Strategy
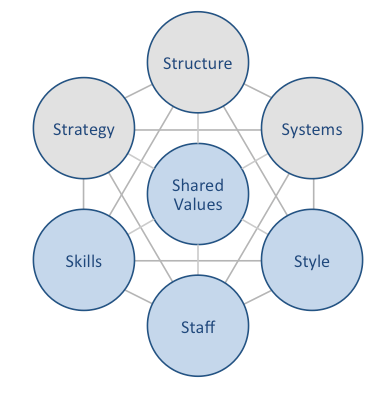
McDonald’s McKinsey 7S framework illustrates the ways in which seven elements of businesses can be aligned to increase effectiveness. According to the framework strategy, structure and systems represent hard elements, whereas shared values, skills, style and staff are soft elements. McKinsey 7S framework stresses the presence of strong links between elements in a way that a change in one element causes changes in others. As illustrated in figure below, shared values are positioned at the core of McDonald’s McKinsey 7S framework, because shared values guide employee behaviour with implications in their performance. McKinsey 7S model Hard Elements in McDonald’s McKinsey 7S Model Strategy McDonald’s pursues business strategy of cost leadership and an aggressive international market expansion. The company is able to operate with low operational costs due to economies of scale enjoyed to an enormous extent. Moreover, along with operating company-managed restaurants, McDonald’s capitalizes on the high level of brand awareness via franchising. High speed of customer services, universality of the taste and cleanliness of restaurants worldwide also belong to the list of competitive advantages for the fast food giant. Structure McDonald’s has divisional organizational structure and fast food chain’s business operations are divided into four divisions according to geographical locations. These divisions consist of United States, Europe, Asia/Pacific, Middle East and Africa (APMEA) and other countries. The company benefits from divisional organizational structure in a way that managers are free to make decisions taking into account unique aspects of respective markets. Systems There is a wide range of systems that enable McDonald’s operations at a global scale. These systems include but not limited to employee recruitment and selection, team development and orientation, transaction processing and customer relationship management system. Moreover, the fast food chain also relies on advanced business intelligence system and knowledge management system.…

McDonald’s business strategy utilizes a combination of cost leadership and international market expansion strategies. Franchising form of new market entry is utilized within McDonald’s business strategy to a great extent. The fast food chain has one of the largest property portfolios on the world and it is a giant real estate company. McDonald’s generates only a fraction of its profit from food and drinks sold by franchisees and the majority of income is generated by renting leased property to franchisees with a considerable mark-up. Moreover, product and service standardization lies in the cornerstone of McDonald’s business strategy. McDonald’s restaurants offer substantially uniform menu that comprises hamburgers and cheeseburgers, Big Mac, Quarter Pounder with Cheese, Filet-O-Fish, several chicken sandwiches, Chicken McNuggets, wraps, french fries, salads, oatmeal, shakes, McFlurry desserts, sundaes, soft serve cones, pies, soft drinks, coffee, McCafé beverages and other beverages.[1] It is important to note that along with maintaining product and service standardization, McDonald’s takes into account local tastes and preferences, when developing its menu and engaging in marketing efforts. McDonald’s competitive advantage is based on the following points: Cheat prices is McDonald’s main competitive advantage. The company is engaged in an extensive utilization of economies of scale to achieve the cost advantage. True to ‘fast food’ format of its restaurants, McDonald’s is famous for the speed of customer service without compromising the quality of the service. Universality of the taste to a great extent represents another base of McDonald’s competitive advantage. Big Mac tastes the same almost all over the world due to the use of the same ingredients in the same quantities and application of the standardized ways of cooking around the globe. Such a consistence in taste has positive implications on consumer loyalty. In late 2020, under the leadership of new President and CEO Mr. Chris…
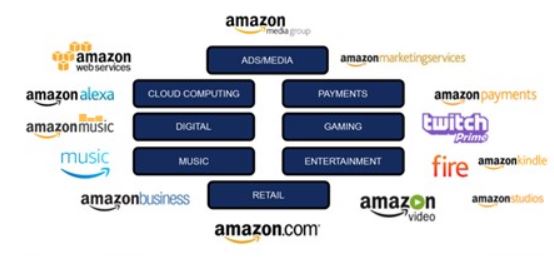
Amazon ecosystem of products and services is vast and it comprises retail, transportation, B2B distribution, payments, entertainment, cloud computing, and other segments. Started only as an online bookstore in 1995 by Jeff Bezos, Amazon has become the e-commerce and cloud computing tech giant consistently increasing the ecosystem of its products and services. The e-commerce giant is competent in focusing on what customers need, designing in-house innovative technology solutions and then commercialising these solutions. Amazon Web Services (AWS) is a stark example for this. This is how Amazon ecosystem has evolved. Increasing range of products and services Today, Amazon is a “retailer, a technology company, an entertainment destination, a growing advertising platform, even a delivery company with its own fleet of planes”.