle McDonald’s targets Resigned, Struggler and Mainstreamer individuals according to Cross Cultural Consumer Characterization developed by Young & Rubican McDonald’s segmentation, targeting and positioning Important aspects of the target customer segment as illustrated in table above serve as the main guiding principle for McDonald’s marketing management to deal with Product, Place, Price,…

PESTEL is a strategic analytical tool and the acronym stands for political, economic, social, technological, environmental and legal factors. McDonald’s PESTEL analysis involves the analysis of potential impact of these factors on the bottom line and long-term growth prospects. Political Factors in McDonald’s PESTEL Analysis McDonald’s revenues and long-term growth prospects are affected by a number of political factors such as levels of bureaucracy and corruption, government stability and the freedom of press. Moreover, activities of trade unions and home market lobby groups can be referred to as noteworthy political factors that may affect multinational corporations. Exiting Russia On March 8, 2022 McDonald’s announced that it had temporarily closed restaurants in Russia and paused operations in the market due to Russia-Ukraine war conflict. The humanitarian crisis caused by the war in Ukraine, and the precipitating unpredictable operating environment, have led McDonald’s to conclude that continued ownership of the business in Russia is no longer tenable, nor is it consistent with McDonald’s values.[1] On May 2022 the fast food chain announced it starts the process of selling its business in Russia, meaning that the company is leaving the country permanently. Exiting one of its biggest markets where McDonald’s had more than 800 restaurants employing 62000 employees[2] due to a war conflict is a stark example for a political factor affecting the fast food chain. Trade Unions Activities of trade unions and their implications belong to the list of important political factors affecting McDonald’s. Trade unions may succeed in their demands to increase employee wages and to improve working conditions and these will have negative implications for the profitability of the business. Accordingly, the fast food giant is known worldwide for its hostility to trade unions. For example, in 2021 it was reported that McDonald’s has, for years, spied…

SWOT is an acronym for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats related to organizations. The following table illustrates McDonald’s SWOT analysis: Strengths 1. Global market leadership 2. Brand value and brand awareness 3. Sustainable business model 4. High level of profitability 5. Effective utilization of digital technologies Weaknesses 1. Unhealthy food on the menu 2. Declining brand image 3. High employee turnover 4. Negative publicity 5. Low differentiation Opportunities 1. Enhancing focus on nutritional menu 2. Product differentiation 3. Improving CSR aspect of the business 4. Reviving the brand image 5. Increasing the extent of localization in international markets Threats 1. Food safety concerns 2. Fast food market saturation in developed countries 3. Lawsuits against the company 4. Currency fluctuations 5. Competition from quality burger chains McDonald’s SWOT analysis Strengths in McDonald’s SWOT Analysis 1. McDonald’s is an undisputed market leader with more than 40000 restaurants worldwide. The fast food giant has a global market share of about 43,8% and its closest competitor Yum Brands that comprises KFC, Pizza Hut, Taco Bell and The Habit Burger Grill has a market share of only 30,9% in the global fast food industry.[1] Market leadership is a considerable strength for McDonald’s in terms of generating cash flow and profits for medium and long-term perspectives. 2. McDonald’s is one of the most valuable brands in the world. According to Forbes McDonald’s is No. 10 most valuable brand in the world with the brand value of USD 46,1 billion[2]. Similarly, Interbrand considers McDonald’s No.9 most valuable brand in the world with the brand value USD 45,87 billion.[3] Brand value and brand awareness are proved sources of competitive advantage. Specifically, brand value is an indicator of a high level of consumer loyalty and it offers a wide range of advantages that include negotiating power with customers…