[1] Importantly, consumption of one type of Amazon products and services encourages the usage of other products and services offered by the company and that is the primary aim of developing an ecosystem. This can be illustrated using Alexa virtual assistant as an example. Amazon smart security camera that is compatible with the Echo smart speakers allows users to stream live video from the camera on the Echo Show or through the Alexa smartphone app. Moreover, Amazon smart glass is based on Alexa voice assistant and can be used only if the device is linked to a user’s smartphone.[2] Figure 1 below illustrates the essence of Amazon ecosystem. Figure 1 Amazon Ecosystem[3] Each of Amazon business segment illustrated in Figure 1 above plays certain role in consumption of other types of products and services belonging to the ecosystem. Let’s take Amazon Kindle for example. As it is illustrated in Figure 2 below, Amazon Fire platform can be used to consume a wide range of products and services belonging to Amazon portfolio. Moreover, Fire platform can also be used…
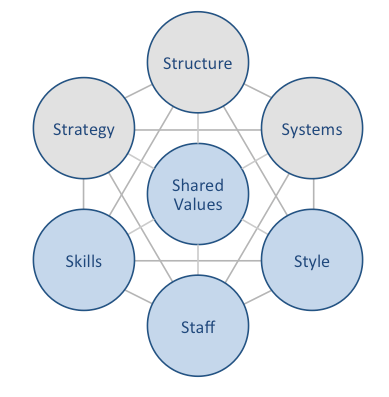
Amazon McKinsey 7S model illustrates the ways in which seven key elements of businesses can be united to increase effectiveness. According to this model strategy, structure and systems represent hard elements, whereas shared values, skills, style and staff are soft elements. McKinsey 7S model stresses the presence of strong links between elements. Specifically, it argues that a change in one element causes changes in others. As it is illustrated in figure below, shared values are positioned at the core of Amazon McKinsey 7S model, since shared values guide employee behaviour with implications in their performance. McKinsey 7S model Hard Elements in Amazon McKinsey 7S Model Strategy Amazon adheres to cost leadership business strategy. Three main pillars of Amazon business strategy are competitive prices, great range and speed of delivery. The largest internet retailer in the world has been able to sustain this strategy thanks to economies of scale, innovation of various business processes and regular business diversification. Moreover, Amazon business strategy places a great emphasis on encouraging communication among various components of its ecosystem. These components of Amazon ecosystem include merchants, writers, reviewers, publishers, apps developers, and the information market of commentators, analysts, journalists and feature writers. Additionally, customer obsession and focus on Amazon leadership values represent important cornerstones of Amazon business strategy. Structure Amazon organizational structure is hierarchical. It is difficult for the company to adapt an alternative structure such as divisional or matrix due to its gigantic size. Specifically, the e-commerce giant employs approximately 1,3 million people who serve hundreds of millions of customers worldwide.[1] The key features of Amazon corporate structure include flexibility of the business; which is unusual for a company of such a big size and stability in the top management, i.e. little turnover in the senior management team. Reliance on hybrid project…

Amazon business strategy can be described as cost leadership taken to the extreme. Range, price and convenience are placed at the core of Amazon competitive advantage. The global online retailer operates with a razor thin profit margin and succeeds due to a combination of economies of scale, innovation of various business processes and a constant business diversification. Founder and first CEO Jeff Bezos believes in focusing as a business strategy on things that do not change. At the outset of the business he reasoned that people always want low prices, selection and fast delivery. Exceeding customer expectations on these points has remained as the core of Amazon business strategy. Innovation and technology the online retail behemoth uses are simply instruments to pursue this core strategy. Moreover, Amazon business strategy is guided by four principles: customer obsession rather than competitor focus, passion for invention, commitment to operational excellence, and long-term thinking.[1] The following four points constitute the cornerstones of Amazon business strategy: 1. Regularly entering into new niches and segments. Started only as an online shop for selling physical books in 1997, today Amazon sells anything that can be sold online in the global scale. Sophisticated global logistics represents one of the solid bases of Amazon competitive advantage. The tech giant has used this advantage extensively to engage in successful business diversification. Recently, the company launched Amazon Home Services, a simple way to buy and schedule local professional services as a continuation of its diversification strategy.[2] Currently, the tech giant operates in increasing range of industries including e-commerce, cloud computing, artificial intelligence, consumer electronics, entertainment, digital distribution, B2B distribution, self-driving cars and supermarkets. As the largest internet company by revenue in the world, Amazon frequently disrupts the industries it chooses to enter. The e-commerce giant occasionally finds new niches and segments accidentally, while…
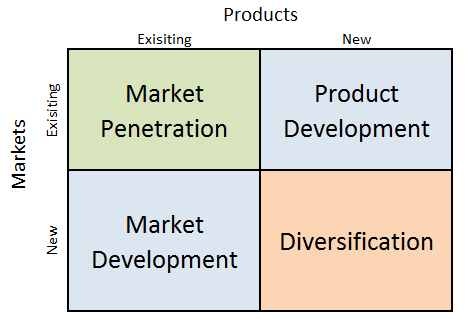
Amazon Ansoff Matrix is a marketing planning model that helps the e-commerce and cloud computing company to determine its product and market strategy. Ansoff Matrix illustrates four different strategy options available for businesses. These are market penetration, product development, market development and diversification. Amazon Ansoff Matrix Within the scope of Ansoff Matrix, Amazon uses all four growth strategies in an integrated manner: 1. Market penetration. Market penetration refers to selling existing products to existing markets. Amazon uses market penetration strategy aggressively. Sophisticated user experience features in general and recommendations feature on e-retailer’s website in particular play an important role in the application of market penetration strategy. Specifically, Amazon focuses on user experience personalization thanks to efficient application of data science and machine learning. The e-commerce giant collects and possesses a vast amount of data related to customers such as age, sex, lifestyle, habits and preferences. The company uses artificial intelligence (AI) to analyse this data and suggest products that a particular customer is highly likely to buy. 2. Product development. This involves developing new products to sell to existing markets. Product development is one of the core strategies used by Amazon. Started by Jeff Bezos selling only physical books online in 1997, today Amazon sells anything that can be sold online. The largest internet retailer in the world by revenue sells more than 500 million products, including products sold by third parties on Amazon platform. Top product categories include clothing, shoes, jewellery, home and kitchen appliances, books, electronic devices, sports and outdoor items and others. The e-commerce and cloud computing company produces increasing number of products under the private label as well. 3. Market development. Market development strategy is associated with finding new markets for existing products. Amazon is engaged in market development in a systematic manner. Started only in…
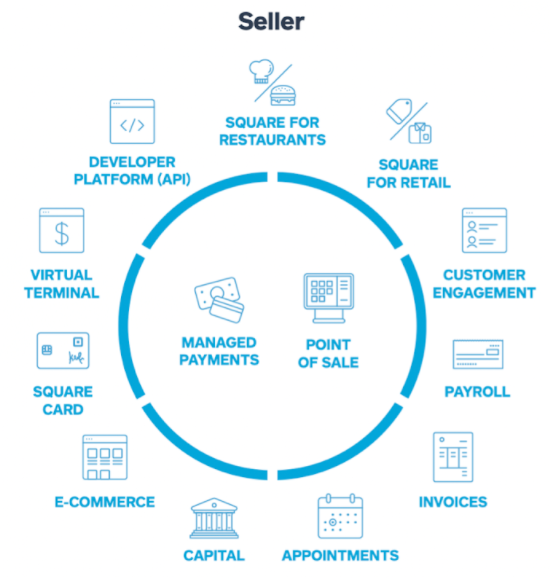
Square ecosystem represents a growing ecosystem of financial services. Ecosystem of Square can be divided into two groups: seller ecosystem and cash ecosystem. Square seller ecosystem is a cohesive commerce ecosystem that helps its sellers start, run, and grow their businesses. As illustrated in Figure 1 below, the core services for sellers are managed payments and points of sales products and services. Specific functionalities that contribute to these services include customer engagement platform, payroll invoices services, functionality to make appointments and capital management tools. Moreover, e-commerce and developer platforms, as well as, virtual terminal are important components of Square ecosystem on the Seller front. Figure 1 Square Seller products and services Square cash ecosystem, represented by Cash App comprises a wide range of financial products and services that are designed to help individuals manage their money. These include a cash card, instant discounts tool Boost. The strongest feature of Cash App that has no analogue in the market is the functionality to purchase Bitcoints and stocks in a simple, secure and hassle-free manner. Figure 2 Square Cash App functionalities The financial services and digital payments company is increasing the linkage between its seller and cash ecosystem in order to from strengthen its position in the market. For example, employers with seller account can pay their employees from seller revenues the next business day using Instant Payments feature when employees use Cash App. There is still room for growth of Square ecosystem on both fronts – Seller and Cash App. Apart from connecting the both ecosystems. The finance sector disruptor can also scale each of them, as well as, engage in optimised cross-selling. Moreover, the developer platform can play an instrumental role in expanding the ecosystem for Square, through exposing Application Program Interface (API) to third party developers to adjust it…

Square business strategy is based on the following two principles: 1. Simplifying financial transactions. Square Inc. was founded when Jim McKelvey, friend of current CEO Jack Dorsey could not sell his glass faucets and fittings because he could not accept credit card. The two co-founders saw a business opportunity in this problem and developed the first card reader, which allowed small businesses and individuals to accept credit cards. The finance sector disruptor simplified a range of other financial transactions. For example, instant payment feature on Seller account allows businesses to pay their employees the next business day. Thanks for this capability, employees do not have to wait for the paycheck for several days or even weeks, which has been the case. Furthermore, Square has also simplified the practice of investing in stocks and bitcoin commission-free for people with no prior investing experience. Customers simply open up the Cash app, decide how much they want to invest in a single stock and click purchase. Challenging the status quo in finance and simplifying financial transactions is the core business strategy for Square. 