McDonald’s organizational culture is somewhat controversial. On one hand, the fast food giant associates its corporate culture with the principles of inclusion, integrity and family values. Moreover, McDonald’s prides its organizational culture with encouraging learning for employees at all levels. On the other hand, the company has faced myriad lawsuits and claims in recent years, some involving allegations of sexual harassment and others around racial discrimination. Even the CEO Steve Easterbrook was fired in 2019 for having consensual relationship with his subordinate employee. Later it was revealed that Mr. Easterbrook awarded generous stock options to one of the female employees he had sexual relationship with. Furthermore, it was reported that the former CEO “in addition to lying about his own misconduct, allegedly tried to cover up the inappropriate behaviour of other McDonald’s executives.”[1] The following two factors have negative effects on McDonald’s organizational culture: 1. Highly hectic work environment. High speed of service is one of the core competitive advantages for McDonald’s. The cashiers are expected to greet customers, take orders, collect payments, recommend products, promote special deals and arrange food items on trays in a couple of minutes. Such a pace to be sustained during long shifts creates tremendous stress for thousands of customer-facing employees worldwide. 2. Low wages. The fast food chain pursues cost leadership business strategy operating with a thin profit margin per item, but selling at large volumes. Operations with low profit margin reflect on floor-level employee wages as well. Specifically, McDonald’s is notorious for paying low wages and exploiting human resources. The current President and CEO Chris Kempczinski attempts to improve McDonald’s organizational culture addressing the negative impact of factors described above. However, Mr. Kempczinski himself courted controversy when he sent a text to Chicago Mayor Lori Lightfoot blaming the kid’s parents for the shooting at McDonald’s location.[2] McDonald’s Corporation Report…

McDonald’s leadership team is headed by the President and CEO, who is aided by nine senior managers, each overseeing a specific aspect of the business. [1] The previous President and CEO Mr. Steve Easterbrook took the helm in 2015 and he was widely considered as an effective leader until he was fired for having consent sexual relationships with subordinate employees. During his leadership tenure Mr. Easterbrook was credited with turning around the company and reviving its falling stock price. Most prominent changes introduced by Easterbrook include reducing costs, introducing touch-screen ordering and establishing all-day breakfast. The new President and CEO Chris Kempczinski has also proved to be effective business leader. Under the new leadership McDonald’s has emerged as a clear winner during the pandemic. Mr. Kempczinski has channelled his energy and focus on digital, drive thru and delivery to adjust the business model to the pandemic environment. McDonald’s leadership is currently faced with a serious challenge. In recent years the fast food chain has faced many lawsuits and claims involving sexual harassment and racial discrimination. The former President and CEO Mr. Easterbrook being found violating company code of conduct is the evidence of severity of the issue. One of the important tasks for the new leader Mr. Kempczinski is to create a corporate culture where sexual harassment and racial discrimination is not tolerated in practice. McDonald’s Corporation Report contains the above analysis of McDonald’s leadership. The report illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces, Value Chain analysis, Ansoff Matrix and McKinsey 7S Model on McDonald’s. Moreover, the report contains analyses of McDonald’s business strategy, organizational structure and organizational culture. The report also comprises discussions of McDonald’s marketing strategy, ecosystem and addresses issues of corporate social responsibility. [1] Annual Report…

McDonald’s Corporation is a global fast food chain that serves more than 70 million customers in 119 countries employing about 200,000 people. McDonald’s operates two types of restaurants – company-owned and franchised restaurants with about 93% of restaurants belonging to the latter category (Annual Report, 2021) McDonald’s had disappointing financial results in 2014 with a sales growth of only 1% and a decline of operating income of 8%. Steve Easterbrook, McDonald’s Chief Brand Officer was promoted as the new CEO and President effective from March 1, 2015 to turn around the business. The list of major changes introduced by Steve Easterbrook includes reducing the use of antibiotics in chicken and massively restructuring the corporation, along with introducing changes in the menu. The turnaround efforts of the new CEO Steve Easterbrook proved to be effective with the company shares hitting record by the third quarter of 2015. However, Mr. Easterbrook