2. Developing and expanding an ecosystem of financial products and services. In its course to simplify financial products and services as discussed above, Square business strategy relies on the development and strengthening of ecosystem. Currently, the payments company is developing two ecosystems simultaneously – seller and cash. Square seller ecosystem is a cohesive commerce ecosystem that helps its sellers start, run, and grow their businesses. Cash ecosystem, on the other hand, consists of a line of products and services that help individuals to manage their money. Although the link between the two ecosystems is rather weak at this stage, the company will attempt to increase the linkage through developing financial products and services that will intersect both. Square Inc. Report contains…

Uber is working towards developing its own ecosystem in order to increase customer loyalty with positive implications on company’s revenues. The development of Uber ecosystem has integrated the following key milestones: 1. Request API The development of Request API (application programming interface) has been viewed by industry analysis as the first step towards developing the ecosystem. It has been noted that “Request API gives third party developers the ability to integrate their application into Uber. So if you’re an airline or a restaurant booking application, you can create a situation whereby your flight delay was automatically notified to your Uber driver so that your pickup is correctly rescheduled.”[1] 2. Uber Eats The launch of food delivery service by the company as UberFRESH in 2015, later renamed as UberEAT in 2015 was an important move for the ride-hailing giant to expand beyond ridesharing. This is a major difference between Uber and its main rival Lyft. Specifically, when Lyft was concentrating solely on taxi services and ride-sharing for a long time before doing anything else; Uber senior management sought to differentiate the business using the same platform early on with positive implications on its ecosystem. 3. Uber Feed The update of app on November 2016 paved a way for further development of Uber ecosystem. Nowadays, Uber app learns from routines of users and scrapes their calendars for the address of their meetings across the town.[2] Particularly, Uber Feed is an important feature and it intends to gain customers attention during the ride. Uber Feed presents a stack of services Uber thinks customers might find useful during their trip. Customers can swipe left on Uber Eats to see which restaurants can deliver to their house in synch with their arrival time. Alternatively, if customers are running late to their destination, they can use…
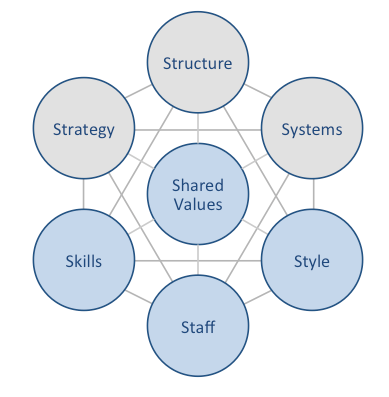
Uber McKinsey 7S model illustrates the ways in which seven elements of businesses can be aligned to increase effectiveness. According to the framework strategy, structure and systems represent hard elements, whereas shared values, skills, style and staff are soft elements. McKinsey 7S model stresses the presence of strong links between elements in a way that a change in one element causes changes in others. As illustrated in figure below, shared values are positioned at the core of Uber McKinsey 7S model, since shared values guide employee behaviour with implications on their performance. McKinsey 7S model Hard Elements Strategy Uber pursues cost leadership business strategy. The ride-hailing giant gains cost advantage thanks to internet-based nature of its business model that disrupted traditional taxi industry in the global scale. The international transportation technology company increases range of its services regularly to cater for the needs of greater numbers of customers. Moreover, Uber business strategy places a great emphasis on a high level of user convenience. Growing the business through acquiring adjacent businesses is another important aspect of Uber business strategy. Structure Uber organizational structure can be classified as hierarchical. Accordingly, the company is disadvantaged by the shortcomings of hierarchical structure such as ineffective communication across various departments, rivalry between departments that may compromise long-term growth prospects and high level of bureaucracy. Following the failed IPO in 2019, the CEO Mr. Khosrowshahi changed Uber organizational structure to increase his role in operational day-to-day management. As part of these changes, the positions of chief operating officer (COO) and chief marketing officer (CMO) were also eliminated. Systems Systems within McKinsey 7S model refer to daily activities and procedures that Uber staff use to provide ride-haling services to millions of customers worldwide. There is a wide range of various systems that are important for Uber’s long-term…