was fired in 2019 due to breaching McDonald’s employee code of conduct through engaging in consent sexual relationship with female employees. New President and CEO Mr. Chris Kempczinski has proved to be effective so far, with McDonald’s emerging from COVID-19 pandemic stronger than before. In 2021, global comparable sales increased 17.0%, primarily due to strong sales performance across all segments from continued execution of the Accelerating the Arches strategy, as well as recovery from the impact of COVID-19 in the prior year. In 2021 consolidated revenues increased 21% (18% in constant currencies) to USD23.2 billion. At the same time, the fast food giant has certain weaknesses as well. These include the menu still consisting of primarily unhealthy food and the declining brand image of McDonald’s. Furthermore, the fast food chain has very high employee turnover and the company has attracted increasing negative publicity in the past few years. McDonald’s Corporation Report…
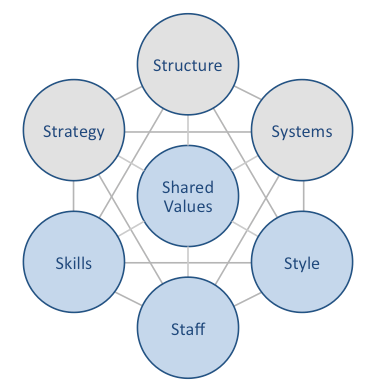
Hilton McKinsey 7S framework focuses on seven elements of a business practice that can be aligned to improve effectiveness of the company. According to the framework strategy, structure and systems represent hard elements, whereas shared values, skills, style and staff are soft elements. McKinsey 7S framework stresses the presence of strong links between elements in a way that a change in one element causes changes in others. As it is illustrated in figure below, shared values are positioned at the core of Hilton McKinsey 7S framework, since shared values guide employee behaviour with implications in their performance. Hilton McKinsey 7S Model Hard Elements Strategy. Hilton business strategy can be classified as service differentiation. The major points of differences of Hilton hotels from the competition include high quality of services and advanced integration of information and communication technologies into various aspects of hotel experience. Moreover, Hilton business strategy attempts to associate the experience of staying in Hilton Hotels with customer perceptions of status, achievement and recognition. Structure. Hilton organizational structure is hierarchical due to the massive size of the business that comprises 13 brands serving 140 million guests in 2015 alone (Annual Report, 2015). Moreover, Hilton organizational structure can also be described as divisional and the business is divided into three divisions: ownership, management and franchise, timeshare. Systems. Hilton Worldwide business operations rely on a wide range of systems such as customer reservations system, quality control system, employee recruitment and selection system, employee performance evaluation system and others. Since his appointment as the President and CEO in 2007, Christopher Nassetta simplified a wide range of Hilton systems to a great extent. For example, an introduction of a single company-wide system for employee performance evaluations simplified relevant processes to a great extent. Hilton Worldwide Holdings Inc. Report contains a detailed discussion of Hilton…
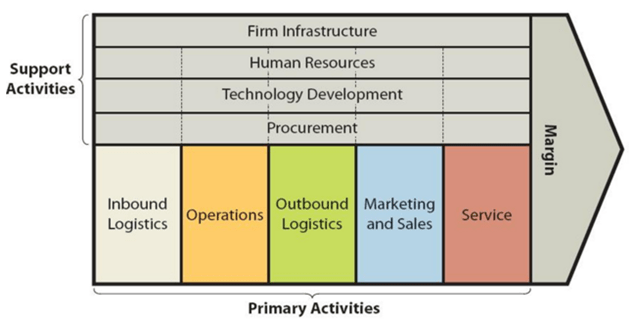
Hilton value chain analysis identifies business activities that can create value and competitive advantage to the business. The framework of value chain analysis divides business activities into two categories: primary and support activities. The figure below illustrates the essence of value chain analysis: Hilton Value Chain Analysis Primary Activities Inbound logistics Hilton inbound logistics represents a highly sophisticated system that ensures smooth operations in 572 hotels and resorts in 85 countries around the world.[1] Hilton’s “procurement group aggregates buying into national contracts for its various brands, and enables local providers where it makes sense to do so”[2] Hilton’s supply chain management and inbound logistics is unique in a way that the company makes deals directly with suppliers, then negotiates markups with the distributors that handle warehousing and delivery. This practice is an important source of value for the business since it enables the control of the whole supply chain. Operations Hilton Worldwide operates its business via the following three segments: Ownership segment. This segment consists of 146 hotels with 59,463 rooms which are owned or leased by Hilton Worldwide. Management and franchise segment consists of 4,419 hotels with 691,887 rooms. These are owned by third parties and managed by Hilton Worldwide. The company also licences its brand to franchises. As of December 2015, Hilton Worldwide franchised 3,875 hotels with 533,039 rooms. Timeshare segment consists of 45 properties comprising 7,152 units. This segment is engaged in marketing and selling timeshare intervals, operating timeshare resorts and timeshare membership clubs and providing consumer financing. Hilton operations are divided into four geographical segments: Americas Europe Middle East and Africa Asia Pacific The main sources of value in Hilton’s business operations include the highest level of standard of service, a high level of service personalization and integration of information and communication technologies into the various…
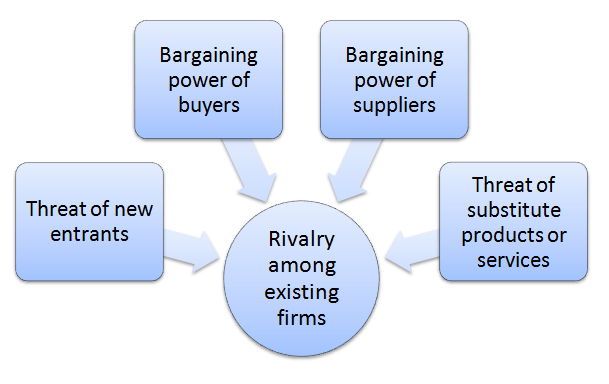
The analytical framework of Porter’s Five Forces developed by Michael Porter (1979)[1] explains five separate forces that shape the overall extent of competition in the industry. These forces are represented in Figure 1 below: Figure 1. Hilton Porter’s Five Forces Rivalry among existing firms in premium segment hotel industry is fierce. Hilton Hotels and Resorts competes with Marriott, Sheraton, Hyatt Regency, Radisson Blu, Renaissance, Westin, Sofitel and other premium segment hotel chains in the global marketplace. As a result of massive investments into various aspects of the service provision during the past few years, Hilton enjoyed greater income growths compared to the competition. Specifically, as it is illustrated in Figure 2 below, Hilton Worldwide Holdings Inc. Net Income in the 1 quarter 2016 grew year on year by 106.67 %, faster than average growth of its competitors. Figure 2. Income growth differences between Hilton Worldwide and its competitors[1] Bargaining power of Hilton suppliers is low. Hilton Worldwide purchases from more than 4000 suppliers globally [2] and the bargaining power of most suppliers is low due to the lack of uniqueness of products and services supplied. Moreover, the importance of order volume for Hilton suppliers is paramount and there is no supplier switching costs for Hilton on most cases. Hilton runs Supplier Diversity Program that ensures purchasing from, and the development of, socially diverse suppliers. Accordingly, the program provides an additional competitive ground for socially diverse suppliers compared to other supplier groups. Threat of substitute products or services in hotel industry is not significant. Direct substitutes for staying in Hilton hotels includes people staying in the homes of friends and relatives and people renting apartments for short periods of time. However, arrangement of these options can be time-consuming and associated with a great deal of hassle. Hotel industry is also faced with…

Hilton marketing communication mix integrates print and media advertising, sales promotions, events and experiences, public relations and direct marketing as discussed below in more details. Advertising Hilton engages in print and media advertising to communicate its marketing message to the target customer segment. Hilton marketing message stresses the highest standard of service provision, a high level of integration of information technology in order to maximise service personalization and the perception of status, achievement and recognition. This marketing message is communicated through a set of specific elements of advertising promotional strategy such as advertisements in newspapers and magazines popular with senior level management professionals such as Forbes, Fortune, The Economist, and Financial Times. Moreover, the communication of Hilton Hotels & Resorts marketing message is also facilitated through broadcast advertisements in selected television channels. ‘Stop Clicking Around’ is one of the recent large-scale marketing campaigns that “challenges the common misconception that third-party Web sites always offer the best prices on hotel rooms”[1]. Sales Promotion Sales promotion relates to attempts by a business to persuade potential customers to purchase products or services through introducing various incentives. Sales promotion is popular in hotel industry and this specific element of promotion mix is used by Hilton Hotels & Resorts in an intensive manner. Specifically, Hilton uses the following forms of sales promotions: HHonors loyalty programs offer discounted prices, digital check-in, free internet access, late check-out and others. Currently, there are more than 50 million Hilton HHonors members worldwide.[2] Discount vouchers are available in official website of the company and a wide range of discount websites. Hilton Hotels & Resorts gains practical advantages from using sales promotion in the forms of increasing the level of revenues and achieving utilisation of their rooms at a greater extend. However, it is important to note that by introducing…
